Mekanisme pertukaran oksigen dan karbondioksida
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the host, Yuningsih, discusses the human respiratory system, focusing on the mechanisms of oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange. She explains how oxygen enters the body, diffuses into the blood, and is carried by hemoglobin to cells for respiration. The process of carbon dioxide exchange is also covered, including its diffusion from cells into the blood, transport in various forms (bicarbonate, carbaminohemoglobin, and dissolved in plasma), and eventual exhalation. The video also touches on common respiratory disorders and encourages viewers to engage by liking and subscribing.
Takeaways
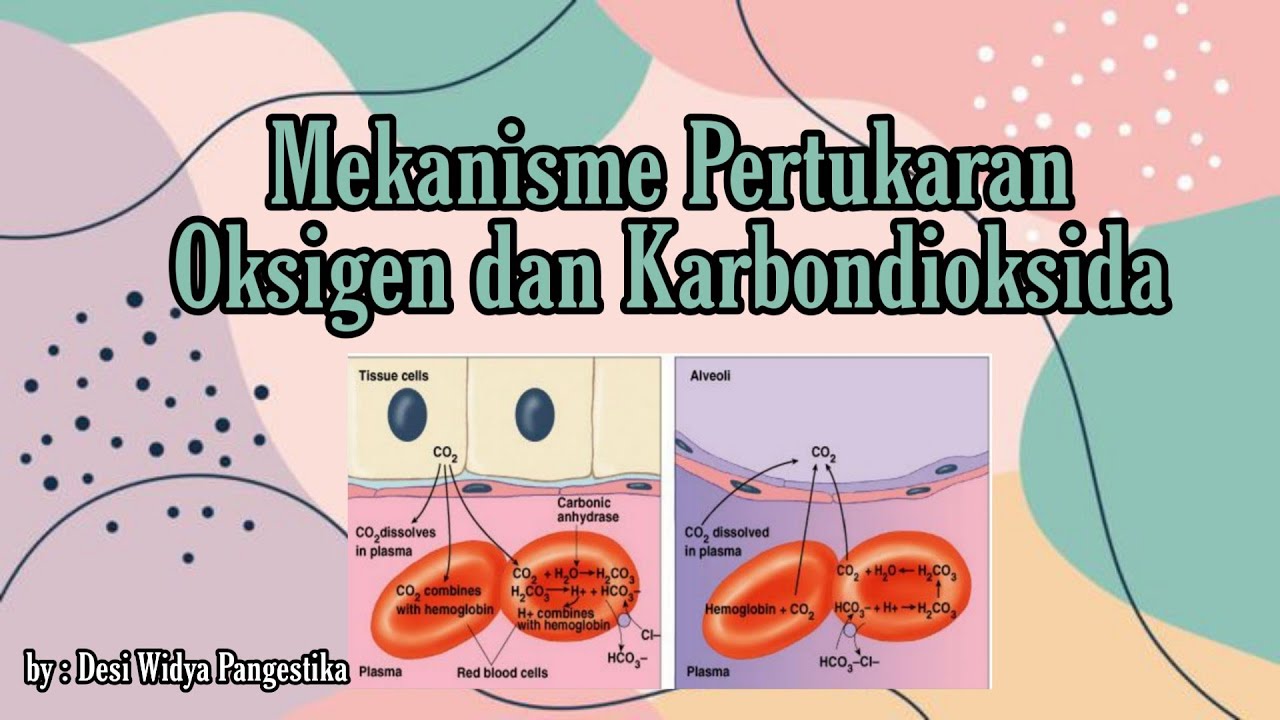
- 😀 Oxygen enters the body through inspiration.
- 😀 Oxygen diffuses from the alveolus to the pulmonary artery capillaries.
- 😀 Oxygen binds with hemoglobin in red blood cells to form oxyhemoglobin.
- 😀 Oxyhemoglobin diffuses into body cells for use in cellular respiration.
- 😀 Carbon dioxide is produced as a waste product of mitochondrial respiration.
- 😀 Carbon dioxide diffuses from cells to venous capillaries due to partial pressure differences.
- 😀 Carbon dioxide is transported from venous capillaries to alveolus in three ways: dissolving in plasma, forming carbaminohemoglobin, or as bicarbonate ions.
- 😀 Carbon dioxide diffuses through the alveolus into the lungs to be expelled.
- 😀 Carbon dioxide is expelled from the body through expiration.
- 😀 The bicarbonate ion in red blood cells exchanges with chloride ions in the plasma during the transport of carbon dioxide.
- 😀 Carbonic anhydrase converts carbon dioxide into carbonic acid in the blood plasma.
Q & A
What is the first step in the oxygen exchange process?
-The first step is that oxygen enters the body through inspiration (inhalation).
How does oxygen move from the alveolus to the bloodstream?
-Oxygen diffuses through the alveolus into the pulmonary capillaries.
What role does hemoglobin play in oxygen transport?
-Hemoglobin in the blood binds to oxygen, forming oxyhemoglobin (HbO2), which allows oxygen to be transported to tissues.
How does oxyhemoglobin reach the cells of the body?
-Oxyhemoglobin diffuses from the bloodstream into the cells, where it is used in cellular respiration.
What is the first step in the carbon dioxide exchange process?
-The first step is that carbon dioxide (CO2) is produced as a waste product in the mitochondria of cells during respiration.
How does carbon dioxide move from the cells to the bloodstream?
-Carbon dioxide diffuses from the cells into the venous capillaries, where the partial pressure of CO2 is higher than in the blood.
What are the three methods by which carbon dioxide is transported in the blood?
-Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood by dissolving in plasma, binding to hemoglobin to form carbaminohemoglobin, and being converted into bicarbonate ions (HCO3-).
How does carbon dioxide move from the bloodstream to the alveolus?
-Carbon dioxide moves from the bloodstream to the alveolus through diffusion, following its partial pressure gradient.
How is carbon dioxide removed from the body?
-Carbon dioxide is expelled from the body through exhalation (expiration).
What is the role of chloride ions in carbon dioxide transport?
-Chloride ions exchange with bicarbonate ions in red blood cells, helping maintain the ionic balance during carbon dioxide transport.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Mekanisme Pertukaran Oksigen dan Karbondioksida | Sistem Pernapasan Manusia

Respiratory System Made Easy

Sistema Respiratório 1/6: Introdução | Anatomia e etc

Sistem Pernapasan Manusia: Gimana Sih Cara Manusia Bernapas? | IPA | SayaBisa
Respiratory System - Introduction | Physiology | Biology | FuseSchool
Journey Of The AIR inside Our Body . Respiratory Gas Exchange ,, #oxygen #alveoli
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)