Circuit Breaker Testing
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the functionality and importance of circuit breakers in energy management, highlighting their role in controlling current flow at various voltage levels. It discusses the operational principles, including the mechanisms for interrupting short circuit currents and the technologies used, such as air, oil, SF6, or vacuum interrupters. Key components like the drive mechanism and the impact of environmental factors on wear are examined. Additionally, diagnostic tests for maintaining circuit breaker integrity are outlined, emphasizing the significance of resistance measurements and performance validation to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Circuit breakers control energy flow by safely switching currents on and off at all voltage levels in the energy grid.
- ⚠️ In the open position, circuit breakers ensure safe isolation across the switching distance, phases, and ground.
- ⚡ In the closed position, they allow energy to flow with minimal losses.
- 🛡️ Circuit breakers must reliably interrupt short circuit currents without damaging themselves or adjacent equipment.
- 🔧 Different technologies are used for circuit breakers depending on the voltage level, application, and design age.
- 🏭 Current interruption occurs in interrupter chambers containing air, oil, SF6, or vacuum.
- 🔄 Circuit breakers often utilize multiple contact systems, including main contacts for operational current and arcing contacts for breaking short circuits.
- 🔋 The breaking mechanism is operated mechanically, with energy typically stored in springs, hydraulic, or pneumatic systems.
- 🔍 Regular diagnostic tests, such as static contact resistance and dynamic resistance measurements, ensure circuit breaker functionality and safety.
- 📊 Maintenance activities can be initiated based on diagnostic results, helping to verify that equipment is in good working condition.
Q & A
What is the primary function of circuit breakers?
-Circuit breakers control the flow of energy by safely switching currents on and off across all voltage levels of the energy grid.
What is meant by the 'open position' of a circuit breaker?
-In the open position, circuit breakers ensure isolation across the switching distance, between phases, and to ground.
How do circuit breakers minimize energy loss?
-In the closed position, circuit breakers allow energy to flow with minimal losses.
What happens during a short circuit event?
-Circuit breakers must reliably interrupt short circuit currents without damaging themselves or adjacent equipment.
What factors influence the technology used in circuit breakers?
-Different circuit breaker technologies depend on the voltage level, application, and the age of their design.
What are the different media used in interrupter chambers?
-Current interruption occurs in interrupter chambers containing air, oil, SF6, or a vacuum.
What are the roles of main contacts and arcing contacts?
-Main contacts allow operating current to flow with minimal losses, while arcing contacts can break short circuit currents with minimal arcing erosion.
How is the mechanical operation of the breaking element typically powered?
-The breaking element is usually operated mechanically by a stored energy system, typically involving springs, hydraulic, or pneumatic devices.
What diagnostic tests are performed on circuit breakers?
-Diagnostic tests include resistance, timing, minimum pick-up, travel, and power factor tests to ensure proper operation throughout the breaker’s lifetime.
What is the significance of measuring static contact resistance?
-Measuring static contact resistance helps determine the performance of the circuit breaker in the closed position by injecting a high DC current and measuring the voltage.
How can an operator verify the condition of a circuit breaker?
-By performing various measurements, such as opening and closing times, trip and close coil currents, and dynamic resistance during operation, an operator can verify the equipment's condition or initiate maintenance.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Electrical Current Explained - AC DC, fuses, circuit breakers, multimeter, GFCI, ampere

Types of Circuit Breaker with Detailed Classifications | TheElectricalGuy
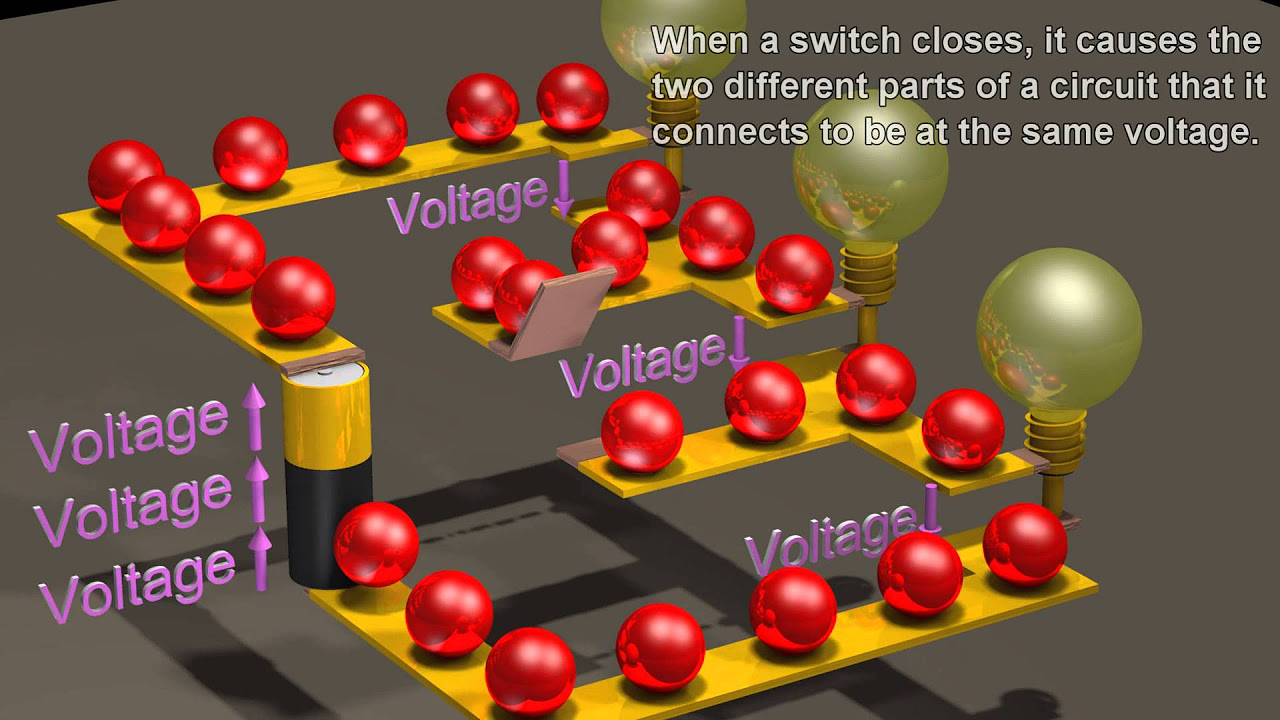
Electric Circuits: Basics of the voltage and current laws.

RAF Modul4 ILB
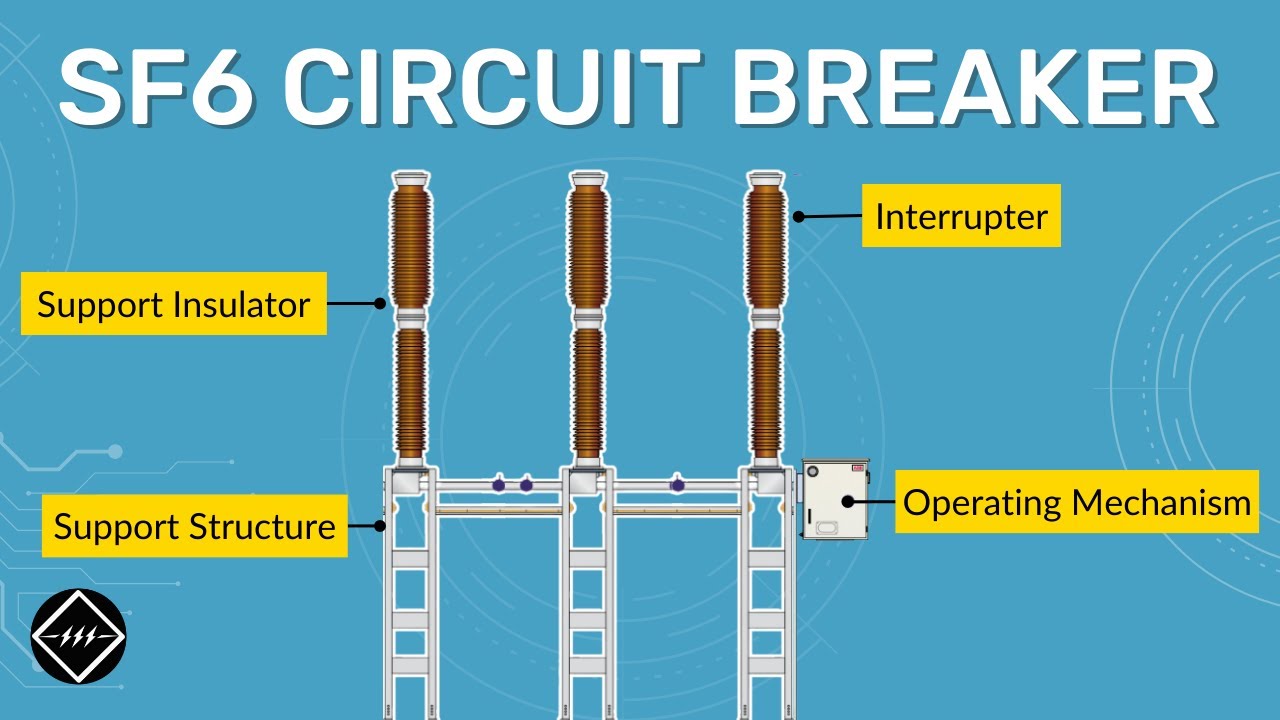
Components of SF6 Circuit Breaker | TheElectricalGuy
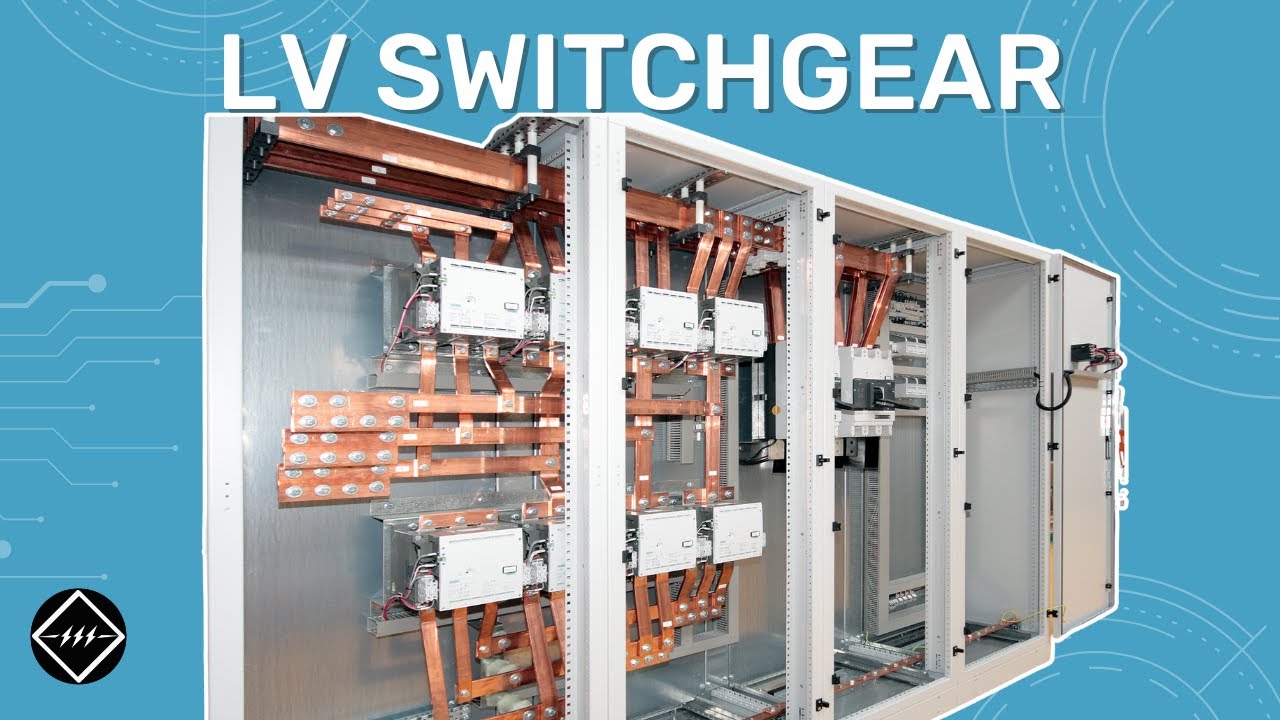
Low Voltage Switchgear : A Beginner’s Guide | TheElectricalGuy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)