RESUMO sobre FOTOSSÍNTESE | Biologia com Samuel Cunha
Summary
TLDRThis video lesson provides an engaging and comprehensive overview of photosynthesis, explaining its essential role in converting light energy into chemical energy. The professor breaks down the process step-by-step, covering both the light-dependent and light-independent reactions, as well as the factors influencing photosynthesis such as temperature, CO2 levels, and light intensity. Emphasizing the importance of photosynthesis in sustaining life on Earth, the video also touches on common misconceptions and highlights the intricacies of plant biology in a way that’s accessible for students preparing for exams like Enem and vestibulares.
Takeaways
- 😀 Photosynthesis is the process where plants, algae, and cyanobacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, mainly producing glucose.
- 😀 The main producers of oxygen on Earth are microscopic algae in oceans, not land plants, despite popular belief.
- 😀 Organisms that perform photosynthesis are called autotrophs because they produce their own food using sunlight.
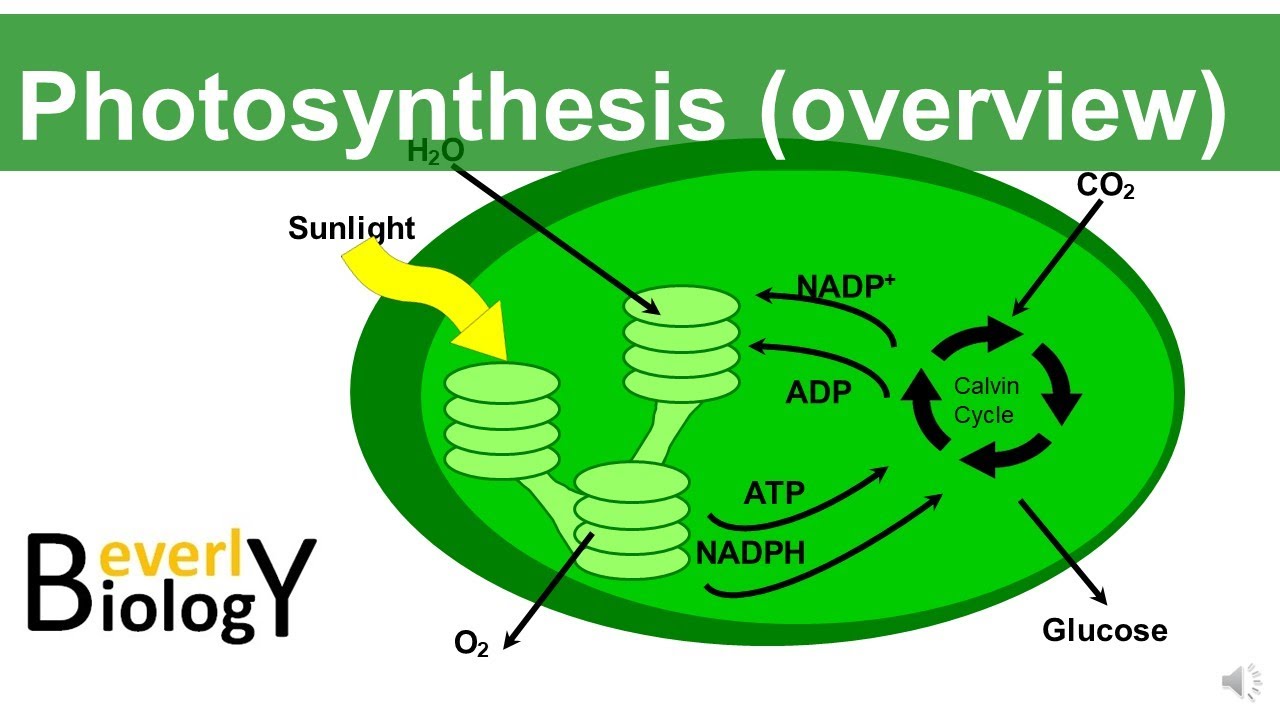
- 😀 Photosynthesis occurs in two stages: the light reaction (photo reaction) and the Calvin cycle (dark reaction).
- 😀 In the light reaction, sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll, producing ATP and NADPH, while splitting water to release oxygen.
- 😀 The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH from the light reaction to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
- 😀 The oxygen produced in photosynthesis comes from the splitting of water molecules, not from carbon dioxide.
- 😀 Factors that influence photosynthesis include light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
- 😀 Plants use energy from photosynthesis for growth, and excess glucose can be stored for later use, but they still rely on respiration to break down glucose for energy.
- 😀 The process of photosynthesis is fundamental to the food chain, as it provides the energy and oxygen needed by other organisms.
- 😀 Misconceptions around photosynthesis, such as confusing oxygen production with carbon dioxide, can be clarified by understanding the role of water and light in the process.
Q & A
What is photosynthesis?
-Photosynthesis is the process by which autotrophic organisms, such as plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy into chemical energy. This energy is stored in organic compounds, mainly glucose, and is essential for sustaining life on Earth.
Which organisms perform photosynthesis?
-The main organisms that perform photosynthesis are plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. These organisms are called autotrophs because they produce their own organic compounds from light energy.
Where does most of the oxygen in the atmosphere come from?
-While plants contribute to oxygen production, most of the oxygen in Earth's atmosphere comes from microscopic algae, particularly those found in the oceans. These organisms release oxygen during photosynthesis.
How do plants use the oxygen they produce?
-Plants utilize the oxygen they produce through photosynthesis for cellular respiration, a process where they break down glucose to release energy for their growth and metabolism.
What is the role of the sun in the food chain?
-The sun is the ultimate source of energy in the food chain. Plants, algae, and other photosynthetic organisms absorb sunlight and convert it into chemical energy, which then passes through various trophic levels in the food chain, ultimately reaching consumers like herbivores and carnivores.
What are the basic requirements for photosynthesis?
-Photosynthesis requires light energy, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O). The plant absorbs these elements and, through a series of biochemical reactions, produces glucose and oxygen as byproducts.
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
-The general chemical equation for photosynthesis is: 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2. This shows that six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water, powered by light energy, produce one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen.
Where does photosynthesis occur in plants?
-In plants, photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts, which are located in the cells of the leaves. The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for capturing light energy.
What is the difference between the light-dependent and light-independent stages of photosynthesis?
-The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts, where light energy is absorbed, and ATP and NADPH are produced. The light-independent reactions, also called the Calvin cycle, occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts, where ATP and NADPH are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
What factors influence the rate of photosynthesis?
-The rate of photosynthesis is influenced by factors such as temperature, light intensity, and the concentration of carbon dioxide. If any of these factors fall outside optimal ranges, photosynthesis can be slowed down or inhibited.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)