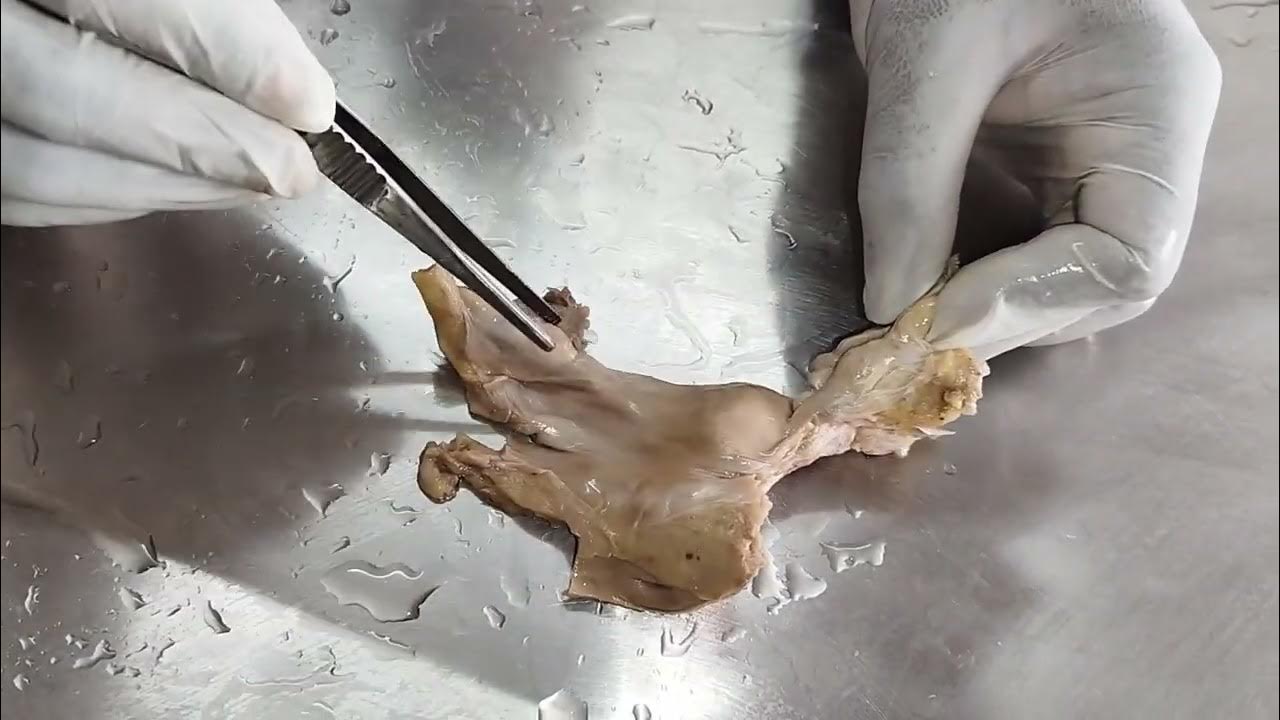
Flower Dissection - Reproduction in flowering plants
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the anatomy and function of a lily flower, highlighting its distinct reproductive parts. It begins by removing the sepals, which protect the flower bud, and then moves on to the petals, which are brightly colored to attract pollinators. The script explains the roles of the male stamen, with its anthers producing pollen, and the female carpel, consisting of the ovary, style, and stigma. The ovary contains ovules, which develop into fruit after fertilization. The video also includes a microscopic examination of pollen grains, emphasizing the flower's intricate structure and its importance in the pollination process.
Takeaways
- 🌷 The flower being dissected is a lily, chosen for its large size and distinct reproductive parts.
- 🌱 The outer layer of the flower, known as the sepals, is removed first. Sepals are green and come out at the top of the stem.
- 🌼 In the lily, sepals and petals can look almost identical in earlier blooming stages, both being brightly colored to attract insects.
- 🍯 The flower contains nectar, a sticky sugar-containing fluid, to attract insects necessary for pollination.
- 🌾 The male reproductive part of the flower is called the stamen, which includes the anther and filament. The anther produces pollen.
- 🔬 Pollen grains can be observed under a microscope to see individual grains released from the anthers.
- 🌸 The female reproductive part is called the carpel, which consists of the ovary, style, and stigma.
- 🍎 The ovary will develop into the fruit and contains ovules with female gametes inside.
- 🔍 Ovules are very tiny and require a microscope for a clear view.
- 🌺 The stigma is the part of the flower that receives pollen, crucial for fertilization.
- 🌿 The overall structure of the flower includes the receptacle at the base, petals for attracting insects, and both male (stamen) and female (carpel) reproductive parts.
Q & A
What type of flower is being dissected in the video?
-A lily is being dissected in the video because it has a large size and very distinct reproductive parts.
What are the first parts of the flower that are removed in the dissection?
-The first parts removed are the sepals, which are the outer layer of the flower.
What is the purpose of the petals in the flower?
-The petals are brightly colored to attract insects, which aids in the pollination process.
What is the sticky sugar-containing fluid found at the base of the petals called?
-The sticky sugar-containing fluid is called nectar, which is used to attract insects for pollination.
What is the male reproductive part of the flower known as?
-The male reproductive part of the flower is known as the stamen.
What are the two main components of the stamen?
-The stamen consists of the anther, which produces pollen, and the filament, which supports the anther.
How can pollen be observed under a microscope?
-Pollen can be observed under a microscope by placing it on a microscope slide and examining it through the lens.
What is the female reproductive part of the flower called?
-The female reproductive part of the flower is called the carpel.
What are the main structures of the carpel and their functions?
-The main structures of the carpel are the ovary, which develops into fruit, the style, which connects the ovary to the stigma, and the stigma, which receives pollen.
What are the tiny structures inside the ovary that are visible under a microscope?
-The tiny structures inside the ovary are the ovules, which contain the female gametes.
What is the purpose of the stigma in the flower's reproductive system?
-The stigma is the part of the carpel where pollen must land for fertilization to occur.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)