8B-Glycolysis and Fermentation
Summary
TLDRThis video explains glycolysis and fermentation, detailing the processes that convert glucose into energy. Glycolysis, occurring in the cytosol, involves ten steps split into two phases: the energy investment phase, where ATP is consumed, and the energy yielding phase, producing ATP and NADH. When oxygen is absent, organisms undergo fermentation, which can be alcoholic or lactic acid. Alcohol fermentation produces ethanol and carbon dioxide, while lactic acid fermentation generates lactic acid, causing muscle soreness. Both processes yield a net gain of two ATPs from one glucose molecule, showcasing the versatility of cellular respiration in energy production.
Takeaways
- 😀 Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration, occurring in the cytosol and consisting of 10 steps divided into two phases.
- 😀 The energy investment phase involves 5 steps where one glucose molecule is cleaved into two glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) molecules, consuming 2 ATP.
- 😀 The energy yielding phase also consists of 5 steps where G3P is converted into two pyruvate molecules, producing 4 ATP and 2 NADH.
- 😀 The net gain from glycolysis is 2 ATP and 2 NADH, as 2 ATP were invested initially.
- 😀 Glycolysis can occur in the absence of oxygen, categorizing it as an anaerobic process.
- 😀 Fermentation follows glycolysis if oxygen is not present, allowing cells to regenerate NAD+ for glycolysis to continue.
- 😀 Alcohol fermentation occurs in plants and fungi, producing ethanol and carbon dioxide from pyruvate.
- 😀 In alcohol fermentation, 2 pyruvate molecules yield 2 ethanol and 2 carbon dioxide, alongside a net gain of 2 ATP.
- 😀 Lactic acid fermentation occurs in animal cells and is responsible for muscle soreness after intense exercise, resulting in lactic acid formation.
- 😀 The overall products of lactic acid fermentation are 2 lactic acids and a net yield of 2 ATP from glycolysis.
Q & A
What is glycolysis and where does it occur?
-Glycolysis is the metabolic process that breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate. It occurs in the cytosol of the cytoplasm.
How many steps are involved in glycolysis, and how are they divided?
-Glycolysis consists of 10 steps, which are divided into two phases: the energy investment phase (first 5 steps) and the energy yielding phase (last 5 steps).
What happens during the energy investment phase of glycolysis?
-In the energy investment phase, glucose (6 carbons) is cleaved into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (3 carbons each), requiring the investment of 2 ATP molecules.
What are the products of the energy yielding phase of glycolysis?
-In the energy yielding phase, the two glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate molecules are converted into two pyruvate molecules, producing 4 ATP and 2 NADH in the process.
Why is there only a net gain of 2 ATP molecules from glycolysis?
-There is a net gain of 2 ATP molecules because 2 ATP molecules are used in the energy investment phase, despite producing a total of 4 ATP in the energy yielding phase.
What occurs when glycolysis takes place in the absence of oxygen?
-When glycolysis occurs without oxygen, the products of glycolysis enter anaerobic respiration or fermentation.
What are the two types of fermentation discussed in the transcript?
-The two types of fermentation are alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation.
What is the process and outcome of alcohol fermentation?
-In alcohol fermentation, two pyruvate molecules are converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. The process yields 2 ATP, 2 CO₂, and 2 ethanol molecules.
How does lactic acid fermentation affect animal muscles during exercise?
-Lactic acid fermentation occurs when there is no oxygen available, converting pyruvate into lactic acid, which can lead to muscle soreness and a burning sensation after intense exercise.
What are the end products of lactic acid fermentation?
-The end products of lactic acid fermentation are 2 lactic acid molecules and 2 ATP.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Bioquímica - Aula 12 - Glicólise e Fermentação

Bioquímica - Aula 13 - Respiração aeróbica

Glycolysis | HHMI BioInteractive Video
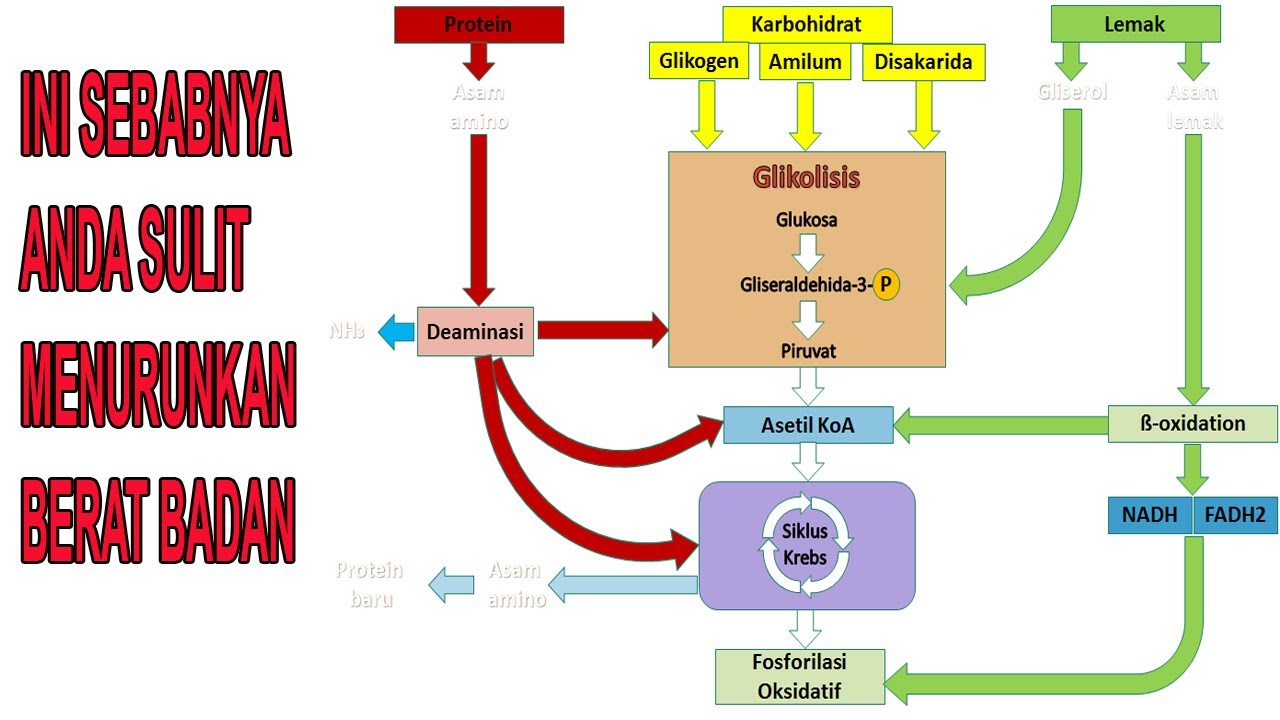
CARBOHYDRATE, FAT AND PROTEIN METABOLISM PATHWAYS

BIOLOGIA - Lezione 16 - La Glicolisi | Metabolismo Cellulare

Video Tahapan Glikolisis | Glikolisis: Tahapan Produksi Energi Sel
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)