BAB 5 DINAMIKA LITOSFER
Summary
TLDRThe script provides an in-depth look into Earth's lithosphere and its dynamics, explaining the different layers of the Earth, such as the crust, mantle, and core. It covers the processes of plate tectonics, including movements like subduction, folding, and faulting. Additionally, it explores volcanic activities, the types of magma intrusions, and the effects of volcanic eruptions. The impact of these geological forces on human life is discussed, ranging from the formation of natural resources like petroleum and gas to the destruction caused by earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions. This comprehensive explanation highlights the powerful forces shaping our planet.
Takeaways
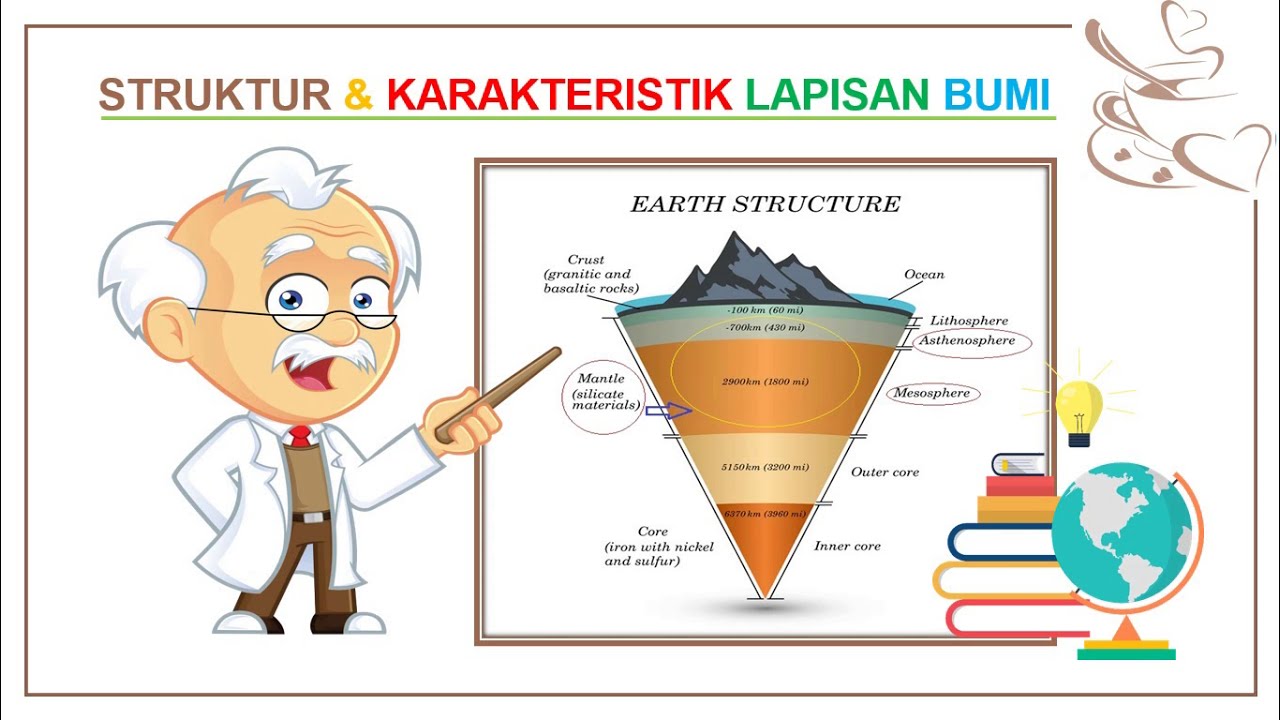
- 😀 The lithosphere is the Earth's outer layer, including the crust and upper mantle, and plays a vital role in shaping the planet's surface.
- 😀 The Earth's crust is divided into two types: oceanic crust (basaltic) and continental crust (granitic and metamorphic), with varying thicknesses.
- 😀 Magma and lava are central to the rock cycle, transforming into igneous rocks, and eventually contributing to sedimentary and metamorphic rocks through geological processes.
- 😀 Tectonic forces, which can be either endogenic (from within the Earth) or exogenic (from outside the Earth), drive the dynamics of Earth's surface.
- 😀 Tectonism refers to movements in the Earth's crust, leading to dislocations and changes in shape, with examples such as volcanic activity and earthquakes.
- 😀 Volcanoes are formed through magma intrusions, and their eruptions can be explosive or effusive, with effects such as lava flows or ash clouds.
- 😀 Seismic activities, including earthquakes, are the result of energy release from within the Earth, often caused by tectonic shifts.
- 😀 Magmatic intrusions include various forms such as laccoliths and batholiths, which are formed by the movement of magma through Earth's crust.
- 😀 The Earth's core is composed of iron and nickel, with a solid inner core and a molten outer core, both playing a key role in maintaining the planet's heat and magnetic field.
- 😀 Volcanic and seismic activity can have both positive and negative impacts, such as soil fertility and energy generation, but also destructive forces like tsunamis and gas emissions.
Q & A
What is the lithosphere?
-The lithosphere is the Earth's outermost layer, consisting of the Earth's crust and the upper part of the mantle.
How is the Earth's crust divided?
-The Earth's crust is divided into two types: continental crust, which is mostly made of granitic rocks, and oceanic crust, which is mainly made of basaltic rocks.
What is the thickness of the oceanic and continental crust?
-The oceanic crust is about 5-10 km thick, while the continental crust ranges from 20-70 km in thickness.
What is the composition of the Earth's mantle?
-The Earth's mantle consists of silicate rocks that are rich in magnesium and iron, with temperatures ranging from about 1300°C to 3000°C.
What is the difference between the Earth's inner and outer core?
-The inner core is solid, composed mainly of iron and nickel, with temperatures reaching around 4800°C, while the outer core is liquid, with temperatures around 3900°C.
What is the rock cycle?
-The rock cycle refers to the continuous process where rocks are formed, altered, and transformed through processes like volcanic activity, erosion, and pressure, which results in the creation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
How do igneous rocks form?
-Igneous rocks form from the solidification of molten magma. Depending on whether the magma cools inside or outside the Earth's crust, the rock can be classified as intrusive or extrusive.
What is the role of tectonism in shaping the Earth's surface?
-Tectonism, which includes processes like orogenesis (mountain building) and epirogenesis (vertical movements of the Earth's crust), plays a major role in shaping the Earth's surface by causing deformation, displacement, and changes in the Earth's structure.
What are the effects of volcanic activity?
-Volcanic activity can have both positive and negative effects. Positively, it can create fertile soil and provide geothermal energy, while negatively it can cause damage through eruptions, tsunamis, and the release of harmful gases.
What are the different types of volcanoes?
-There are several types of volcanoes, including stratovolcanoes (which form from alternating explosive and effusive eruptions), shield volcanoes (formed from fluid lava), and maar volcanoes (resulting from explosive eruptions).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
STRUKTUR DAN KARAKTERISTIK LAPISAN BUMI

Geo X. 19. Dinamika Litosfer dan Dampaknya Bagi Kehidupan Manusia.

Day-8 || BA 1st semester geography Unit-1 ( Interior of Earth 🌍) by Mukul Sir #geography #earth

Compositional and mechanical layers of the earth | Cosmology & Astronomy | Khan Academy

Definisi Litosfer & Karakteristik Lapisan Bumi

Geologia: Formação do Planeta Terra - Brasil Escola
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)