Immunology MicroFlix
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the immune response to a rhinovirus infection, focusing on both innate and adaptive defenses. It describes how the virus bypasses first-line defenses, infects cells, and triggers a complex immune response. Dendritic cells process the virus and activate helper T cells, which stimulate B cells to produce antibodies. Cytotoxic T cells identify and destroy infected cells through apoptosis. Together, these humoral and cellular defenses protect the body against the current infection and create lasting immunity against future infections. The video emphasizes the roles of key immune cells and how they work together to fight rhinoviruses.
Takeaways
- 😀 Rhinoviruses cause colds by entering the nasal passages and overcoming first-line innate defenses like mucous and cilia.
- 😀 Rhinoviruses replicate in respiratory epithelial cells, releasing more viruses into the nasal passages and tissue fluids.
- 😀 Dendritic cells, part of the second line of innate defense, engulf and digest the rhinoviruses, presenting their fragments (epitopes) on MHC2 molecules.
- 😀 Dendritic cells travel to the lymph nodes, where they interact with helper T cells, activating adaptive defenses.
- 😀 Helper T cells recognize rhinovirus epitopes presented by dendritic cells, leading to activation and immunity against future infections.
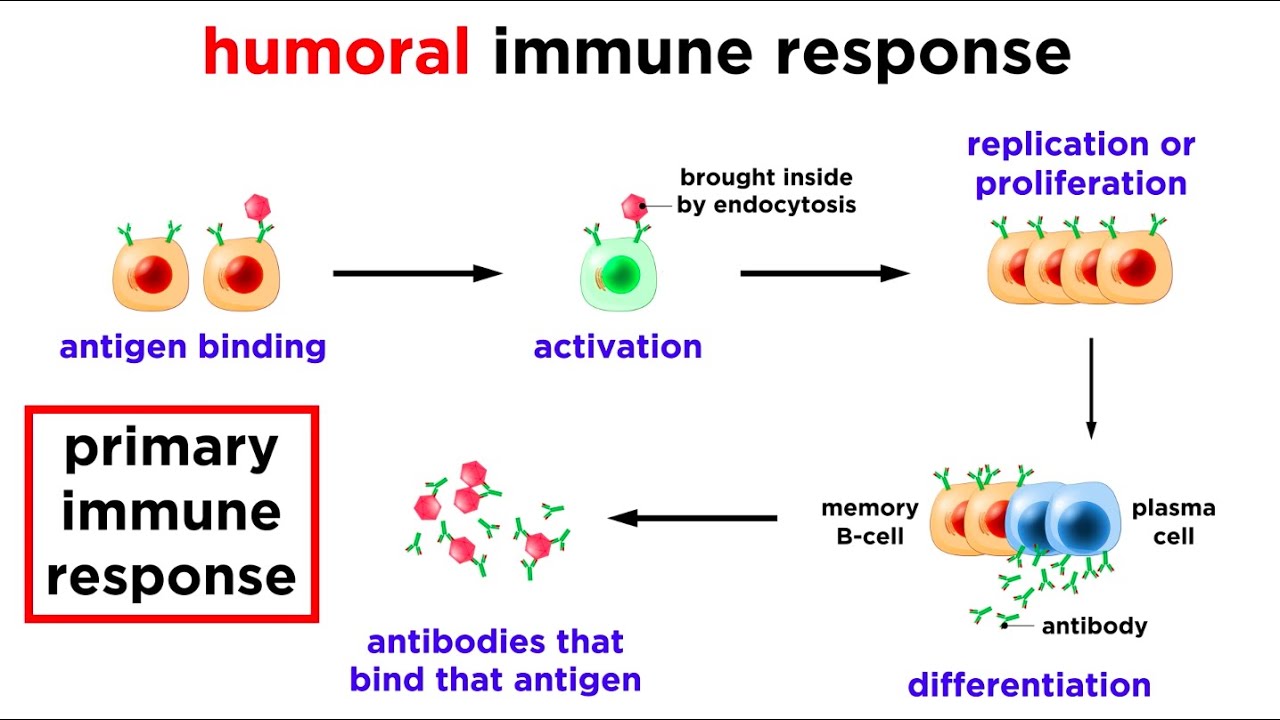
- 😀 B cells use B cell receptors (BCRs) to recognize specific rhinovirus epitopes, undergo clonal selection, and present the epitopes with MHC2 molecules.
- 😀 Helper T cells stimulate B cells through cytokines, resulting in the proliferation and differentiation of B cells into plasma cells and memory B cells.
- 😀 Plasma cells secrete antibodies that neutralize free rhinoviruses by preventing them from attaching to host cells.
- 😀 Cytotoxic T cells provide cellular immunity by locating and destroying rhinovirus-infected cells through apoptosis.
- 😀 The activation of cytotoxic T cells occurs through recognition of rhinovirus epitopes presented by MHC1 molecules on infected cells.
- 😀 Both humoral (antibodies) and cellular (cytotoxic T cells) defenses work together to fight rhinovirus infections, with memory cells aiding in faster responses to future infections.
Q & A
What is the main cause of the patient's cold in the script?
-The cold is caused by rhinoviruses, which entered the patient's nasal passages and bypassed the first line of innate defenses like mucus and cilia.
What happens when the rhinoviruses enter the respiratory epithelial cells?
-The rhinoviruses replicate inside the epithelial cells and release more rhinoviruses, which spread into the patient's nasal passages and tissue fluids.
What role do dendritic cells play in the immune response?
-Dendritic cells are part of the second line of innate defense. They perform surveillance by engulfing rhinoviruses, digesting them, and presenting fragments (epitopes) to activate adaptive immunity.
How do dendritic cells activate helper T cells?
-Dendritic cells present the rhinovirus epitopes on MHC2 molecules, which are recognized by helper T cells. The helper T cells are activated through cytokine signaling.
What is clonal selection in B cells?
-Clonal selection occurs when a B cell recognizes a specific epitope, such as a rhinovirus epitope, and is selected for activation. This leads to its proliferation and differentiation into memory B cells and plasma cells.
What is the function of plasma cells in the immune response?
-Plasma cells secrete antibodies that bind to free rhinoviruses, neutralizing them and marking them for destruction by phagocytes.
What are antibodies and how do they help fight rhinoviruses?
-Antibodies are proteins secreted by plasma cells that bind to the surface molecules of rhinoviruses, preventing them from attaching to host cells and neutralizing the virus.
How do cytotoxic T cells contribute to the immune response?
-Cytotoxic T cells identify and destroy cells infected by rhinoviruses. They secrete perforin to create holes in infected cells' membranes, allowing granzyme to enter and induce apoptosis, or programmed cell death.
What is the difference between MHC1 and MHC2 molecules?
-MHC1 molecules are recognized by cytotoxic T cells, while MHC2 molecules are recognized by helper T cells. Both are important for presenting viral epitopes to activate different immune responses.
What is the significance of memory B cells and T cells?
-Memory B cells and T cells remember the pathogen and enable the immune system to respond more rapidly and effectively if the same pathogen infects the body again in the future.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

IMAT Biology Lesson 6.13 | Anatomy and Physiology | Immune System Part II

Immunology | Immune System: Overview

Sistema Imunológico e Imunidade Inata | Anatomia etc

How Do Outbreaks Start? Pathogens and Immunology: Crash Course Outbreak Science #2
The Immune System: Innate Defenses and Adaptive Defenses

Sistem Pertahanan Tubuh : (1) Pertahanan Eksternal dan Internal BIOLOGI 11 SMA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)