Hibridisasi Tanaman
Summary
TLDRThis lecture covers the process of plant hybridization, focusing on its role in expanding genetic diversity in plant breeding. It explains various types of hybridization, such as intraspecific, interspecific, and intergeneric crosses. The lecture outlines essential principles, such as the importance of species relationships, the selection of parent plants, and the potential barriers in hybridization. Practical techniques for successful hybridization are discussed, including emasculation, isolation, and labeling. The lecture emphasizes the importance of planning and strategy in plant breeding to achieve desired traits, and provides a task for students to deepen their understanding of crossbreeding methods.
Takeaways
- 😀 Hybridization is a process used in plant breeding to expand genetic diversity by crossing two or more genetically different plants to develop a new cultivar.
- 😀 There are four main categories of hybridization: intraspecific, intervarietal, interspecific, and intergeneric, each with varying success rates based on genetic similarity.
- 😀 Intraspecific hybridization (within the same species) generally has the highest success rate compared to intervarietal (within different varieties of the same species) and interspecific (between different species within the same genus) hybridizations.
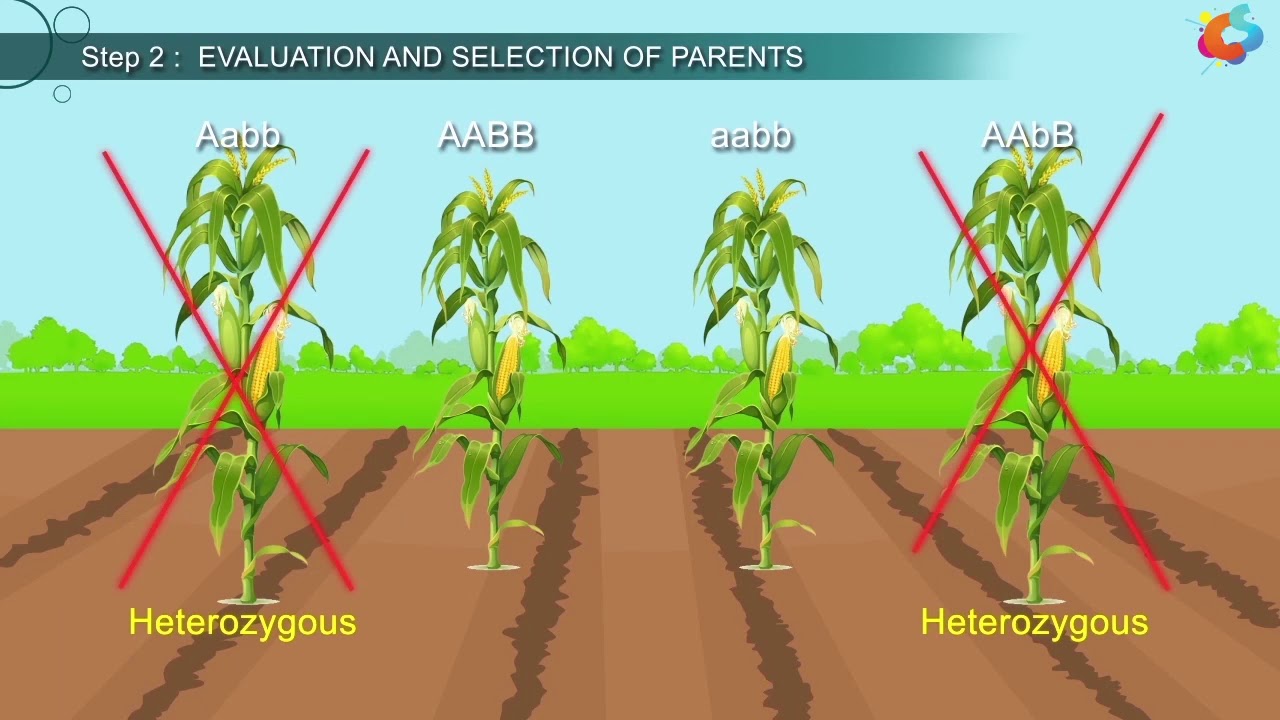
- 😀 The success of hybridization depends on understanding the genetic relationships between the plants being crossed and selecting appropriate parent plants for the desired traits.
- 😀 The goals of hybridization include combining beneficial traits from different varieties, expanding genetic variability, utilizing hybrid vigor, and testing potential offspring characteristics.
- 😀 Selecting the right species for hybridization requires understanding the genetic compatibility, ploidy levels, and the desired traits to transfer from wild relatives to cultivated plants.
- 😀 Wild plant species often possess superior traits, such as resistance to biotic and abiotic stress, which can be transferred to cultivated varieties through hybridization.
- 😀 Hybridization may face barriers such as pre-fertilization issues (e.g., pollen germination failure) and post-fertilization issues (e.g., embryo abortion or chromosomal elimination).
- 😀 In hybridization, three key concepts guide the selection of parent plants: variety, trait, and gene. The specific approach depends on whether the goal is to improve a particular variety, acquire certain traits, or introduce genes at the molecular level.
- 😀 Modern hybridization techniques, including genetic engineering and gene cloning, allow for precise control over traits, such as disease resistance in crops like wheat, through the insertion of specific genes.
- 😀 The hybridization process includes multiple steps, such as preparing the plants, emasculation (removal of male parts), castration (removal of female parts), isolation, labeling, and sometimes pollen collection to facilitate successful breeding.
Q & A
What is hybridization in plant breeding?
-Hybridization in plant breeding refers to the process of crossing two or more plants with different genetic makeup to combine specific desirable traits, creating a new cultivar with enhanced characteristics.
What are the four categories of hybridization?
-The four categories of hybridization are: 1) Intraspecific hybridization (between varieties of the same species), 2) Intervarietal hybridization (between different varieties within the same species), 3) Interspecific hybridization (between different species within the same genus), and 4) Intergeneric hybridization (between plants from different genera).
Which type of hybridization has the highest success rate?
-Intraspecific hybridization has the highest success rate, as the plants involved are more genetically similar compared to interspecific or intergeneric hybridizations.
What factors should be considered when crossing plants?
-When crossing plants, it's important to consider the genetic relationship between the plants, the ploidy level of the species, the stability and inheritance of the desired traits, and the goal of the hybridization (e.g., to combine traits or improve resistance).
What is the role of wild relatives in plant hybridization?
-Wild relatives are often used in hybridization to introduce superior traits such as resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses, which cultivated plants may lack. These wild species can offer genetic advantages that improve crop resilience and productivity.
What are some barriers that may occur during interspecific hybridization?
-Barriers in interspecific hybridization may include pre-fertilization barriers (such as failure of pollen germination) and post-fertilization barriers (like embryo abortion or chromosome elimination). These barriers can reduce the success of hybridization.
What are the three concepts in selecting parent plants for hybridization?
-The three concepts in selecting parent plants for hybridization are: 1) Variety-based concept (choosing parents to improve specific variety traits), 2) Trait-based concept (focusing on desirable traits rather than variety), and 3) Gen-based concept (introducing new genetic traits or genes into the crop through molecular methods).
What are some common methods used for emasculation in hybridization?
-Common emasculation methods include clipping or pinching the male flower parts, using vacuum pumps (especially for crops like rice), and using heat or chemicals (such as hot water or alcohol) to inactivate pollen and prevent unwanted pollination.
Why is it important to isolate flowers during hybridization?
-Isolating flowers is crucial to prevent unwanted cross-pollination with other plants, ensuring that the hybridization process results in the desired cross and not contamination by external pollen.
What is the role of labeling in hybridization?
-Labeling the plants involved in hybridization is important for tracking the success of the cross. It helps the breeder identify which parent plants were used and allows for accurate recording and evaluation of the results.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)