Química - Lei de Lavoisier: Conservação das Massas
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the chemistry teacher introduces the Law of Conservation of Mass, famously known as Lavoisier's Law. The teacher explains its historical context, emphasizing Lavoisier's pivotal role in the development of chemistry, including his discovery of oxygen. Through examples of chemical reactions like the formation of methane and calcium oxide, the teacher demonstrates how mass is conserved in chemical reactions, reinforcing the idea that matter cannot be created or destroyed. The lesson includes practical applications, encouraging viewers to understand the importance of mass conservation in solving chemical equations and experiments.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lavoisier is known as the father of chemistry and is credited with naming the element oxygen.
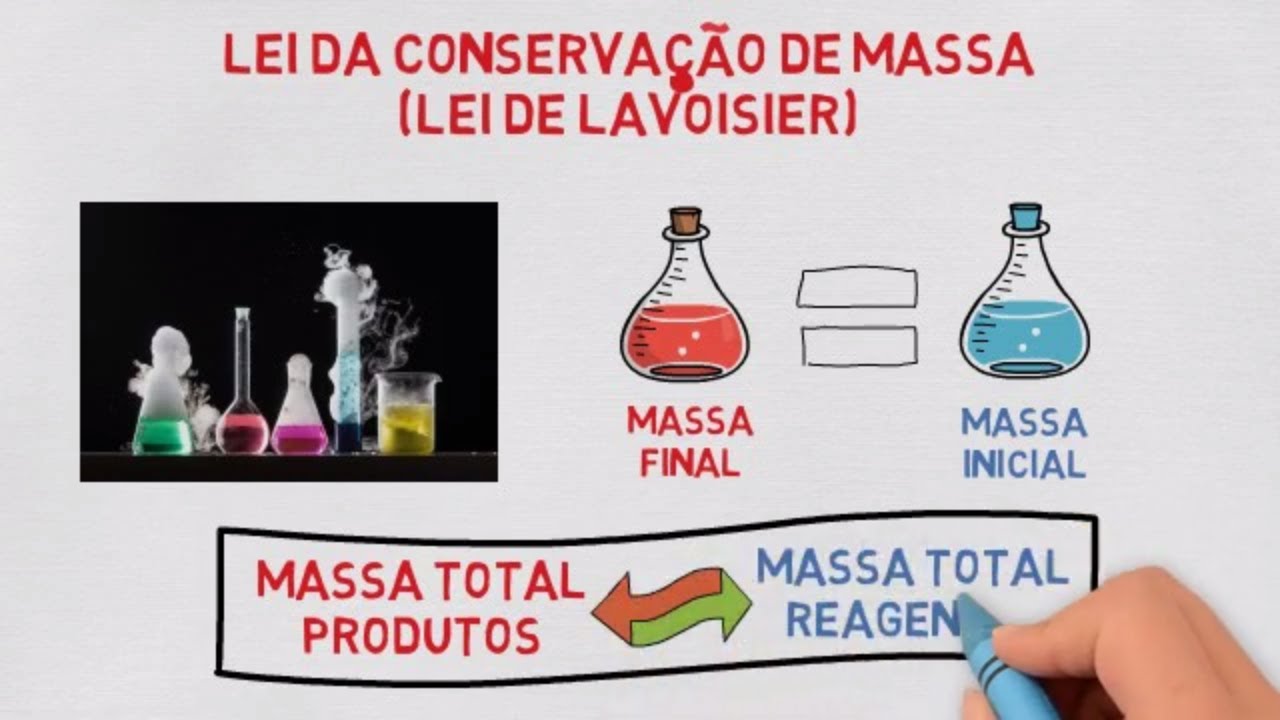
- 😀 The Law of Conservation of Mass, proposed by Lavoisier, states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- 😀 A popular phrase related to Lavoisier’s law is 'Nothing is created, nothing is lost, everything transforms'.
- 😀 In a chemical reaction, the mass of the reactants must be equal to the mass of the products.
- 😀 Example 1: When hydrogen reacts with carbon to form methane, the mass of the reactants will equal the mass of the methane produced.
- 😀 Example 2: When calcium reacts with oxygen to produce calcium oxide (quicklime), the mass of calcium and oxygen equals the mass of calcium oxide.
- 😀 The importance of Lavoisier’s law is evident in chemical calculations, such as determining the mass of unknown reactants or products.
- 😀 Example 3: When carbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, the mass of carbon and oxygen will be equal to the mass of the carbon dioxide produced.
- 😀 The law of conservation of mass is fundamental to chemical processes and is crucial for accurate chemical analysis.
- 😀 The video provides multiple examples to demonstrate the practical application of Lavoisier’s law in chemical reactions.
Q & A
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass?
-The Law of Conservation of Mass, introduced by Antoine Lavoisier, states that the total mass of the reactants in a chemical reaction is equal to the total mass of the products. This means that matter is neither created nor destroyed during chemical reactions.
Who is Antoine Lavoisier, and why is he important in chemistry?
-Antoine Lavoisier is known as the father of modern chemistry. He made significant contributions to the field, including naming the element oxygen and developing the Law of Conservation of Mass, which is fundamental in understanding chemical reactions.
What is the significance of Lavoisier's Law of Conservation of Mass in chemistry?
-Lavoisier's Law of Conservation of Mass is a cornerstone of chemistry. It ensures that in any chemical reaction, the mass remains constant. This principle helps scientists understand and predict the behavior of substances during chemical processes.
How does the Law of Conservation of Mass apply to chemical reactions?
-In any chemical reaction, the mass of the reactants must equal the mass of the products. For example, if you react hydrogen and carbon to form methane, the total mass of hydrogen and carbon will be the same as the mass of the produced methane.
Can you explain the example with hydrogen and carbon forming methane?
-In the reaction between hydrogen and carbon to form methane, if you start with 2 grams of hydrogen and 16 grams of carbon, you will obtain 18 grams of methane. This demonstrates the Law of Conservation of Mass because the mass of the reactants equals the mass of the product.
What role does oxygen play in the chemical reaction with calcium?
-In the reaction between calcium and oxygen to form calcium oxide (also known as lime or cal virgem), oxygen combines with calcium. The mass of the oxygen used in the reaction can be calculated based on the mass of calcium and the final mass of calcium oxide produced.
How do you calculate the mass of an unknown substance in a reaction?
-To calculate the mass of an unknown substance in a chemical reaction, you can use the Law of Conservation of Mass. By knowing the masses of the other reactants and products, you can deduce the missing mass to ensure that the total mass is conserved.
What is the importance of balancing chemical equations in relation to the Law of Conservation of Mass?
-Balancing chemical equations ensures that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. This is necessary for the Law of Conservation of Mass because it guarantees that mass is conserved during the reaction.
What does the phrase 'Nothing is created, nothing is lost, everything transforms' refer to?
-This phrase refers to the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Instead, it can only be transformed from one form to another, such as in the conversion of reactants to products.
Why is the Law of Conservation of Mass important in understanding chemical reactions?
-The Law of Conservation of Mass is important because it allows scientists to predict the outcomes of chemical reactions. By knowing the mass of reactants, scientists can calculate the expected mass of the products, ensuring consistency in reactions and providing a foundation for further scientific discovery.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Lei de Lavoisier: Lei de Conservação das Massas!

Hukum Kekekalan Massa - Part 1 ⚖️🍎

Kimia SMA - Hukum Dasar Kimia (1) - Hukum Lavoisier dan Hukum Proust (D)

Praktikum Hukum Lavoisier ( Kekekalan Massa ) Hukum Dasar Kimia Kelas X

tugas kimia praktik hukum kekekalan massa/hukum lavoisier

Esperimento legge di Lavoisier
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)