Por que não clonamos HUMANOS?
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fascinating world of cloning, starting with Dolly the sheep, the first mammal cloned from an adult cell. It explains the different types of cloning, including natural and induced cloning, and the potential benefits and ethical concerns of human cloning. The video touches on the science behind cloning animals, breakthroughs in cloning technology, and even the controversial claims of human cloning. It concludes by discussing future possibilities, such as digital cloning and the potential for achieving immortality through AI and cloning. The ethical dilemmas and risks are carefully considered, leaving viewers to ponder the implications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Dolly, the first cloned mammal, was the first successful adult mammal clone, and her creation sparked discussions about cloning technologies.
- 😀 Cloning refers to creating genetically identical copies of a biological entity. This concept stems from Greek and botany, where plants, fungi, and bacteria reproduce asexually.
- 😀 There are two main types of animal cloning: natural (like identical twins) and induced (which uses genetic engineering techniques).
- 😀 Induced cloning includes therapeutic cloning, which involves stem cells for disease treatment, and reproductive cloning, which creates a fully developed organism.
- 😀 Reproductive cloning has been successfully done with animals, starting with sea urchins in the late 1800s, and advancing through the 20th century.
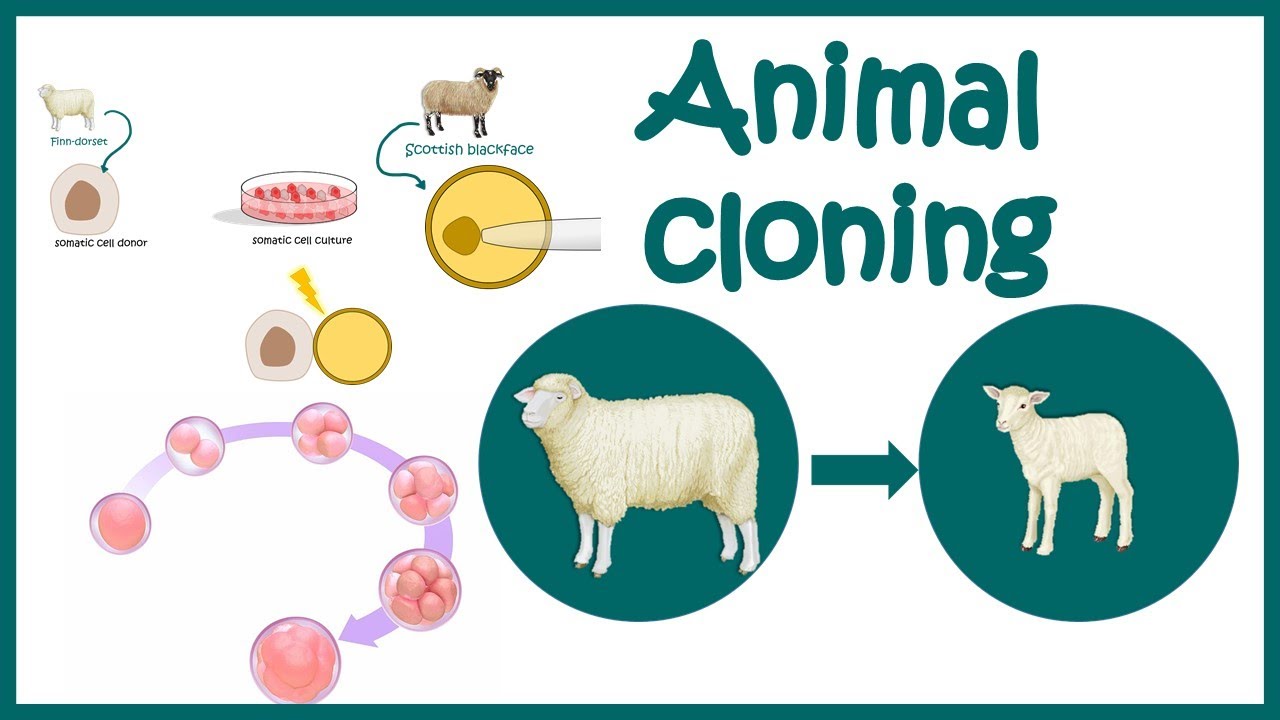
- 😀 Dolly’s success in 1996 showed that an adult somatic cell could be used to create a clone, challenging existing beliefs about cell totipotency.
- 😀 Cloning of other animals has followed, with clones being created for agricultural purposes, like the famous cloned cow, Penta, in Brazil in 2002.
- 😀 The ethical and legal concerns surrounding human cloning have led to bans, such as the UNESCO declaration against reproductive human cloning.
- 😀 While the idea of cloning humans may sound futuristic, some doctors have claimed success in cloning humans, though evidence remains unclear.
- 😀 The potential benefits of cloning include aiding infertile couples and possibly resurrecting extinct species, though there are significant risks, such as the ethical dilemmas of creating clones of historical figures.
- 😀 The future of cloning could involve combining traditional cloning with digital minds, where memories and personalities are digitally transferred to clones, opening possibilities for 'eternal life.'
Q & A
What was the first cloned mammal?
-The first cloned mammal was Dolly, a sheep, who was cloned from an adult somatic cell in 1996.
What is the main difference between natural cloning and induced cloning?
-Natural cloning occurs without scientific intervention, such as identical twins, while induced cloning is a process where scientists replicate a living being using techniques of genetic engineering in a lab.
What is therapeutic cloning?
-Therapeutic cloning involves the creation of cloned cells, typically for medical purposes, like producing stem cells to treat diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's, or Parkinson's.
How does reproductive cloning differ from therapeutic cloning?
-In reproductive cloning, the cloned embryo is implanted into a uterus to develop into a genetically identical organism, whereas in therapeutic cloning, the goal is to harvest stem cells from the embryo for medical treatments, not to create a full organism.
Why did Dolly the sheep become famous?
-Dolly became famous because she was the first mammal cloned from an adult somatic cell, proving that adult cells could be used to create a genetically identical organism.
What challenges were faced in cloning Dolly?
-It took 277 attempts to successfully clone Dolly, and she suffered from premature aging and health issues, eventually dying at a young age from a lung disease.
What did scientists learn from Dolly's cloning?
-Dolly's cloning provided insights into cloning techniques, the potential for cloning animals, and the challenges of premature aging in cloned organisms.
What ethical concerns arise from human cloning?
-Human cloning raises concerns about identity, the potential for misuse, and ethical dilemmas regarding the creation of individuals with specific traits, as well as the possibility of reviving harmful figures from history.
Is human cloning legal?
-In many countries, including Brazil, human cloning is illegal, with laws prohibiting reproductive cloning due to ethical concerns. However, therapeutic cloning using stem cells is allowed in some contexts.
What would be the potential benefits and dangers of widespread human cloning?
-The potential benefits of human cloning include addressing infertility and possibly reviving extinct species. However, dangers include ethical dilemmas, health risks for clones, and the creation of genetically engineered individuals or even armies.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Do clones age faster? #InstanteBiotec 51

The Story of Dolly the cloned Sheep - Animal Cloning

The History Of Cloning Explained

How Dolly the Sheep was cloned
Animal cloning : Story of Dolly the sheep | The world of animal cloning | Animated biology

The Story of Dolly the Cloned Sheep | Retro Report | The New York Times
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)