SPtDV Matematika Kelas 10 • Part 1: Pertidaksamaan Linear & Kuadrat Dua Variabel
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces inequalities in two variables, focusing on linear and quadratic inequalities. It explains how to express inequalities, graph the corresponding functions, and determine the solution region through a systematic four-step process. The presenter reviews the characteristics of linear and quadratic functions, including how to find their intercepts and vertices for accurate graphing. The video aims to clarify these concepts and provides viewers with the tools necessary to solve and visualize inequalities effectively.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video introduces the concept of two-variable inequalities, specifically linear and quadratic inequalities.
- 📊 Linear inequalities have the general form Ax + By * C, where * denotes the inequality symbol.
- 📐 Quadratic inequalities take the form Y * X^2 + BX + C, similar to quadratic functions, but with inequality symbols.
- 🖊️ To graph the solution area of these inequalities, there are four main steps to follow.
- ✏️ Step 1 involves converting the inequality into an equation to obtain the corresponding linear or quadratic function.
- 📈 Step 2 consists of graphing the function derived from the inequality, using solid lines for inequalities that include equality and dashed lines for strict inequalities.
- 🔍 Step 3 is to perform a point test, selecting a point not on the line to determine if it satisfies the inequality.
- 🖍️ Step 4 determines the solution area, which is where the valid solutions lie, marked by shading.
- 🔢 For linear functions, graphing requires finding at least two points, usually the x-intercept and y-intercept.
- 📏 For quadratic functions, a minimum of three points is necessary for accuracy, typically including x-intercepts, y-intercept, and the vertex.
Q & A
What are the two main types of inequalities in two variables discussed in the video?
-The two main types discussed are linear inequalities and quadratic inequalities.
What is the general form of a linear inequality in two variables?
-The general form is Ax + By * C, where * represents the inequality sign (such as <, >, ≤, or ≥) and A, B, and C are real numbers.
How does a linear inequality differ from a linear equation?
-A linear inequality resembles a linear equation, but it includes an inequality sign instead of an equality sign.
What is the general form of a quadratic inequality in two variables?
-The general form is Y * (AX^2 + BX + C), where * indicates the inequality sign.
What is the first step in graphing the solution region for an inequality?
-The first step is to convert the inequality into an equation by replacing the inequality sign with an equality sign.
What is the significance of the type of line drawn when graphing inequalities?
-If the inequality includes ≤ or ≥, a solid line is drawn; if it includes < or >, a dashed line is used.
What is the purpose of testing a point when graphing an inequality?
-Testing a point helps to determine which side of the line is the solution region. If the point satisfies the inequality, that region is shaded; if not, the opposite region is shaded.
How do you determine the solution region after shading?
-The solution region is the area that remains unshaded, representing all the possible solutions to the inequality.
What are the steps to graph a linear function?
-To graph a linear function, find the x-intercept and y-intercept, and then plot these points to draw the line.
How many points are generally recommended to accurately graph a quadratic function, and why?
-It is recommended to use at least three points, preferably four or five, to accurately depict the shape of the parabola.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Materi Sistem pertidaksamaan Linear dua Variabel (Matematika) - Bagian 1

ILLUSTRATING LINEAR INEQUALITIES IN TWO VARIABLES || GRADE 8 MATHEMATICS Q2
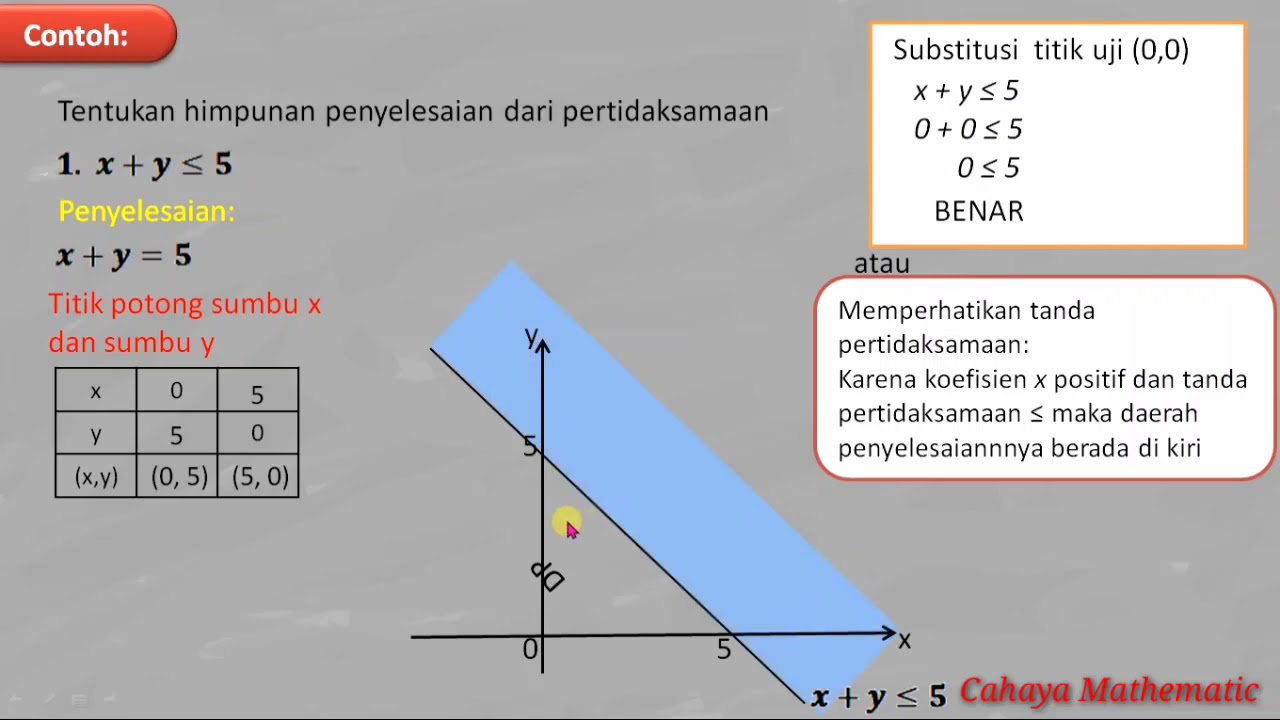
PERTIDAKSAMAAN LINEAR DUA VARIABEL
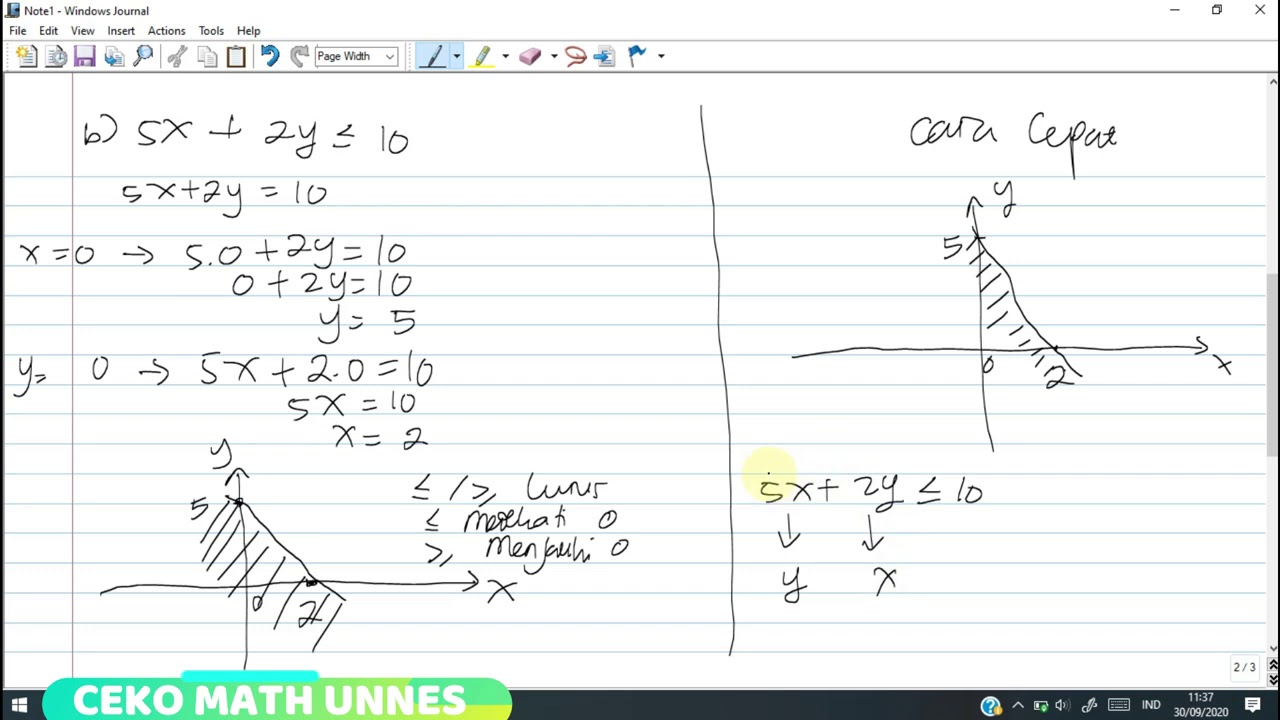
Pertidaksamaan linear dua variabel kelas X. SOAL DAN PEMBAHASAN TRIK CEPAT. Part #1

SPtDV • Part 3: Cara Menentukan Pertidaksamaan Dua Variabel dari Grafik Daerah Penyelesaian

SPtLDV (Sistem Pertidaksamaan Linear Dua Variabel) Kelas 10 Kurikulum Merdeka
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)