COVID19 WINNER Dance Your PhD 2021: Biochemical & Biophysical Studies of the COVID-19 N Protein
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the role of nucleocapsid proteins in the SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for COVID-19. It details how these proteins bind to viral RNA, aiding in viral replication and structure. Using NMR technology, scientists investigate the flexibility and structural regions of the nucleocapsid protein, understanding how mutations affect its function. The pandemic has accelerated scientific collaboration and public engagement with science, highlighting the importance of effective communication in addressing global health challenges. Ultimately, this research could lead to the development of drugs that inhibit RNA binding, potentially disrupting the virus's ability to replicate.
Takeaways
- 🧬 All cells contain double-stranded DNA, which must be transcribed into single-stranded RNA for gene expression.
- 📦 RNA carries building instructions that are translated into proteins, which have various functions depending on their size and structure.
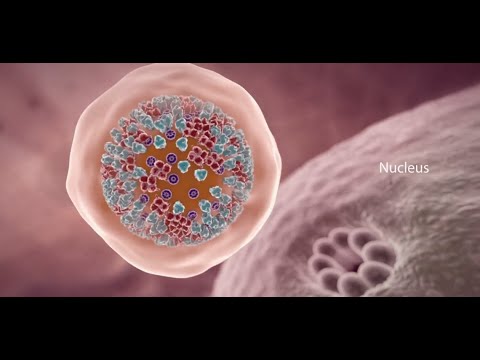
- 🦠 The SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for COVID-19, is made up of key proteins including spike, envelope, and membrane proteins.
- 🔬 Nucleocapsid proteins play a crucial role in packaging viral RNA and are essential for understanding viral replication.
- 🎶 Proteins can be structured (rigid) or disordered (flexible), with the nucleocapsid protein exhibiting both characteristics.
- 🧪 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is used to study protein structure and flexibility by observing protein behavior in a magnetic field.
- 🧩 Understanding the structure of the nucleocapsid protein allows researchers to identify its functional regions.
- 🔄 Researchers compare free nucleocapsid proteins with those bound to RNA to understand how binding alters protein structure and function.
- 💊 Insights into RNA binding mechanisms could lead to the development of drugs that inhibit viral replication.
- 🌍 The COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrated the power of scientific collaboration and public engagement in advancing research and innovation.
Q & A
What is the role of RNA in protein synthesis?
-RNA carries the building instructions transcribed from DNA, which are then translated into proteins.
What key proteins make up the SARS-CoV-2 virion?
-The SARS-CoV-2 virion is composed of spike, envelope, membrane, and nucleocapsid proteins.
Why is the nucleocapsid protein important for understanding SARS-CoV-2?
-The nucleocapsid protein plays a crucial role in viral replication and packaging of the viral RNA, making it essential for understanding the virus's structure and function.
How does Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) help in studying proteins?
-NMR allows scientists to observe the structure, movement, and chemical environment of proteins by analyzing the behavior of their atoms in a magnetic field.
What are the characteristics of the nucleocapsid protein in SARS-CoV-2?
-The nucleocapsid protein has both structured regions, which are rigid, and disordered regions, which allow flexibility.
How do scientists determine the function of different regions of the nucleocapsid protein?
-Scientists break the full-length nucleocapsid protein into smaller parts, comparing them to understand which sections are responsible for specific functions.
What happens to the nucleocapsid protein when it binds to RNA?
-When the nucleocapsid protein binds to RNA, its structured regions attach to the RNA, while the disordered regions remain flexible, leading to stabilization over time.
What is the significance of understanding RNA binding in SARS-CoV-2?
-Understanding RNA binding can inform the development of drugs that block this interaction, potentially disrupting the virus's ability to replicate.
How has the COVID-19 pandemic affected scientific collaboration?
-The pandemic has demonstrated how rapidly science can advance when researchers communicate and collaborate openly, sharing resources towards a common goal.
What impact has the pandemic had on public engagement with science?
-The pandemic has led to increased public interest in science, providing scientists with opportunities to share their research and explain the scientific process more broadly.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
COVID-19 Animation: What Happens If You Get Coronavirus?

Coronavirus: Under the microscope | ABC News

Corona Virus | COVID-19 | Covid-19 Pathogenesis | Covid-19 Lab diagnosis | Corona vaccines

Micologia, Virologia e Microbiologia Clínica 02/05

virus corona bereplikasi atau memperbanyak diri

What Happens If You Get Covid-19?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)