IoT Concepts Characteristics and Applications by Dr Maitreyee Dutta
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth introduction to the Internet of Things (IoT), explaining its key concepts, characteristics, and applications. IoT connects everyday physical objects through sensors, software, and networks, enabling real-time data exchange and smarter control of devices. The video covers the four evolutionary phases of IoT, its system and service characteristics, and the benefits of increased resource efficiency, reduced human effort, and AI development. Challenges like scalability, interoperability, and security are also discussed. Practical examples range from smart homes to healthcare and agriculture, illustrating IoT's wide-reaching potential in various industries.
Takeaways
- 😀 IoT (Internet of Things) connects physical objects in the real world to the internet, making them smarter and more connected through sensors and software.
- 😀 The evolution of IoT includes four phases: Connectivity, Network Economy, Immersive Experiences, and the current Internet of Things phase.
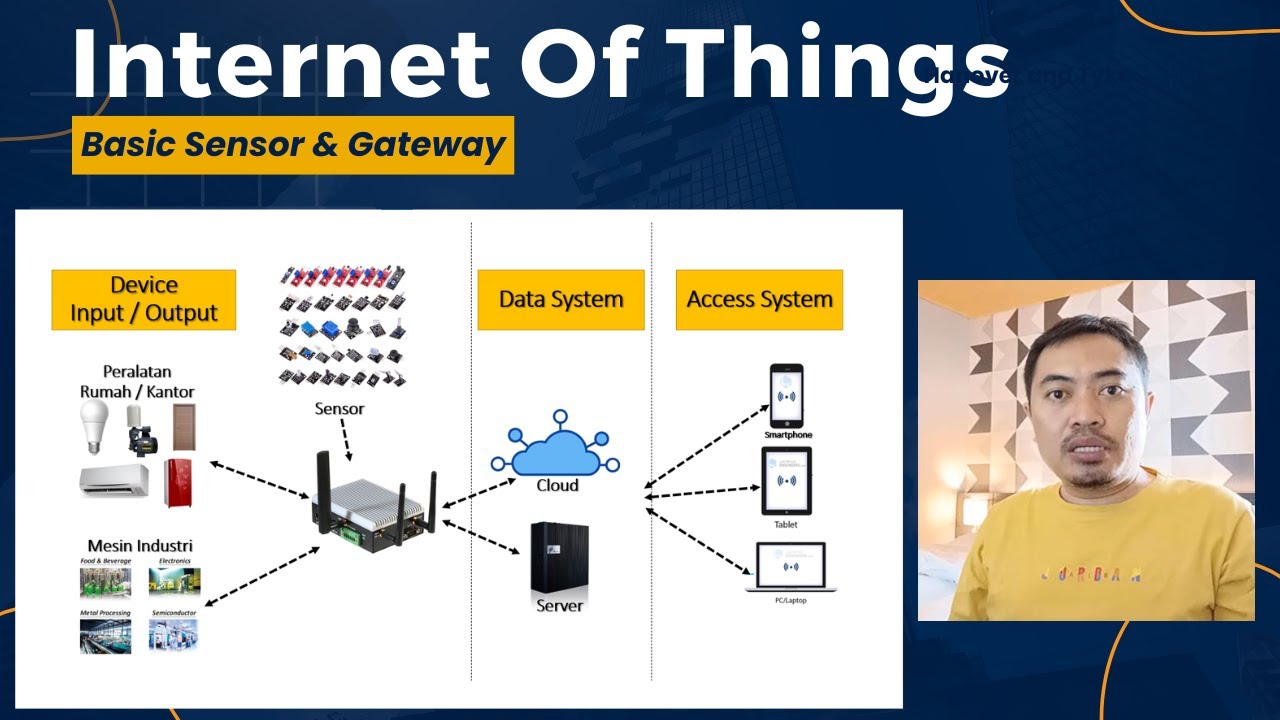
- 😀 IoT works in four key phases: Collection (gathering data through sensors), Communication (sending data to the cloud), Analysis (extracting insights), and Action (executing responses based on the analysis).
- 😀 Key IoT characteristics include self-configuration, distributed systems, real-time data collection, and the ability to manage networks and collaborate between devices.
- 😀 IoT devices and components are modular, interoperable, and heterogenous, allowing different types of devices to connect and communicate with each other.
- 😀 The three main service characteristics of IoT are content awareness, location awareness, and time awareness, which enable devices to gather data anytime, anywhere.
- 😀 IoT benefits include efficient resource utilization (e.g., automatic control of lights and ACs), minimizing human effort (e.g., automating home systems), saving time, and developing AI through data collected by IoT devices.
- 😀 Scalability, security, interoperability, data privacy, and power supply limitations are the primary challenges in IoT systems, with researchers focusing on improving these areas.
- 😀 Common applications of IoT include smart homes, smart transportation, agriculture, healthcare, and environmental monitoring, such as using sensors for livestock health or weather stations.
- 😀 Various IoT products available in the market include smart thermostats (e.g., Google Nest), smart bulbs (e.g., Philips Hue), and wearable health trackers, among others.
- 😀 IoT working groups such as the IEEE, IETF, and OCF (Open Connectivity Foundation) are actively involved in research and development, providing resources and support to those in the IoT field.
Q & A
What is the basic purpose of the Internet of Things (IoT)?
-The basic purpose of IoT is to connect physical objects or things, which were previously unconnected, through the internet. This allows these objects to sense, communicate, and interact with the physical world, making them smarter and more connected.
What are the four evolutionary phases of the Internet?
-The four evolutionary phases of the internet are: 1) Connectivity phase (connecting people via email or web services), 2) Network economy phase (digitizing businesses and enhancing e-commerce), 3) Immersive experiences phase (enhancing internet usage through video and social media), and 4) The Internet of Things phase (connecting people and physical objects).
How does the Internet of Things (IoT) differ from the traditional internet?
-The traditional internet connects computers and other digital devices, whereas IoT connects physical objects (like cars, appliances, and sensors) to the internet, enabling them to exchange data and interact intelligently.
What are the four main phases through which IoT works?
-IoT works through four main phases: 1) Collection (sensors collect data), 2) Communication (data is transmitted to the cloud), 3) Analysis (data is processed and visualized), and 4) Action (based on the analysis, actions are taken automatically).
What are the main characteristics of IoT systems?
-IoT systems have several key characteristics: auto-configuration, highly distributed systems, real-time data collection, network communication, and the ability to share data. Additionally, they often have components like sensors, actuators, and embedded systems that work together seamlessly.
What is the significance of real-time data in IoT?
-Real-time data is crucial in IoT because it allows for instant action and decision-making based on the most current information, such as triggering an automated response when certain conditions are met (e.g., turning on the AC when a person arrives home).
What are the benefits of IoT in resource management?
-IoT helps improve resource utilization by automating processes. For example, IoT-enabled systems can automatically turn off lights and appliances when not in use, leading to energy savings and more efficient use of resources.
What are the challenges IoT faces in terms of scalability?
-Scalability challenges in IoT arise as the number of devices and data points increases. Ensuring that adding more devices does not degrade system performance is a significant concern. This includes challenges in data scalability, network scalability, and device scalability.
Why is security a major concern for IoT devices?
-Security is a major concern because IoT devices often collect sensitive data and are connected to cloud networks. If data is not properly secured, it can be vulnerable to hacking, privacy breaches, and misuse, leading to significant risks for users.
Can you provide examples of IoT applications in real life?
-Some real-world IoT applications include: Smart homes (automating household devices), healthcare (monitoring health through wearable devices), smart transportation (self-driving cars and smart traffic systems), agriculture (monitoring farm animals and crops), and industrial applications (monitoring bridges and equipment in real-time).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)