Entenda de vez COMO FUNCIONA O MOTOR DO CARRO!
Summary
TLDRIn this detailed video, the host explains the inner workings of a car engine, focusing on key components like the pistons, valves, and fuel injection system. The process of combustion is explored step by step, revealing how fuel and air mix, ignite, and drive the pistons to generate power. The video also touches on the synchronization of engine cylinders, the role of the crankshaft, and the importance of oil and coolant. Aimed at viewers with little technical knowledge, it breaks down complex concepts in an accessible, engaging way, making it easier to understand how a modern car engine operates.
Takeaways
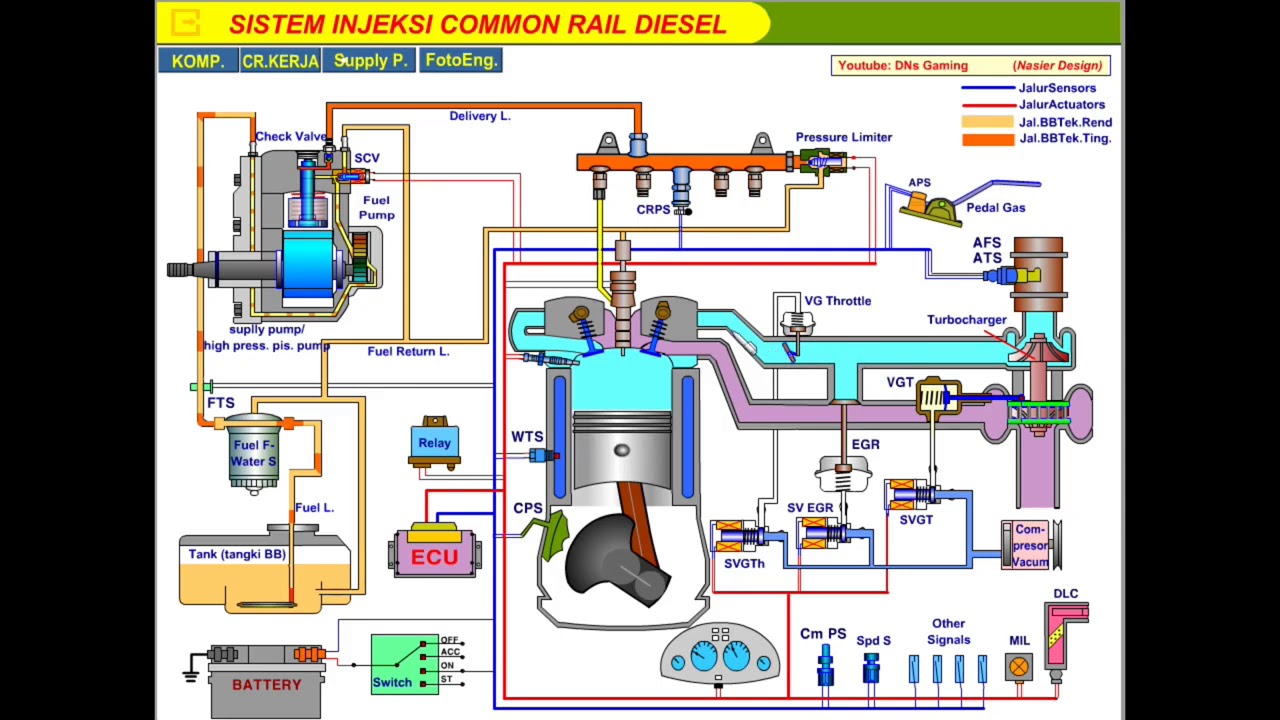
- 😀 The engine requires both fuel (gasoline or ethanol) and air to function, with the air first filtered and then passed through ducts to mix with the fuel.
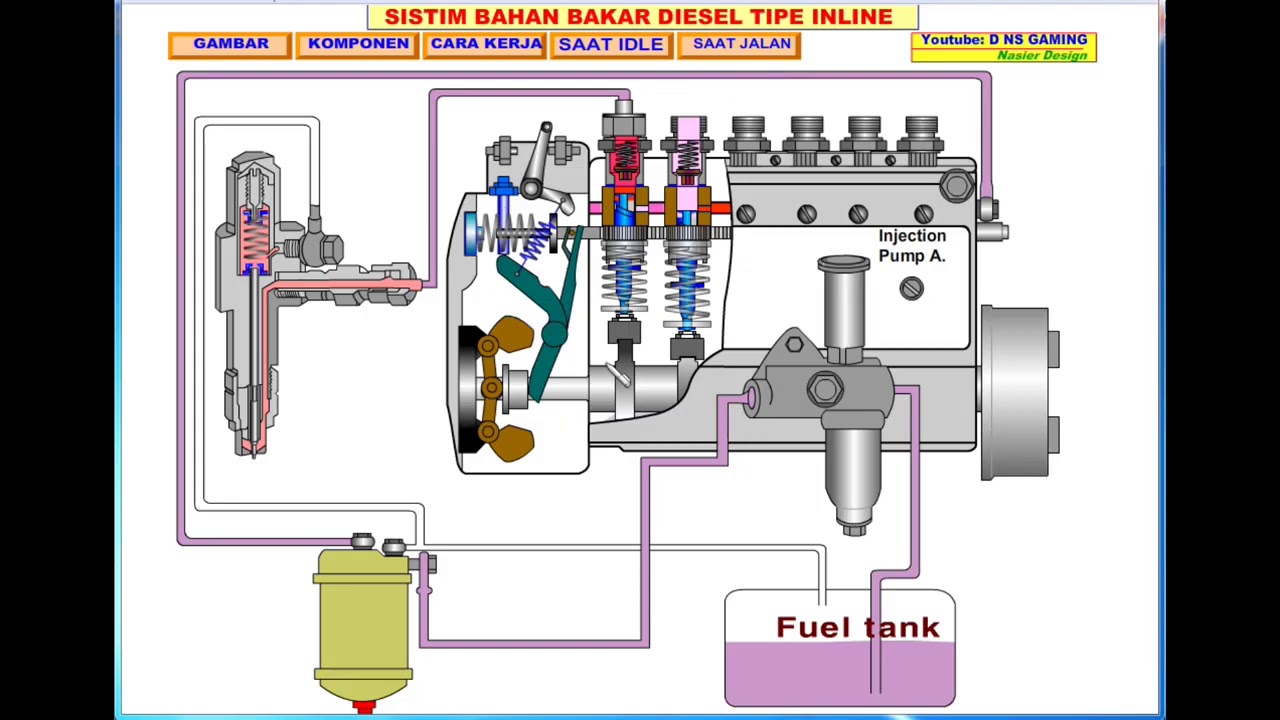
- 😀 The fuel is injected into the engine by a component called the fuel injector, which ensures proper mixing of fuel and air for combustion.
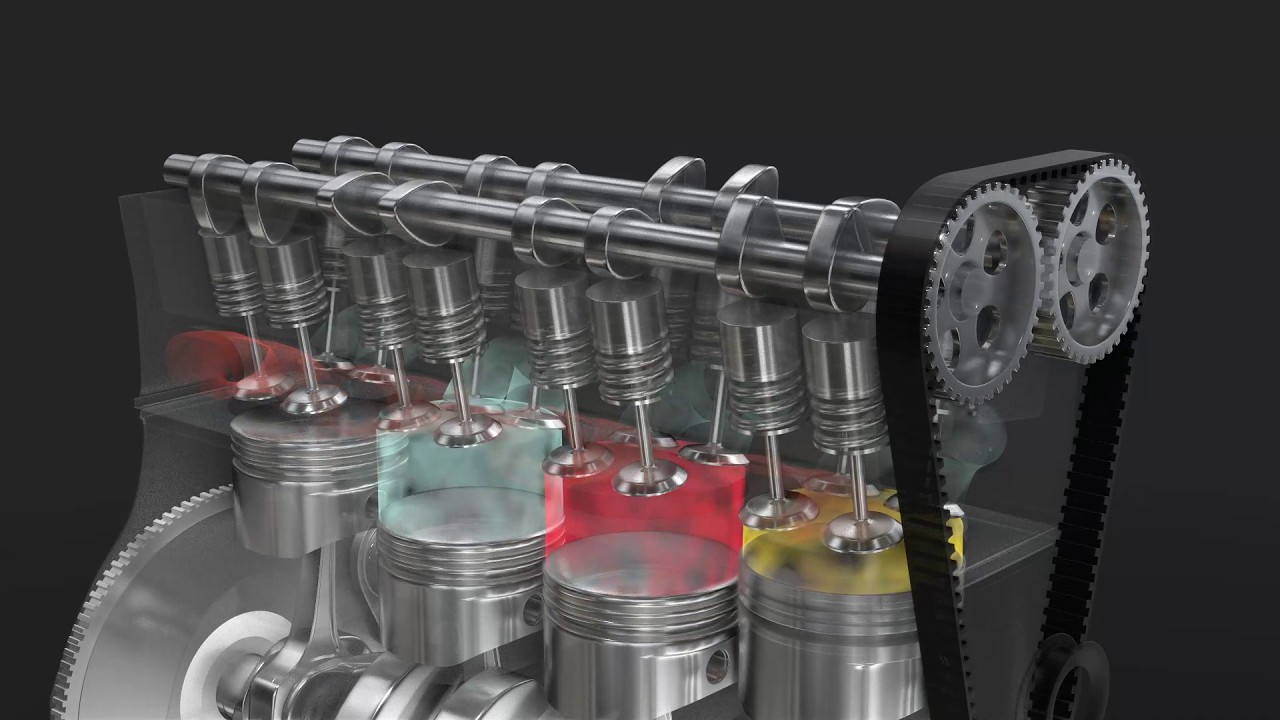
- 😀 The cylinder is a key component where combustion happens; it houses the piston, which moves up and down, mimicking the action of a syringe's plunger.
- 😀 A typical car engine operates on a 'four-stroke' cycle: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust.
- 😀 The first stroke, intake, allows the air-fuel mixture to enter the cylinder when the piston moves down and the intake valves open.
- 😀 The second stroke, compression, occurs when the intake valves close, and the piston moves upward, compressing the air-fuel mixture.
- 😀 The third stroke, combustion, happens when a spark from the spark plug ignites the compressed mixture, causing an explosion that drives the piston downward.
- 😀 The fourth stroke, exhaust, allows the piston to push out the burned gases through the exhaust valves, readying the cylinder for the next cycle.
- 😀 Modern engines often have multiple cylinders, with their strokes staggered to ensure the engine runs smoothly and avoids excessive vibration.
- 😀 The engine's reciprocating motion (up and down movement of the piston) is converted into rotational motion via the crankshaft, which drives the car's wheels.
- 😀 Other important components powered by the engine include the alternator (which generates electricity) and the air conditioning compressor (which uses engine power to cool the vehicle).
Q & A
What is the primary function of the engine's combustion process?
-The combustion process in the engine transforms chemical energy from the fuel into mechanical energy, which powers the vehicle.
How is air introduced into the engine for combustion?
-Air is filtered and then enters the engine through an intake system, passing through several pipes before mixing with fuel.
What role do fuel injectors play in the engine?
-Fuel injectors spray the fuel into the intake air, ensuring that the fuel and air mix properly for combustion.
What happens during the compression stage in a four-stroke engine?
-During the compression stage, the intake valves close, and the piston rises to compress the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder, preparing it for combustion.
How is the spark for ignition generated in the engine?
-A spark plug generates a spark that ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture, causing combustion.
What happens to the piston after combustion in the engine?
-After combustion, the piston is pushed down by the release of energy, converting the chemical energy into mechanical work.
What is the function of the exhaust valves in the engine cycle?
-The exhaust valves open to release the combustion gases after the combustion stage, allowing the engine to expel the exhaust and prepare for the next cycle.
What is the purpose of the crankshaft in the engine?
-The crankshaft converts the up-and-down motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which powers the vehicle's wheels.
How does the engine's cooling system work?
-The engine is cooled by water that circulates through the engine block, absorbing heat, and then passes through the radiator where it is cooled by airflow before returning to the engine.
Why is oil important in an engine?
-Oil lubricates the moving parts, such as the crankshaft and pistons, reducing friction and preventing wear that could damage the engine.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)