Transformações de energia nos eletrodomésticos
Summary
TLDRThis lesson explores the different types of energy, such as mechanical, thermal, electric, chemical, and nuclear, with a focus on how they transform in household appliances. The instructor explains energy conservation, highlighting key energy transformations—electricity to heat (e.g., electric shower, iron) and electricity to motion (e.g., fan, blender). Essential electrical concepts like voltage, power, current, and frequency are also introduced. The lesson provides practical insights into how energy operates in everyday life, helping viewers understand the functioning of common household devices and their efficiency.
Takeaways
- 😀 **Energy is essential for human survival**: It represents the ability to do work, and everything that is working consumes energy.
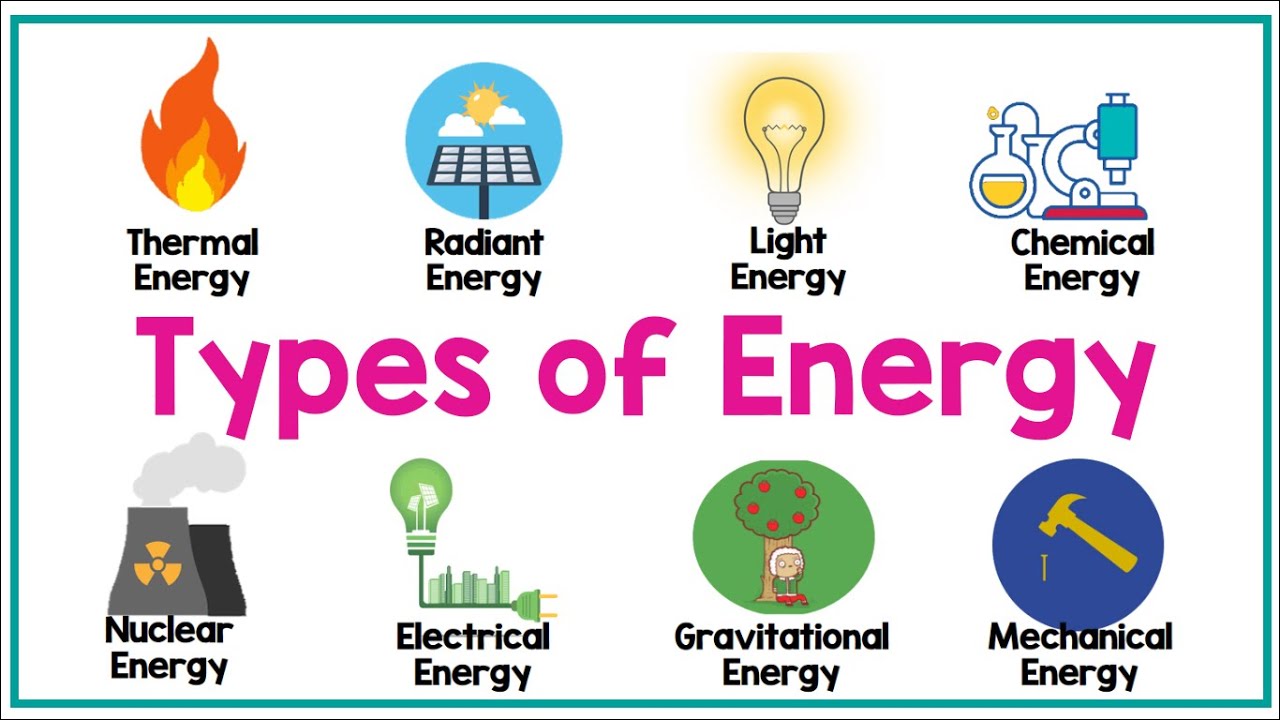
- 😀 **Types of energy**: The main types discussed are mechanical, thermal, electrical, chemical, and nuclear energy.
- 😀 **Mechanical energy**: This type of energy results from the motion of objects.
- 😀 **Thermal energy**: This is related to heat and arises from the movement of molecules in a substance.
- 😀 **Electrical energy**: It is based on the difference in electrical potential between two points.
- 😀 **Chemical energy**: Stored in the bonds of atoms and released during chemical reactions.
- 😀 **Nuclear energy**: Released during nuclear reactions, involving the transformation of atomic nuclei.
- 😀 **Energy transformation**: This is the process of changing energy from one form to another, which occurs constantly in the world and in daily life.
- 😀 **Conservation of energy**: Energy can be transformed or transferred, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
- 😀 **Everyday appliances transform energy**: Examples include electric showers and irons converting electrical energy to thermal energy, and fans and blenders converting electrical energy to mechanical energy.
- 😀 **Key scientific concepts**: Voltage (the force moving electrons), power (energy consumption rate), current (ordered flow of electrons), and frequency (number of occurrences of events per unit time).
Q & A
What is energy and why is it important?
-Energy is the capacity to do work or produce an effect. It is essential for human survival, as all living beings and machines depend on energy to function.
What is mechanical energy?
-Mechanical energy is the energy that results from the movement of objects or bodies. It is one of the basic forms of energy discussed in the script.
How is thermal energy related to molecular movement?
-Thermal energy is the energy associated with heat and is generated by the movement of molecules and particles in a material.
What is electrical energy, and why is it so important?
-Electrical energy is the form of energy that results from the difference in electric potential between two points. It is crucial because most modern devices and appliances rely on electrical energy.
What is chemical energy?
-Chemical energy is stored in the bonds between atoms and molecules. It is released during chemical reactions, such as the burning of fuel.
What is nuclear energy?
-Nuclear energy is the energy released during nuclear reactions, such as the splitting of atomic nuclei in a process called fission.
What is the principle of energy conservation?
-The principle of energy conservation states that energy can be transformed or transferred, but it can never be created or destroyed.
How do household appliances transform electrical energy into other forms?
-Household appliances like electric showers, irons, and lamps transform electrical energy into thermal energy through a resistor. Other appliances, like fans and blenders, transform electrical energy into mechanical energy using motors.
What is the function of a resistor in energy conversion?
-A resistor in an appliance converts electrical energy into thermal energy. It does this by resisting the flow of electricity, which generates heat.
What is the difference between voltage, current, and power in electrical circuits?
-Voltage (or potential difference) is the force that moves electrons through a conductor. Current is the flow of electrons, and power is the rate at which energy is consumed by an appliance. Power is calculated by dividing energy by time and is measured in watts.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Transformações de energia no ar condicionado e no microondas | Parte I

Fontes e tipos de Energia – Ciências – 8º ano – Ensino Fundamental
TYPES OF ENERGY | Physics Animation

Fisika Kelas 10: Ragam Bentuk Energi, Energi | Portal Sekolah

Lesson 8: Electric Motors and Generators

Eletricidade no Cotidiano/ Transformações de energia – Ciências – 8º ano – Ensino Fundamental
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)