TEKNOLOGI WAN
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth overview of Wide Area Networks (WAN), focusing on the different types of computer networks such as LAN, MAN, and WAN, and their geographical coverage. It covers key WAN characteristics like large geographical coverage, the use of public lines, and serial connections. The video explains various connection types like leased line, circuit-switching, and packet-switching, alongside components like routers, bridges, and switches. Additionally, it touches on network encapsulation methods, standards, and protocols like HDLC and PPP. The aim is to equip viewers with knowledge about WAN's role in global networking and its technical complexities.
Takeaways
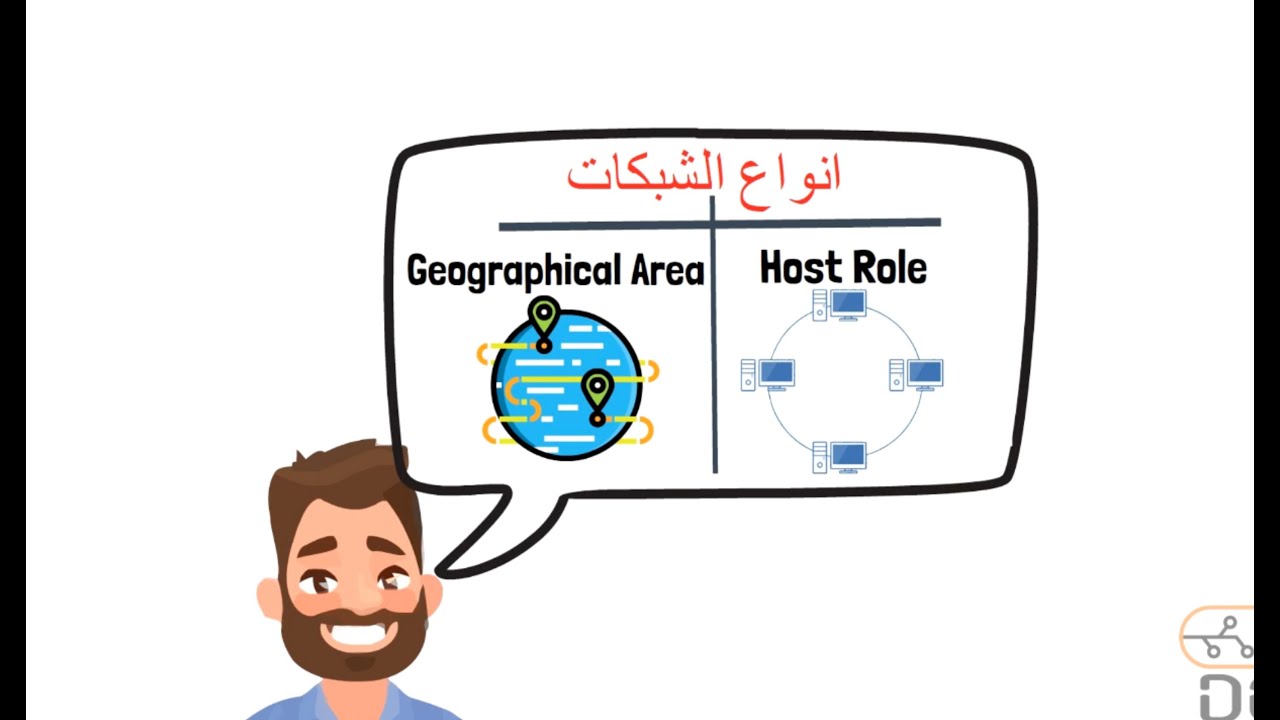
- 😀 WAN (Wide Area Network) is a network that spans large geographical areas, connecting multiple LANs and MANs.
- 😀 WAN networks require advanced management due to their complexity compared to LAN and MAN networks.
- 😀 WAN uses public communication services like leased lines or packet switching for data transmission.
- 😀 Leased Line (Point-to-Point) offers a dedicated connection, ensuring fast and reliable transmission but at a high cost.
- 😀 Circuit Switching establishes a connection only when needed, offering a cheaper alternative but with potential delays and blocking.
- 😀 Packet Switching allows bandwidth sharing among multiple users, making it a more cost-effective solution with faster connections than leased lines.
- 😀 WAN devices such as repeaters, hubs, bridges, switches, and routers play essential roles in data transmission and network management.
- 😀 Repeater boosts signal strength, commonly used in wireless networks to extend range.
- 😀 Bridge works at the data link layer, dividing networks into segments and recognizing MAC addresses to manage traffic.
- 😀 WAN protocols like HDLC, PPP, X.25, ATM, and Frame Relay ensure efficient communication over wide area networks, each with distinct benefits.
- 😀 Software-Defined Networking (SDN) separates the control plane from the data plane, offering more flexibility in WAN network management.
Q & A
What is a Wide Area Network (WAN)?
-A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that connects devices over large geographic areas, such as cities, countries, or even continents. It is used for long-distance communication and data exchange.
How does a WAN differ from a Local Area Network (LAN)?
-A LAN is a smaller network that connects devices within a limited area, such as a building or campus, while a WAN connects devices over much larger geographical areas, often spanning across multiple regions or countries.
What are the key characteristics of a WAN?
-The key characteristics of a WAN include: geographical spread over large distances, reliance on technologies like packet-switching, use of physical and data link layers, and the need for complex management of data transfer.
What are the different types of WAN connections?
-There are three main types of WAN connections: Leased Lines (dedicated and costly), Circuit Switching (temporary connection based on demand), and Packet Switching (cost-effective, shared bandwidth for multiple users).
What is packet switching in WANs?
-Packet switching is a method of data transmission where data is broken into packets and sent independently over the network, where each packet may take a different route to the destination before being reassembled.
What devices are used in WANs, and what do they do?
-Common WAN devices include repeaters (to extend signal range), routers (to direct data packets across networks), and switches (to manage data transfer within a network and avoid collisions).
What is the function of a router in a WAN?
-A router forwards data packets between different networks, ensuring that the data reaches its correct destination, thus enabling communication between devices located across various regions or networks.
What is HDLC, and how is it used in WANs?
-HDLC (High-Level Data Link Control) is a data link layer protocol used for communication in WANs. It supports full-duplex data transmission and ensures reliable data transfer between devices in a WAN.
What role does encapsulation play in WANs?
-Encapsulation in WANs involves adding headers and trailers to data packets, which provide important routing information and ensure that the packets reach their destination correctly and in the right order.
Why are WANs more complex to manage than LANs?
-WANs are more complex because they span large geographical areas, require more advanced devices and technologies for data routing and signal management, and have more intricate protocols for data transfer and security.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Reti Lan-#1.Definizione di rete Informatica (LAN , MAN , WAN ,GAN)

Tipe Jaringan Komputer (PAN, LAN, WLAN, CAN, MAN, WAN) | Administrasi Infrastruktur Jaringan (AIJ)

Bab 3 Akm Awal
شرح أنواع الشبكات LAN, WAN, PAN, CAN, MAN, SAN

Mengenal Jenis Jaringan Komputer (LAN MAN WAN)

LAN MAN WAN Area Network Dalam Arti Yang Berbeda di Dalam Dunia Internet
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)