GENÉTICA: LEIS DE MENDEL, GENES, DNA E CROMOSSOMOS | QUER QUE DESENHE?
Summary
TLDRThis video offers a fun and engaging breakdown of genetics, covering the basics like genotype vs. phenotype, Mendel's laws of inheritance, and the role of chromosomes and alleles in determining traits. With humorous analogies, such as comparing DNA to a necklace of pearls, the script makes complex topics accessible for students. It encourages viewers to understand how traits are inherited, explaining dominant and recessive alleles, and provides helpful study tips for those preparing for exams like the ENEM.
Takeaways
- 😀 Genetics studies hereditary information passed from parents to offspring, which is carried by genes in DNA.
- 😀 The genome refers to the complete set of genes in an organism, influencing both genotype (genetic makeup) and phenotype (observable traits).
- 😀 Phenotype is influenced by both genetics and environmental factors, and includes visible traits like eye color and height.
- 😀 The genotype consists of the genes that are inherited, but these may not always be visible in the phenotype.
- 😀 Genetic inheritance occurs through gametes (sperm and egg cells), which are formed through meiosis and combine to form a diploid zygote.
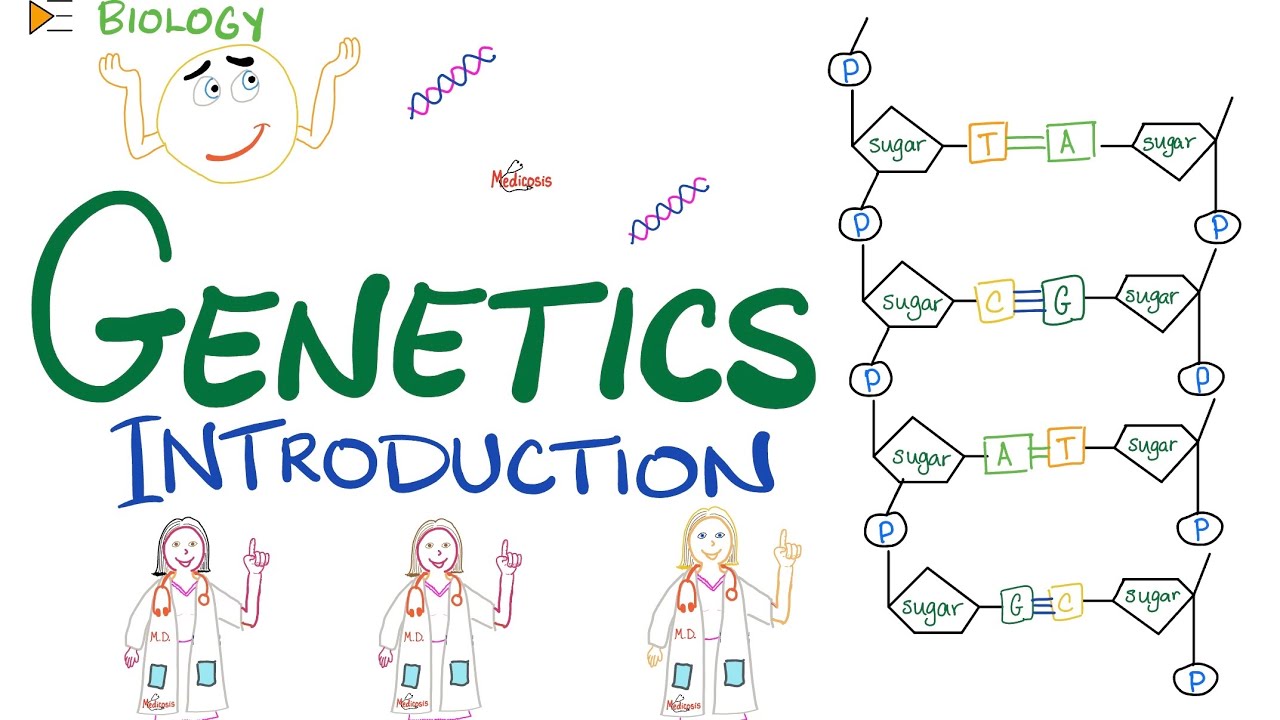
- 😀 Chromosomes are structures within DNA that determine unique physical traits, and are inherited from both parents.
- 😀 Homologous chromosomes come in pairs, and their segregation during gamete formation is the basis of Mendel's laws of inheritance.
- 😀 Mendel's First Law states that each parent passes on one gene from each pair of genes to their offspring.
- 😀 Mendel's Second Law explains the independent assortment of genes on different chromosomes, meaning the inheritance of one trait does not affect the inheritance of another.
- 😀 Alleles are variations of a gene that occupy the same position on homologous chromosomes. Dominant alleles are expressed even if only one copy is present, while recessive alleles require two copies to be expressed.
Q & A
What is the basic definition of genetics?
-Genetics is the study of hereditary information passed down from parents to offspring. It involves understanding how traits and characteristics are inherited through genes, which are made up of DNA.
What are genes and what role do they play in genetics?
-Genes are segments of DNA that carry the information needed to produce proteins, which define traits and characteristics in organisms. They are the fundamental units of inheritance.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
-The **genotype** refers to the genetic makeup inside an organism's cells, while the **phenotype** is the physical expression of those genes, such as eye color or height. The phenotype is influenced by both the genotype and environmental factors.
How are genetic traits passed from parents to offspring?
-Genetic traits are passed through **gametes** (sperm and eggs), which carry half of the genetic information. When a sperm and egg combine during fertilization, they form a zygote with a full set of genes, resulting in the inheritance of traits.
What are chromosomes and what is their role in inheritance?
-Chromosomes are structures in the cell that store DNA. They carry genes that are passed from parent to offspring. Humans typically have 46 chromosomes arranged in 23 pairs, with one set inherited from each parent.
What is the significance of Mendel's Laws of Inheritance?
-Mendel's Laws explain how traits are inherited. The **Law of Segregation** states that each parent contributes one gene from each pair to their offspring, while the **Law of Independent Assortment** states that genes located on different chromosomes are inherited independently.
What does the Law of Segregation state?
-The Law of Segregation states that during the formation of gametes, pairs of genes separate so that each gamete receives only one allele from each gene pair. This ensures genetic variation in offspring.
What does the Law of Independent Assortment describe?
-The Law of Independent Assortment explains that the inheritance of one gene does not affect the inheritance of another gene, especially when they are located on different chromosomes. This means that traits like height and eye color are inherited independently.
What are dominant and recessive alleles?
-Dominant alleles are those that express their traits even when only one copy is present, represented by a capital letter. Recessive alleles only express their traits when two copies are present, one from each parent, and are represented by a lowercase letter.
How does the analogy of a pearl necklace help explain genetics?
-In the analogy, DNA is compared to a necklace and genes to the pearls. Just like pearls are strung on a necklace, genes are arranged on chromosomes. Small changes in the 'pearls' (genes) can result in significant differences in the organism, illustrating how even small genetic variations can have a big impact.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)