ATPL Radio Navigation - Class 2: Antennas.
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the importance of antenna shape and design for transmitting and receiving radio signals, explaining how different antenna types serve unique purposes. It covers basic antenna functions, such as polarization, and explores a range of antennas like loop, parabolic, phased array, and helical antennas. The video also discusses the limitations of antenna range based on transmitter and receiver height, demonstrating how to calculate the theoretical maximum range. Ideal for learners, the video explains how the right antenna ensures effective communication in aviation, satellite TV, radar systems, and GPS technologies.
Takeaways
- 😀 Antenna shapes impact the ability to transmit and receive radio signals effectively.
- 😀 Antennas generate electromagnetic fields when electricity flows through them, which is the basis of radio waves.
- 😀 The polarization of a radio wave (vertical or horizontal) dictates the ideal orientation of the antenna for optimal signal reception.
- 😀 Antennas are ideally half the wavelength of the signal they are designed to receive, though this can be impractical for large wavelengths.
- 😀 The wavelength for high-frequency signals ranges from 10m to 100m, making it difficult to use full-length antennas in practical applications like aircraft.
- 😀 Loop antennas are useful for determining the direction of a signal, often used in non-directional beacon (NDB) systems in aviation.
- 😀 Parabolic antennas, such as those used in satellite TV, reflect signals toward a receiver at the focus point, amplifying weak signals.
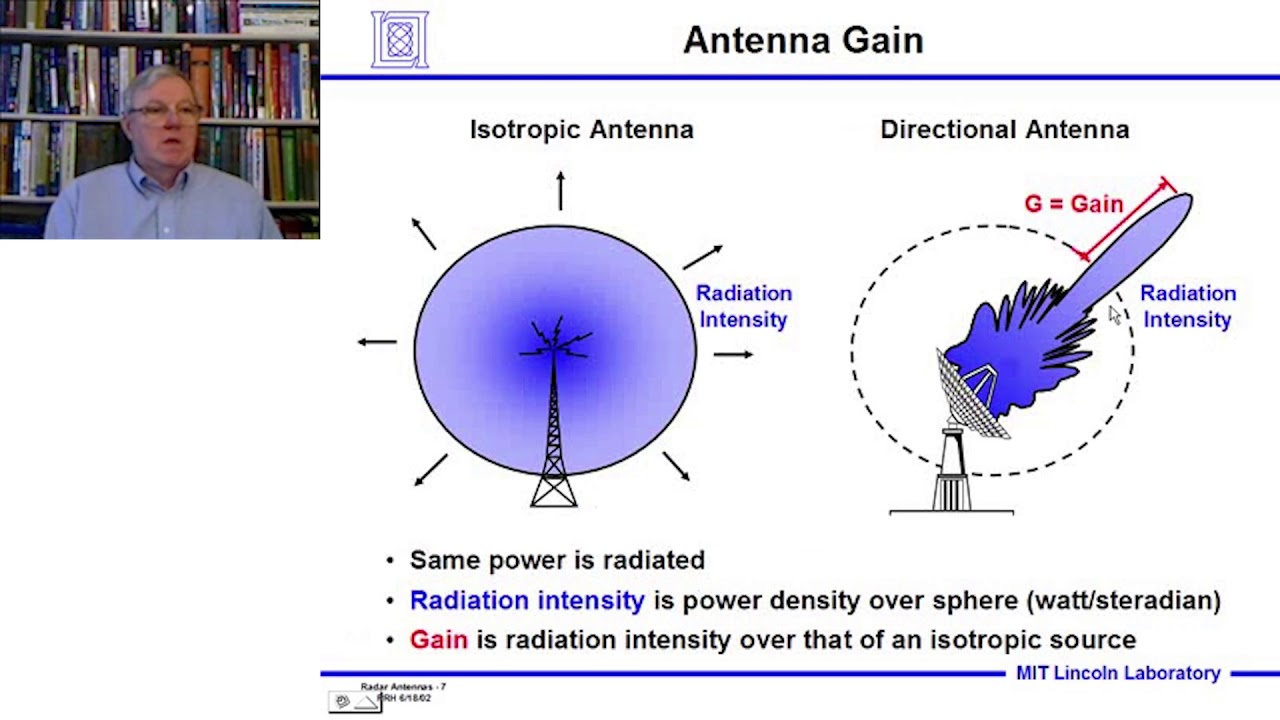
- 😀 Phased array antennas can focus radio wave signals in a specific direction without requiring a large dish, useful in radar systems like those used at airports.
- 😀 Slotted planar array antennas can electronically steer radio wave beams and are commonly used in weather radar systems.
- 😀 Helical antennas are used for GPS signals, offering compact design and efficient reception of circularly polarized waves.
- 😀 Antenna signal range is limited by the height of the transmitter and receiver, and the curvature of the Earth, with a formula available for calculating the maximum theoretical range.
Q & A
Why does the shape of an antenna matter for signal transmission and reception?
-The shape of an antenna affects how efficiently it can transmit and receive radio waves. The design influences the polarization, directionality, and the focus of the signal, which is crucial for optimizing signal strength and range.
What is the relationship between the electric field and the magnetic field in a radio wave?
-In a radio wave, the electric field (E) and magnetic field (H) are perpendicular to each other and travel at right angles. The electric field defines the polarization of the wave, which is important for antenna alignment.
What is polarization in the context of radio waves and antennas?
-Polarization refers to the orientation of the electric field in a radio wave. If the electric field is vertical, the wave is vertically polarized. For optimal reception, the receiving antenna should match the polarization of the incoming wave.
Why is the ideal antenna size related to the wavelength of the radio signal?
-The ideal antenna size is typically half the wavelength of the radio signal. This ensures efficient transmission and reception. If the antenna is too short, the signal strength decreases, and the reception becomes weaker.
What are the challenges when dealing with very long wavelengths for antenna design?
-Long wavelengths, like those in the high-frequency band, require large antennas that are impractical for most applications, such as on aircraft. To solve this, smaller fractions of the wavelength, such as a quarter or eighth, are used, although this may reduce signal strength.
How does a loop antenna work in detecting the direction of a signal?
-A loop antenna detects the direction of a signal by measuring the phase difference across different parts of the loop. When aligned with the radio wave, the phase difference generates a voltage, which can then be used to indicate the direction of the signal.
Why is a parabolic antenna used in satellite TV and space telescopes?
-A parabolic antenna uses a reflective dish to focus incoming signals onto a receiver located at the focus point. This allows weak signals from far distances, such as satellite broadcasts or deep-space signals, to be amplified and received efficiently.
What is the function of a phased array antenna in radar systems?
-A phased array antenna consists of multiple antennas arranged in a way that allows the signals to be concentrated in one direction. This enables highly directional radar transmissions without needing a large, rotating dish.
What is the advantage of a slotted planar array antenna over traditional rotating antennas?
-A slotted planar array antenna can digitally sweep the beam of radio waves back and forth without the need for rotating parts, making it lighter and more cost-effective. It's commonly used in aircraft weather radar systems.
How does a helical antenna differ from a simple wire antenna in terms of size and performance?
-A helical antenna can offer similar performance to a straight wire antenna but with a much smaller size. It achieves this by using a coiled structure, where the spacing and diameter of the coils define the antenna's sensitivity to different wavelengths.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)