Propriedades Periódicas e Aperiódicas - Brasil Escola
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the presenter explains the difference between periodic and aperiodic properties of chemical elements. Periodic properties, such as atomic radius and electronegativity, follow a regular repeating pattern as atomic number increases. In contrast, aperiodic properties, including specific heat and atomic mass, do not exhibit predictable cycles. The video highlights the importance of the periodic table in organizing elements and understanding these properties. Viewers are encouraged to like, comment, share the video, and follow the channel for more updates.
Takeaways
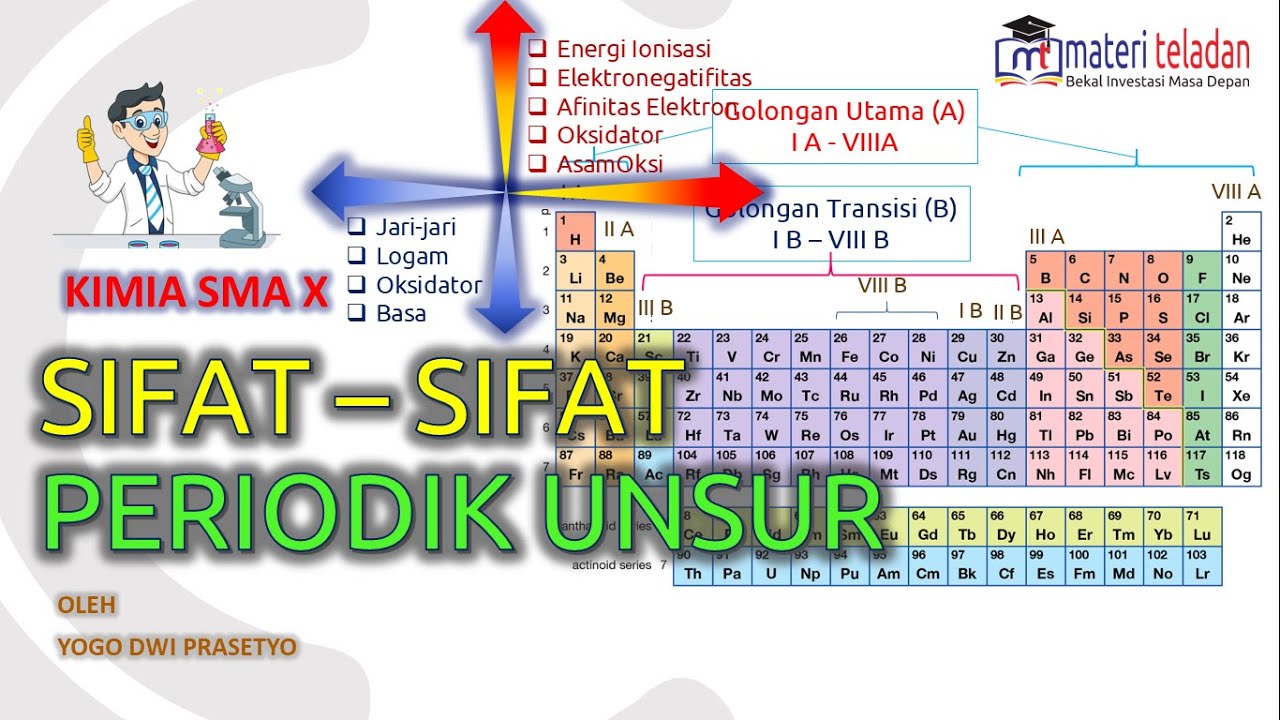
- 😀 Periodic properties are those that repeat in a regular pattern as the atomic number increases.
- 😀 Examples of periodic properties include atomic radius, electronegativity, electron affinity, and ionization energy.
- 😀 These properties follow a periodic pattern, similar to the repeating days of the week or months of the year.
- 😀 Aperiodic properties do not repeat in a predictable pattern with increasing atomic number.
- 😀 Examples of aperiodic properties include specific heat, refractive index, hardness, and atomic mass.
- 😀 The periodic table was designed not just for organizing elements by atomic number, but also by their properties.
- 😀 Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties that changes regularly as you move across the table.
- 😀 Electronegativity is another periodic property that measures an atom's ability to attract electrons.
- 😀 Ionization energy is a periodic property that refers to the energy required to remove an electron from an atom.
- 😀 Both periodic and aperiodic properties help us understand the behavior and characteristics of elements.
- 😀 The lesson emphasizes the importance of recognizing the difference between periodic and aperiodic properties.
Q & A
What are periodic properties in chemistry?
-Periodic properties are characteristics of chemical elements that repeat in a regular, predictable pattern as the atomic number increases. These properties change in a periodic manner, similar to how days of the week or months of the year repeat regularly.
Can you give examples of periodic properties?
-Examples of periodic properties include atomic radius, electronegativity, electron affinity, electropositivity, ionization energy, atomic volume, melting point, boiling point, and density.
What is the difference between periodic and aperiodic properties?
-Periodic properties repeat in a regular, predictable pattern as the atomic number increases, while aperiodic properties do not follow a predictable pattern and can change without a regular repetition.
What are aperiodic properties in chemistry?
-Aperiodic properties are characteristics of chemical elements that do not follow a regular pattern or repetition. They change irregularly as the atomic number increases.
Can you give examples of aperiodic properties?
-Examples of aperiodic properties include specific heat, refractive index, hardness, and atomic mass.
Why was the periodic table created beyond just organizing elements by atomic number?
-The periodic table was created not only to organize elements by atomic number but also to group them according to their chemical properties, allowing scientists to better understand their relationships and behaviors.
What does the term 'periodicity' mean in the context of the periodic table?
-In the context of the periodic table, 'periodicity' refers to the repeating pattern of certain properties, such as atomic size or electronegativity, as you move across a period or down a group in the table.
How does the atomic number affect periodic properties?
-As the atomic number increases, certain properties, such as atomic radius or electronegativity, change in a predictable way. For example, atomic radius typically decreases across a period and increases down a group.
What role do periodic properties play in understanding the elements?
-Periodic properties help scientists predict the behavior of elements, how they will react with other substances, and their physical characteristics based on their position in the periodic table.
How are holidays like summer and winter breaks related to periodic properties?
-Holidays like summer and winter breaks are an analogy used to explain periodic properties. Just like how holidays occur at regular intervals, periodic properties repeat at regular intervals based on the atomic number, creating predictable patterns.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)