Pertemuan10 SIM-SPK
Summary
TLDRThis lecture provides a detailed overview of Decision Support Systems (DSS), explaining their role in assisting decision-making processes within organizations. It covers the definition, characteristics, types of decisions (structured, semi-structured, unstructured), and the main functions of DSS, such as enhancing decision-making ability, generating alternatives, and increasing efficiency. The script also highlights the key components of DSS, including database management, model-based systems, and user interfaces. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and limitations of DSS, along with real-world applications, such as employee performance monitoring, academic evaluations, and financial management.
Takeaways
- 😀 Decision Support Systems (DSS) are computer-based information systems that help organizations make decisions based on data and information processing.
- 😀 DSS assists in addressing semi-structured and unstructured problems by supporting decision-making in complex scenarios.
- 😀 The goal of DSS is to improve decision-making effectiveness and efficiency, providing better alternatives and outcomes for managers.
- 😀 The DSS process includes stages like problem exploration, design, choice selection, and implementation, each contributing to a structured decision-making approach.
- 😀 DSS helps managers choose between alternative solutions by analyzing criteria based on the problem's goal and available data.
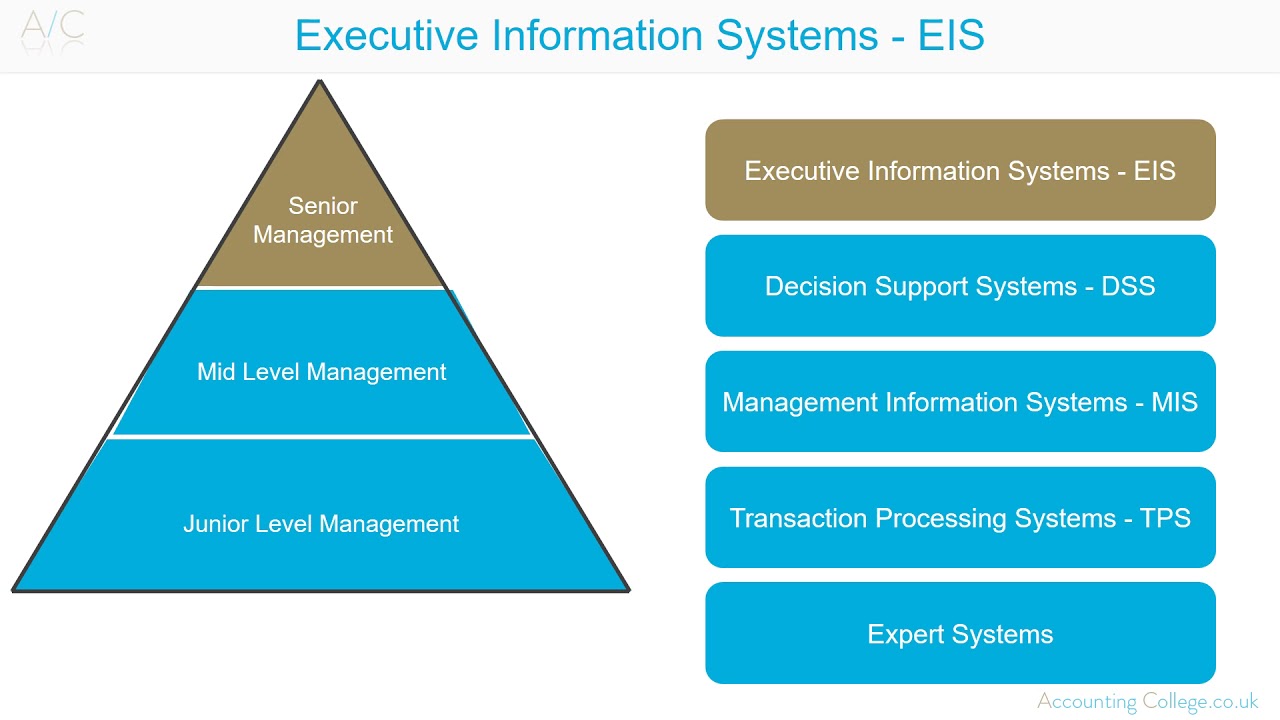
- 😀 There are three types of decisions in DSS: structured (routine and repetitive), semi-structured (a mix of computer support and human judgment), and unstructured (complex and rare decisions).
- 😀 The system offers various advantages such as quicker decision-making, alternative solutions, and reliable data-driven insights to support informed choices.
- 😀 Key components of DSS include database management, model-based approaches, and user interfaces, ensuring the integration and presentation of data for effective decision-making.
- 😀 DSS can be applied in various fields, including finance, human resources, and education, such as determining scholarships or employee performance evaluations.
- 😀 While DSS provides valuable support, it is not a replacement for human judgment and must evolve to stay aligned with changing data, conditions, and organizational needs.
Q & A
What is a Decision Support System (DSS)?
-A Decision Support System (DSS) is a computer-based system that assists in decision-making within organizations. It helps solve semi-structured and unstructured problems by providing relevant data, models, and analysis tools to support decisions.
What are the main objectives of a DSS?
-The main objectives of a DSS are to help in solving problems, support decision-making processes, improve efficiency and effectiveness, and provide data-driven alternatives for decisions.
What are the four stages of decision support in a DSS?
-The four stages of decision support are: 1) Search Phase (identifying and understanding the problem), 2) Design Phase (developing and verifying potential solutions), 3) Choice Phase (selecting the best alternative), and 4) Implementation Phase (applying the chosen solution).
What are the three types of decisions handled by a DSS?
-The three types of decisions are: 1) Structured Decisions (routine and repetitive), 2) Semi-Structured Decisions (partially routine, requiring human input), and 3) Unstructured Decisions (complex, requiring expert judgment and experience).
What are the main components of a DSS?
-The main components of a DSS are: 1) Database Management System (DBMS), which stores relevant data; 2) Model-Based System, which provides analytical models for decision-making; and 3) User Interface, which presents the information and alternatives in an accessible way for the user.
How does a DSS help in decision-making processes?
-A DSS helps by processing large amounts of complex data quickly, offering alternative solutions, and making the decision-making process more reliable and efficient. It helps decision-makers by providing data-driven insights and alternatives for informed choices.
What are the advantages of using a DSS?
-The advantages include faster decision-making, reliable data-based outcomes, the ability to generate multiple alternatives, increased confidence in decision-making, and a competitive edge for organizations.
What are the challenges or limitations of using a DSS?
-Some challenges include the inability to model certain human management skills, dependency on software capabilities, and the need for continuous updates to the system as data and external factors change over time.
Can DSS be applied in various sectors? Provide examples.
-Yes, DSS can be applied in many sectors. Examples include education (e.g., determining scholarship recipients), human resources (e.g., employee performance evaluation), and businesses (e.g., sales forecasting and product development).
What are the characteristics of DSS that make it effective in decision-making?
-DSS characteristics include the ability to process and analyze data for decision-making, provide alternatives, integrate subsystems, and present data in an accessible format for users, helping them make informed and effective decisions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Topik 3 : Karakteristik dan Arsitektur Sistem Pengambilan Keputusan

Decision Support Systems Video Lecture - Business Intelligence Concepts, Tools, and Applications

Understanding Decision Support Systems

Sebuah gambaran: Konsep, Metodologi, dan Teknologi Sistem Pendukung Keputusan
Executive Information Systems - A-Z of business terminology

Desicion-Making Systems, Modelling and Support
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)