Eletrônica de Potência 1: (A.07) Retificador Monofásico de Meia Onda - Carga RL e Diodo de Retorno
Summary
TLDRThis lesson covers the analysis of a monophase uncontrolled rectifier with an RL load and a freewheeling diode (D2). It explains the operation of the circuit, breaking it into two stages, and focuses on how the diodes conduct during positive and negative half cycles of the AC input. The impact of adding the freewheeling diode on the output voltage and current is discussed, improving the performance compared to a simple RL load. The lesson also includes calculations for the average and RMS current values, with an example to enhance understanding of the concepts presented.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lesson focuses on the analysis of a single-phase uncontrolled half-wave rectifier with an RL load and a freewheeling diode (D2) to prevent negative voltage at the output.
- 😀 The freewheeling diode (D2) ensures the current in the load does not reach zero, reducing ripple in the current waveform.
- 😀 The circuit operates in two stages: the first during the positive half-cycle, where D1 conducts, and the second during the negative half-cycle, where D2 conducts.
- 😀 In the first stage, the output voltage is equal to the source voltage (Vs), while D1 conducts and D2 remains off.
- 😀 In the second stage, the source voltage is negative, and D2 conducts, providing an alternate path for the current, while D1 is reverse biased and does not conduct.
- 😀 The average output voltage (Vout) of the circuit is calculated to be VM/pi, which results in a value of 0.318 times the peak voltage (VM).
- 😀 The analysis uses Fourier series to calculate the harmonic components of the output voltage and current, showing the contributions of the fundamental, second, fourth, and sixth harmonics.
- 😀 The average current in the load (I_avg) is derived from the average output voltage, calculated as VM/pi * R.
- 😀 The RMS current (I_rms) is calculated using the harmonic amplitudes, including the fundamental and higher-order harmonics, and is obtained by applying the RMS formula for multi-component waveforms.
- 😀 In the exercise example, the RMS value of the current is calculated to be 5.1 A, based on the voltage and harmonic components of the output waveform.
- 😀 The analysis and calculation methods provide insights into how different parameters, like the load resistance (R) and inductance (L), affect the waveform and current behavior in a half-wave rectifier with an RL load.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the class in the provided script?
-The main focus of the class is the study of a monophase half-wave rectifier with an RL load and the introduction of a freewheeling diode (D2) in the circuit.
What role does the freewheeling diode (D2) play in the circuit?
-The freewheeling diode (D2) is connected in parallel with the RL load to prevent the emergence of negative voltage on the output, which increases both the average output voltage and the average current through the load.
Why are the analysis and forms of wave considered only from the perspective of the secondary side of the transformer?
-The analysis focuses on the secondary side of the transformer to simplify the study, concentrating on the effects of the rectification process on the load and the current flow.
What happens during the first stage of the operation of the circuit?
-During the first stage, from 0 to pi, the diode D1 conducts when the input AC voltage is positive, while diode D2 is blocked, causing the current through D1 to be equal to the load current and resulting in a zero current for D2.
How does the second stage of the operation differ from the first?
-In the second stage, from pi to 2pi, the AC voltage is negative, which makes D2 conduct and D1 stop conducting. This provides an alternate current path through D2 and prevents the load current from reaching zero, reducing ripple.
What is the impact of the inductance (L) in the circuit?
-The inductance helps prevent the load current from reaching zero during the second stage, thus reducing the ripple. If the inductance is very small, the current may still be in discontinuous mode.
How is the average output voltage (Vout) related to the peak voltage (VM)?
-The average output voltage (Vout) for a half-wave rectifier with an RL load and a freewheeling diode is equal to VM/pi, or approximately 0.318 times VM.
What is the method used to calculate the RMS value of the current in the circuit?
-The RMS value of the current is calculated using a formula that incorporates the fundamental and harmonic components of the output voltage, considering the impedance at each harmonic frequency.
What are the key components of the Fourier series expansion in this analysis?
-The Fourier series expansion for the output voltage consists of a DC component (VM/pi), a fundamental sine wave component, and higher-order harmonics (second, fourth, sixth, etc.) with decreasing amplitudes.
How did the class calculate the DC and RMS components of the load current?
-The DC component of the load current was calculated using the average output voltage (Vout), while the RMS component was computed by summing the squared contributions of the fundamental, second harmonic, fourth harmonic, and sixth harmonic components, then taking the square root.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Eletrônica de Potência 1: (A.10) Retificador Monofásico Não Controlado de Onda Completa - Carga RL

Eletrônica de Potência 1: (A.05) Retificador Monofásico Não Controlado de Meia Onda - Carga R
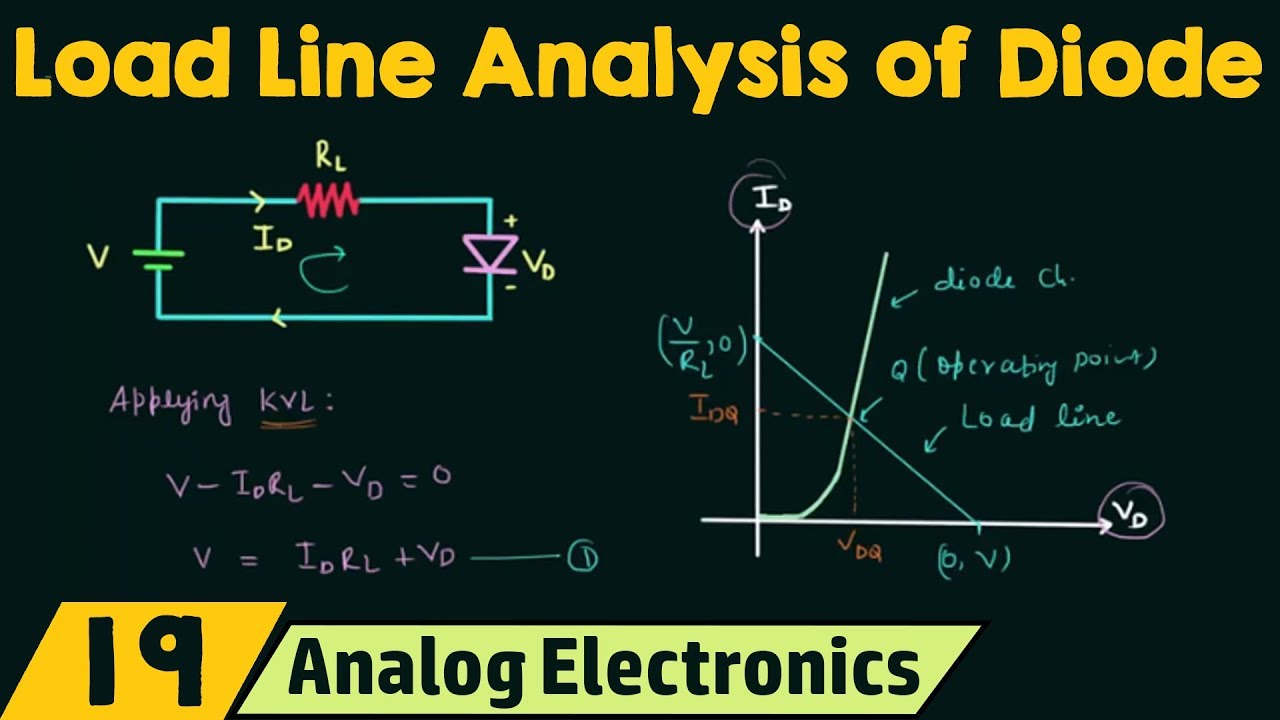
Load Line Analysis of Diode
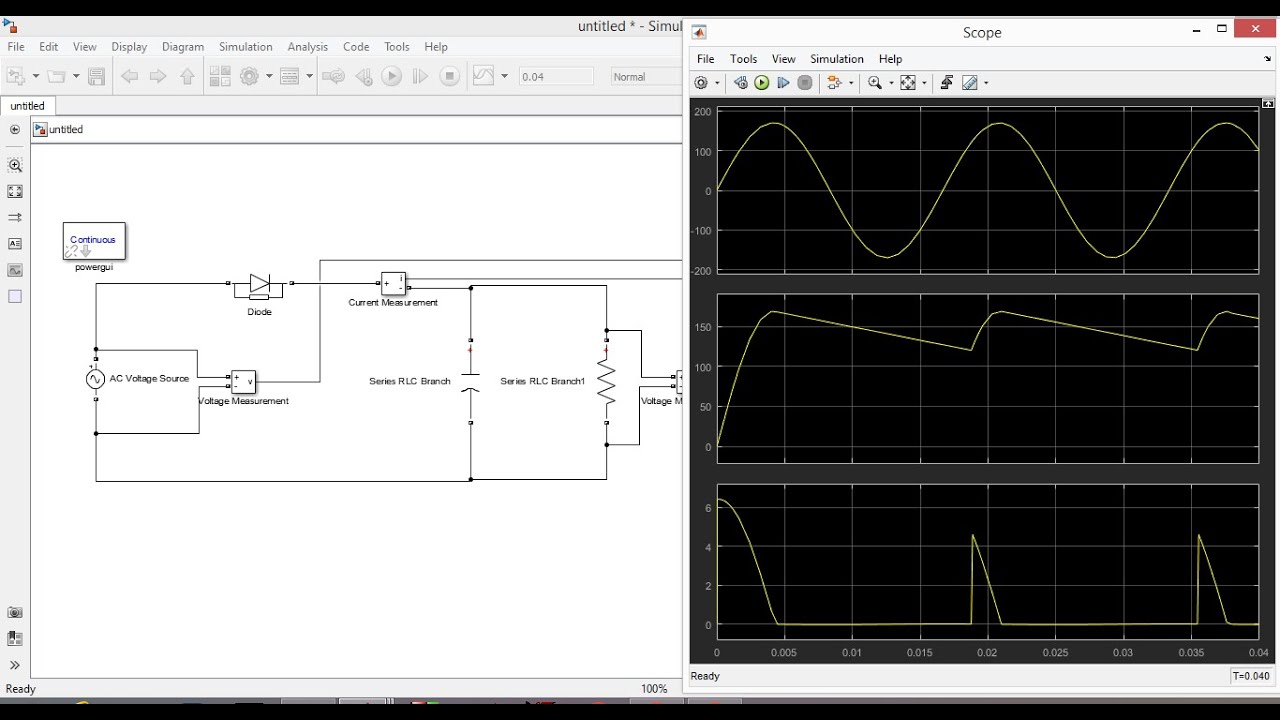
Half Wave Unctrolled Rectifier with C filter Matlab Simulink
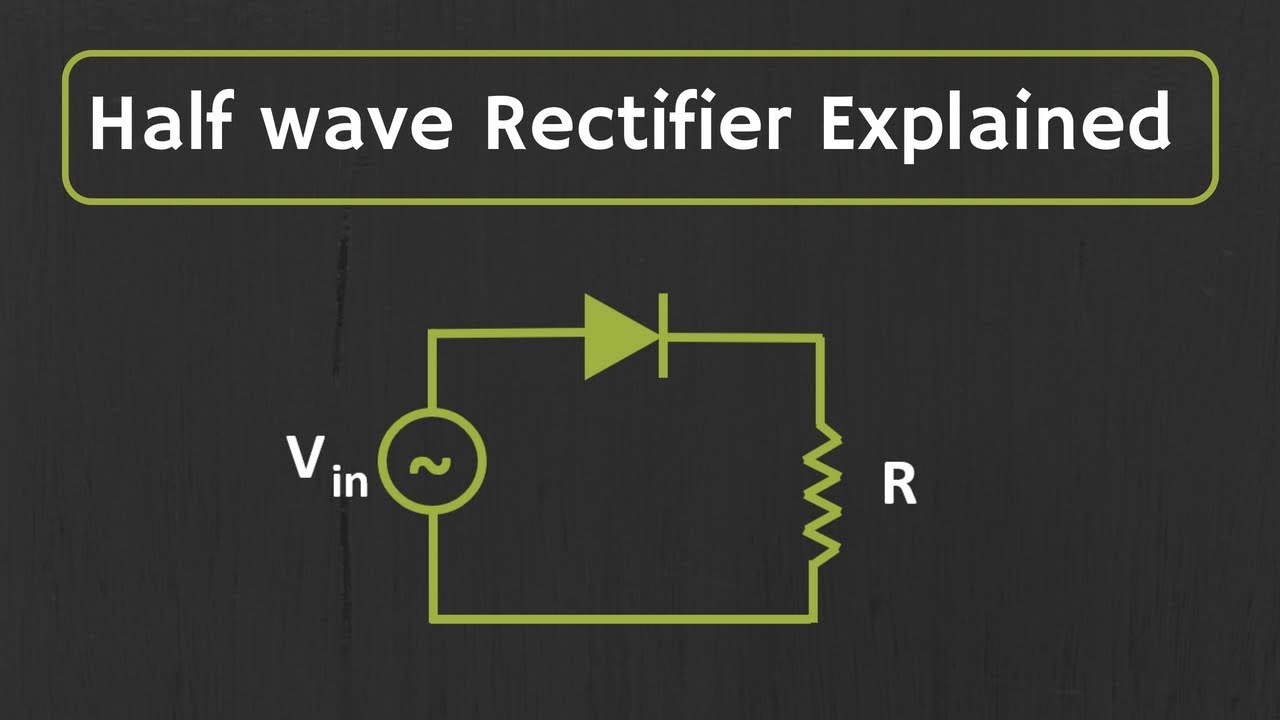
Half wave Rectifier Explained

What is a rectifier?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)