Abscesses - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the process of abscess formation, from the invasion of bacteria into the body to the immune response that leads to the creation of pus. It details the role of immune cells, such as neutrophils, and the formation of a fibrinogen barrier around the infection site. The video covers common causes, symptoms, diagnosis methods like ultrasound and imaging, and the primary treatment for abscesses, which is incision and drainage. The risks for those with weakened immune systems and the potential for reinfection are also discussed, along with the use of antibiotics post-drainage.
Takeaways
- 😀 An abscess is essentially a pimple, which forms when normal tissue like skin is invaded by bacteria after a cut or break.
- 😀 The human body hosts about ten bacterial cells for every one human cell, making any injury a potential invitation for bacterial infection.
- 😀 When an abscess forms, the immune system responds by releasing chemicals (cytokines and chemokines) to attract immune cells to fight the infection.
- 😀 Cytokines help dilate blood vessels, allowing white blood cells to reach the infected area and engage with the bacteria.
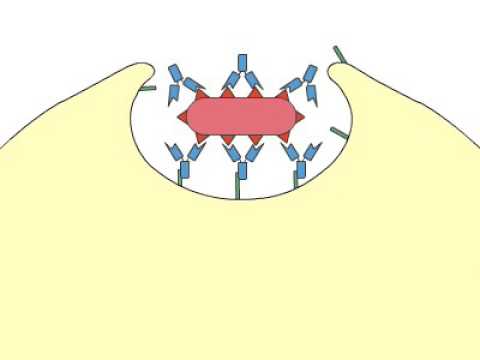
- 😀 Neutrophils are often the first immune cells to respond, releasing enzymes to kill bacteria and break down dead tissue, forming pus.
- 😀 Suppurative inflammation (pus formation) occurs as immune cells die and mix with bacteria and dead tissue, resulting in liquefied necrosis.
- 😀 In response to the pus pool, fibrinogen forms a wall around the abscess to contain the infection, and can even form multiple loculations (abscesses within abscesses).
- 😀 Staphylococcus aureus, a common bacteria in abscesses, helps accelerate the formation of the fibrinogen wall with the enzyme coagulase.
- 😀 Abscesses can form in deeper areas of the body (e.g., the gallbladder), where bacteria thrive in oxygen-deprived conditions.
- 😀 Symptoms of abscesses include redness, warmth, swelling, pain, and sometimes fever or vomiting, particularly in people with weakened immune systems.
- 😀 Abscesses are diagnosed through physical examination (fluctuance), ultrasound, or imaging studies (CT/MRI), with ring-enhancement indicating inflammation around the abscess.
- 😀 While antibiotics can help treat abscesses, drainage is the most effective treatment, as antibiotics alone cannot penetrate the abscess effectively.
- 😀 Proper drainage is essential to remove all pus and prevent reinfection, sometimes requiring packing of the cavity with gauze to promote healing.
Q & A
What exactly is an abscess?
-An abscess is a pocket of pus that forms when the body's tissue is damaged and bacteria invade the space. It’s a common response to infections, where the immune system tries to fight off the bacteria by forming a fluid-filled cavity of dead cells, bacteria, and tissue.
How do abscesses form on the skin?
-Abscesses on the skin form when bacteria invade a break in the skin, like a cut or pimple. The body responds by sending immune cells to the area, which causes inflammation and leads to pus formation.
What role do cytokines play in the formation of an abscess?
-Cytokines are chemicals released by injured tissue that attract white blood cells to the site of infection. They also dilate blood vessels, allowing more immune cells to enter the tissue, and promote the inflammation process that leads to abscess formation.
What is 'fluctuance' in the context of abscesses?
-Fluctuance refers to the sensation of fluid movement within an abscess, which can be felt when pressing on the swollen area. This indicates the presence of fluid (pus) inside the abscess.
Why are abscesses sometimes difficult to treat with antibiotics alone?
-Antibiotics are less effective in abscesses because the area lacks blood vessels, which are necessary for the antibiotics to reach the bacteria. The antibiotics can only diffuse into the outer edges of the abscess, leaving bacteria in the middle unaffected.
What is the most common treatment for an abscess?
-The most common treatment for an abscess is incision and drainage (I&D), where the abscess is cut open to allow the pus to drain out. This helps relieve pressure and removes the infected material.
What is the significance of fibrinogen in abscess formation?
-Fibrinogen is a protein that helps form a barrier around the abscess. This fibrin wall helps contain the infection, but can also create multiple pockets or loculations of pus inside the abscess, making drainage more complex.
How do internal abscesses, like those in the gallbladder, form?
-Internal abscesses, such as those in the gallbladder, form when a blockage, like a stone, prevents normal fluid flow. This creates an environment for bacteria to thrive, leading to an infection and the eventual formation of an abscess.
What are some diagnostic methods for detecting abscesses?
-Abscesses are diagnosed through physical examination and imaging studies. On the skin, doctors may feel for fluctuation. For deeper abscesses, ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs are used to visualize the abscess and assess its size and location.
Why are people with weakened immune systems at higher risk for abscess complications?
-People with weakened immune systems, like those undergoing chemotherapy or newborns, are less able to contain infections, making it easier for bacteria to spread and enter the bloodstream. This increases the risk of more severe symptoms like fever, vomiting, and septicemia.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)