Protein Synthesis (Biochemistry) | Sketchy MCAT
Summary
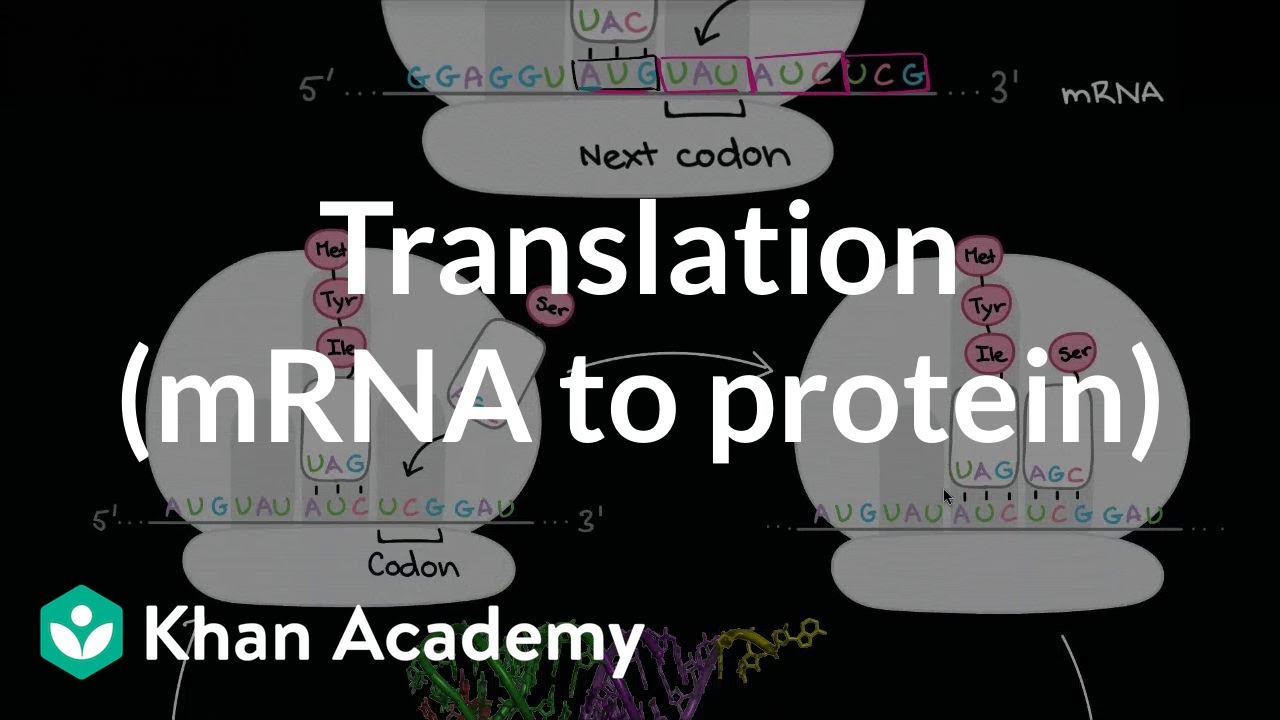
TLDRThis video explains the process of eukaryotic translation, where ribosomes use mRNA and tRNA to synthesize proteins. The process involves initiation, elongation, and termination stages. It starts with the small ribosomal subunit attaching to the mRNA and scanning for the start codon. The large subunit joins, and tRNA molecules add amino acids to form a growing polypeptide chain. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, adding more amino acids until a stop codon signals the release of the completed protein. The video creatively uses dim sum analogies to simplify complex biological processes for easier understanding.
Takeaways
- 😀 Protein synthesis (translation) is the process where ribosomes use mRNA and tRNA to create proteins.
- 🍚 Ribosomes make intracellular proteins in the cytoplasm, while proteins to be secreted are made in the rough ER.
- 🧬 mRNA serves as a template, tRNA helps bring amino acids, and ribosomes are the machines assembling proteins.
- 🔋 ATP is required to charge tRNA with the correct amino acid using an enzyme called aminoacyl tRNA synthetase.
- 🛠️ There are 20 different aminoacyl tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid, to ensure proper protein construction.
- 🔄 During elongation, a new tRNA enters the A site, pairing with mRNA codons, and amino acids are joined by peptide bonds.
- 🧑🍳 The ribosome's ribozyme activity helps link amino acids, creating a growing polypeptide chain during elongation.
- 🔁 The ribosome moves along the mRNA in a process called translocation, freeing the E site for the next tRNA.
- ⏹️ Termination occurs when a stop codon (UGA, UAA, or UAG) is reached, signaling the end of translation.
- 💥 Release factors recognize the stop codon, ending translation and releasing the completed protein from the ribosome.
Q & A
What is protein synthesis more commonly called, and what is its purpose?
-Protein synthesis is more commonly called translation. It is the biological process where ribosomes utilize mRNA to make proteins.
Where do intracellular proteins get made in eukaryotic cells?
-Intracellular proteins are made in free-floating ribosomes found in the cytoplasm.
How do proteins destined for secretion differ in terms of where they are made?
-Proteins that will eventually be secreted are made in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), which has ribosomes attached to it.
What role do tRNAs play in translation?
-tRNAs link the mRNA codons with the corresponding amino acids, adding them to the growing polypeptide chain during translation.
What is the process of charging a tRNA molecule, and why is ATP required?
-Charging a tRNA involves the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase using ATP to attach an amino acid to the tRNA molecule. ATP is required for the energy needed to attach the amino acid.
How many versions of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase are there in the human body, and why?
-There are 20 versions of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, one for each of the 20 different amino acids used in protein synthesis.
What happens during translation initiation in eukaryotic cells?
-In initiation, eukaryotic initiation factors help attach the small ribosomal subunit to the initiator tRNA carrying methionine. This complex then binds to the 5' cap of mRNA and scans for the start codon AUG.
What is the wobble effect in translation, and why is it important?
-The wobble effect allows for non-specific base pairing in the third position of the codon, which accounts for redundancy in the genetic code. It enables multiple mRNA codons to code for the same amino acid.
What is the role of the ribozyme during elongation?
-The ribozyme, which is part of the ribosome, catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids, elongating the polypeptide chain.
What occurs during translation termination?
-During termination, release factors recognize a stop codon (UAA, UGA, or UAG), causing the ribosome to stop translation and release the newly synthesized polypeptide.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)