Cell structure topical past papers paper 2 (part 1) - AS Level Biology
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the instructor discusses key concepts from AS Level Biology (9700) related to cell structure. The video covers various organelles in plant and animal cells, explaining their functions and characteristics, such as mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum, and chloroplasts. It also explores the processes of protein synthesis, modification, and secretion, guiding viewers through the sequence of events in protein production. The video provides helpful diagrams and explanations to reinforce understanding of cellular structures and their roles in biological processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Plant cells can be identified by the presence of a cellulose cell wall, plasmodesma, and a large central vacuole.
- 😀 Electron micrographs are images taken by electron microscopes to visualize cell structures, like plant and animal cells.
- 😀 Mitochondria are involved in aerobic respiration and ATP synthesis, and they have inner membrane folds called cristae.
- 😀 Centrioles are cylindrical, non-membrane bound organelles that assemble microtubules to form mitotic spindles during mitosis.
- 😀 Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is involved in protein synthesis and modification, with ribosomes attached to its surface.
- 😀 The Golgi apparatus modifies, processes, and packages proteins, including the formation of secretory vesicles and lysosomes.
- 😀 Chloroplasts, found in plant cells only, are involved in photosynthesis.
- 😀 Transcription occurs in the nucleus to form mRNA, which is then translated in the ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- 😀 Exocytosis, the release of proteins from the cell, involves fusion with the plasma membrane and requires secretary vesicles.
- 😀 The nucleus, mitochondrion, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus are involved in protein production and transport.
Q & A
What is an electron micrograph?
-An electron micrograph is a picture taken using an electron microscope, which allows for detailed imaging of cells and their structures at the microscopic level.
How can we identify a plant cell from an electron micrograph?
-A plant cell can be identified by the presence of a cellulose cell wall, plasmodesma (a hole in the cell wall connecting cytoplasm to neighboring cells), and a large central vacuole (or sap vacuole).
What is the function of mitochondria?
-Mitochondria are involved in aerobic respiration, where glucose or other organic molecules are broken down to release energy. They are also responsible for synthesizing ATP, which is the energy currency of the cell.
What is the role of centrioles in animal cells?
-Centrioles are involved in the assembly of microtubules, which form the mitotic spindle during cell division (mitosis). They are found only in animal cells.
What is the main function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
-The rough endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein synthesis, protein modification, and protein transport. Ribosomes are attached to its surface, aiding in the synthesis of proteins.
What are the functions of the Golgi apparatus?
-The Golgi apparatus is responsible for processing, modifying, and packaging proteins. It also plays a role in the formation of secretory vesicles and lysosomes.
What is the role of chloroplasts in plant cells?
-Chloroplasts are involved in photosynthesis, where they convert light energy into chemical energy, producing glucose and oxygen as byproducts. Chloroplasts are found only in plant cells.
What is the sequence of events in protein production within a cell?
-The sequence begins with transcription in the nucleus, followed by translation at the ribosome. The protein is then modified in the rough endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi apparatus, packaged into vesicles, and finally released from the cell via exocytosis.
Which cellular structures are involved in protein synthesis?
-The main structures involved in protein synthesis are the nucleus (for transcription), ribosomes (for translation), and the rough endoplasmic reticulum (for protein synthesis and modification).
What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
-The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the synthesis of lipids and steroids, as well as in the transport of these molecules throughout the cell.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Top 40 biology MCQ | biology mcq for all competitive exam | biology Mcq 2025 | neet biology
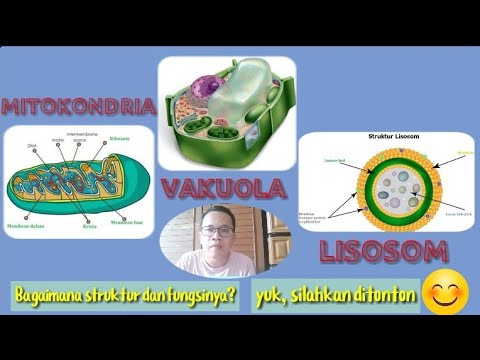
MITOKONDRIA, VAKUOLA DAN LISOSOM

QUAL A IMPORTÂNCIA DA BIOLOGIA NA SOCIEDADE

ORGANELAS CITOPLASMÁTICAS - Resumo | Biologia com Samuel Cunha

SISTEM ORGANISASI KEHIDUPAN : IPA KELAS 7 SMP

Animal and Plant Cells eLearning Video Lesson for Kids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)