12/05/2018 - Videoaula 06 – Plantas Ornamentais: Propagação e Produção de Mudas
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the technique of micropropagation, used to clone and multiply ornamental plants in controlled lab conditions. It explains the benefits and challenges of micropropagation, including its high cost but superior plant quality and uniformity. The video also contrasts seed propagation with vegetative propagation, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. With the ornamental plant market growing, producers are urged to stay updated on propagation methods and market demands. The lesson concludes with an invitation to the next course on accident prevention and first aid, encouraging continuous learning in agriculture.
Takeaways
- 😀 Micropropagation is a technique for cloning plants on a large scale, ensuring rapid multiplication of plant individuals for various purposes.
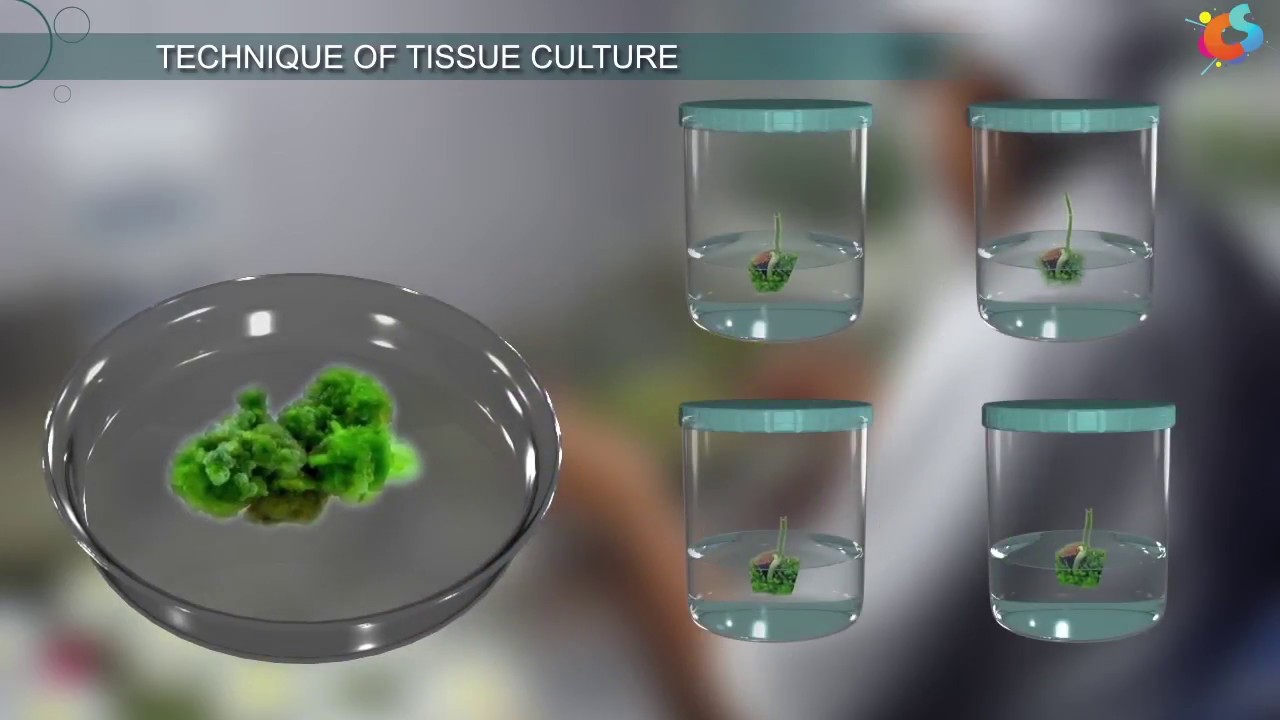
- 😀 This technique involves isolating small portions of a mother plant, such as leaves, roots, or seeds, and growing them in controlled laboratory conditions.
- 😀 Micropropagation requires strict control over light, temperature, and humidity to regenerate new plants, similar to hydroponic cultivation without using soil.
- 😀 While micropropagation is not feasible on most farms, understanding the process is crucial, as many ornamental plant seedlings are produced this way.
- 😀 Although micropropagation requires significant investment in facilities and skilled labor, it results in high-quality, uniform, and healthy plants.
- 😀 In Brazil, many companies specialize in micropropagating ornamental plants, especially orchids, lilies, chrysanthemums, and calla lilies, often delivering nationwide.
- 😀 Choosing the best propagation method depends on factors like knowledge of the producer, available resources, and the plant species' needs.
- 😀 Seed propagation is beneficial for producing large quantities of plants quickly, with some species offering high-quality seeds, but it can lead to variability in plant characteristics.
- 😀 Vegetative propagation ensures identical plant characteristics to the mother plant, offering faster development and precocity in blooming, though it requires more space and labor.
- 😀 The ornamental plant market is growing rapidly, with an increasing demand for quality products, pushing producers to rethink production methods and enhance sustainability.
- 😀 The production of ornamental plants is a strategic, high-growth sector in Brazilian agriculture, requiring continuous learning, investment, and adaptation to market trends for success.
Q & A
What is the main objective of micropropagation in ornamental plants?
-The main objective of micropropagation is the large-scale cloning and multiplication of plants to produce a significant number of individuals in a short amount of time, often for commercial purposes.
What materials can be used for micropropagation?
-Materials used for micropropagation include small portions of the parent plant, such as leaves, roots, seeds, shoots, or even cells, which are then cultured under controlled conditions.
Why is micropropagation conducted in a laboratory?
-Micropropagation is conducted in a laboratory because it requires strict control of environmental factors like light, temperature, and humidity to ensure the successful regeneration of new plants.
What are the benefits of micropropagation in ornamental plant production?
-The benefits of micropropagation include the production of high-quality, uniform, and healthy plants, which are essential for the commercial success of ornamental plant businesses.
What are some of the challenges of using micropropagation?
-Some challenges include the high initial investment in infrastructure, the need for skilled labor, and the elevated costs associated with producing plants through this method.
Which types of ornamental plants are commonly produced through micropropagation?
-Commonly produced ornamental plants through micropropagation include orchids, lisianthus, chrysanthemums, and lilies.
What is the main difference between seed propagation and vegetative propagation?
-Seed propagation involves producing plants from seeds, which can result in genetic variability, while vegetative propagation involves cloning the parent plant, ensuring identical characteristics in the offspring.
What are the advantages of seed propagation?
-Advantages of seed propagation include faster production of large quantities of plants, the ability to use high-quality seeds, and the possibility of propagating species without available vegetative materials.
What are the disadvantages of seed propagation?
-Disadvantages of seed propagation include the potential for genetic variability, high costs for acquiring improved seeds, and the delicate nature of seed germination, which requires specialized equipment and techniques.
How does vegetative propagation compare to seed propagation in terms of plant production?
-Vegetative propagation typically produces fewer plants compared to seed propagation but ensures that each plant has identical characteristics to the parent, which is important for commercial uniformity.
Why is it important for ornamental plant producers to stay informed about market trends?
-It is important because the ornamental plant market is becoming increasingly competitive, and producers need to adapt to changing consumer demands for high-quality, diverse, and innovative products to stay successful.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Pabrik Benih Kultur Jaringan Ibu kota, Mampu Hasilkan 20.000 Benih Pertahun

PRAKARYA KELAS 10 SEMESTER 2 Budidaya Tanaman Hias

KULTUR JARINGAN TANAMAN KENTANG BY JUNIARTI PRIHATINY SAHAT

The Future of Houseplants: Tissue Culture (TC)
Tissue Culture

Vegetative Propagation-Asexual Reproduction in Plants-Leaving Cert Biology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)