Ikatan Kimia (2) | Ikatan Ion (Elektrovalen) | Kimia kelas 10
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the presenter explains chemical bonding, focusing on ionic (electrovalent) bonds. The video details how atoms form stable electron configurations by either losing or gaining electrons, with a specific emphasis on metals and non-metals. Through several examples, such as the formation of NaCl and MgCl2, the video demonstrates the process of ion formation, explaining how atoms like sodium and chlorine bond to achieve stability. The presenter also introduces a simplified method for determining the resulting compound from ionic bonds, making the concept accessible and engaging for viewers.
Takeaways
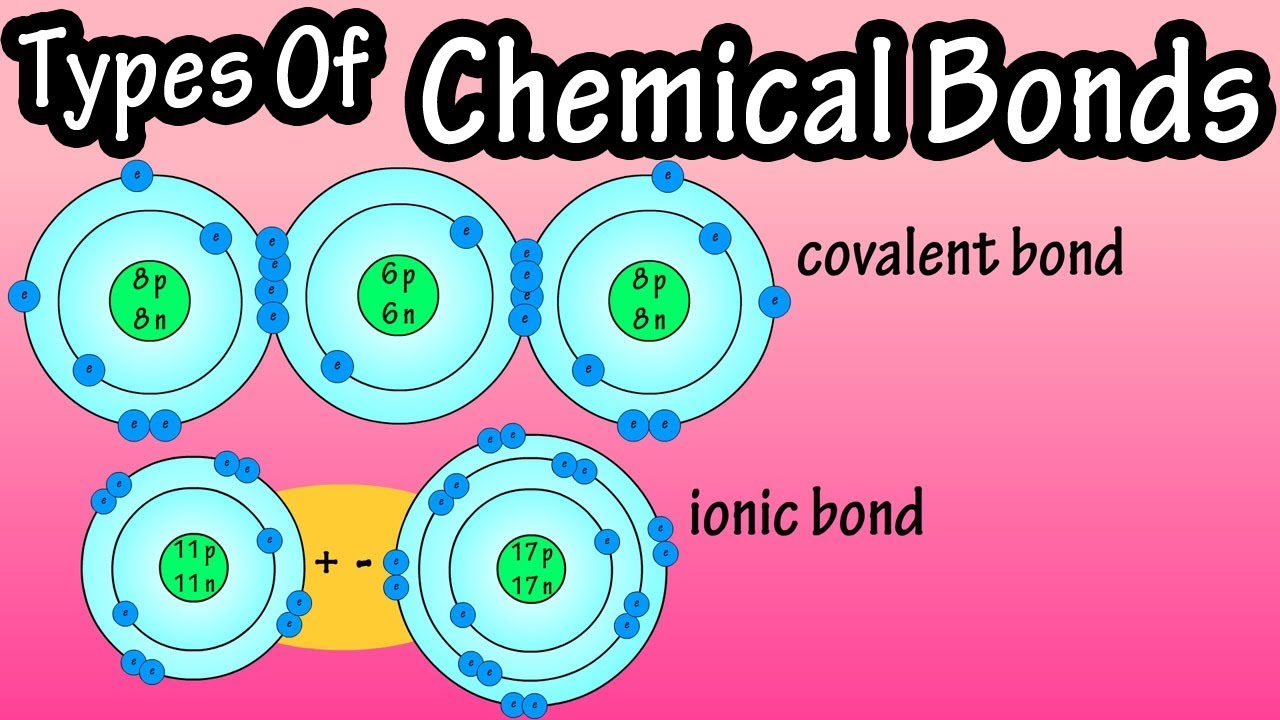
- 😀 Chemical bonds are interactions between atoms that result in a stable electron configuration, often resembling that of noble gases.
- 😀 The three main types of chemical bonds are ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds.
- 😀 Ionic bonds occur between a metal and a non-metal atom, where electrons are transferred from the metal to the non-metal.
- 😀 Metal atoms (from groups 1A, 2A, 3A) tend to lose electrons and form positive ions, while non-metal atoms (from groups 4A to 7A) tend to gain electrons and form negative ions.
- 😀 Ionic bonds are formed through the transfer of electrons, creating positive and negative ions that attract each other due to their opposite charges.
- 😀 In the case of NaCl (sodium chloride), Na loses one electron to form Na⁺, while Cl gains that electron to form Cl⁻, resulting in the formation of NaCl.
- 😀 For MgCl₂ (magnesium chloride), Mg loses two electrons to form Mg²⁺, while each Cl gains one electron to form Cl⁻. The result is MgCl₂.
- 😀 The formula for ionic compounds can be determined by balancing the number of positive and negative charges, ensuring that they are equal.
- 😀 A simpler method to determine the formula of ionic compounds is by comparing the electron configurations of atoms to the nearest noble gas.
- 😀 For example, Mg (12 electrons) will lose two electrons to resemble the electron configuration of Ne (10 electrons), while Cl (17 electrons) will gain one electron to resemble Ar (18 electrons), forming MgCl₂.
Q & A
What is a chemical bond?
-A chemical bond is the attraction between atoms that holds them together. It occurs when atoms interact to achieve a stable electron configuration, similar to that of noble gases.
What are the three main types of chemical bonds?
-The three main types of chemical bonds are ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. Ionic bonds occur between metals and non-metals, covalent bonds between non-metals, and metallic bonds between metals.
What is the role of valence electrons in chemical bonding?
-Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom and play a crucial role in chemical bonding. Atoms bond to achieve a stable electron configuration, usually aiming for 8 electrons (octet) or 2 electrons (duplet) in their outer shell.
How do atoms form ions in ionic bonding?
-In ionic bonding, atoms form ions by either losing or gaining electrons. Metal atoms tend to lose electrons and become positively charged (cation), while non-metal atoms gain electrons and become negatively charged (anion).
What is the difference between an ionic bond and a covalent bond?
-An ionic bond forms between a metal and a non-metal, where electrons are transferred from the metal to the non-metal. A covalent bond forms between two non-metals, where electrons are shared between the atoms.
What is the electron configuration of Sodium (Na) and how does it relate to ionic bonding?
-Sodium (Na) has an electron configuration of 2, 8, 1, meaning it has 1 valence electron. Sodium tends to lose this electron to achieve a stable electron configuration similar to the nearest noble gas, Neon, forming a Na+ ion.
How does Chlorine (Cl) form an anion in ionic bonding?
-Chlorine (Cl) has an electron configuration of 2, 8, 7, meaning it has 7 valence electrons. It tends to gain 1 electron to complete its octet, forming a Cl- ion.
What is the ionic compound formed when Sodium (Na) and Chlorine (Cl) bond?
-When Sodium (Na) and Chlorine (Cl) bond, Sodium loses 1 electron to form Na+, and Chlorine gains 1 electron to form Cl-. The resulting ionic compound is Sodium Chloride (NaCl).
How does Magnesium (Mg) form an ion in ionic bonding?
-Magnesium (Mg) has an electron configuration of 2, 8, 2, meaning it has 2 valence electrons. Magnesium tends to lose these 2 electrons to form a Mg2+ ion, achieving the stable electron configuration of Neon.
How do you determine the formula of an ionic compound formed between Magnesium (Mg) and Chlorine (Cl)?
-To determine the formula, balance the charges. Magnesium forms a Mg2+ ion, while Chlorine forms a Cl- ion. To balance the charges, you need two chloride ions (Cl-) for each magnesium ion (Mg2+), resulting in the formula MgCl2.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Ikatan Ion (Ikatan Kimia) / Kimia Kelas XI SMA Kurikulum Merdeka

IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Partikel Penyusun Materi (Part 3: Ikatan Kimia)

LIGAÇÃO IÔNICA - Entendendo as ligações químicas

Chem Done Easy - Chemical Bonding (Ionic Vs Covalent)

Soal-soal Ikatan Kimia Kelas 10 dan 11 SMA/MA Pilihan
Types Of Chemical Bonds - What Are Chemical Bonds - Covalent Bonds And Ionic Bonds - What Are Ions
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)