Spectra Interference: Crash Course Physics #40
Summary
TLDRThis episode explores the fascinating properties of light, including its wave nature and how it interacts with different materials. Viewers learn about diffraction, spectra, and the tools used to analyze light, such as spectrometers. The video explains phenomena like thin film interference, exemplified by soap bubbles and Newton's Rings, as well as the concept of polarization and its practical application in polarized sunglasses. By examining these concepts, the episode reveals how light can provide insights into the universe and enhance our understanding of its composition and behavior.
Takeaways
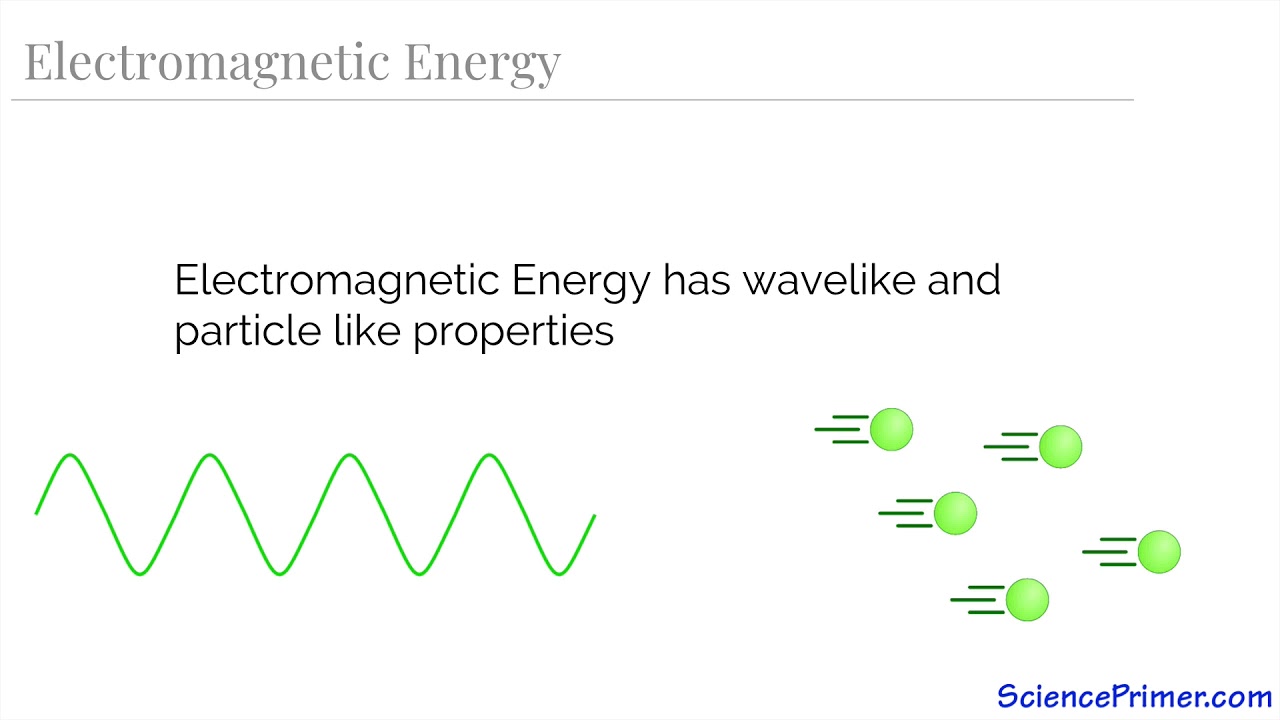
- 🌈 Light behaves as both a wave and a particle, traveling in straight lines while also reflecting and refracting.
- 🔍 Diffraction is the phenomenon that creates patterns when light passes through slits, with bright lines resulting from constructive interference and dark spaces from destructive interference.
- 🧪 A diffraction grating enhances diffraction patterns, making it easier to measure the light source's characteristics.
- 🌈 Spectra can be studied to determine the composition of light sources, with line spectra revealing the specific wavelengths emitted by heated gases.
- ☀️ The Sun emits a continuous spectrum of light, which contains absorption lines due to elements in its atmosphere absorbing specific wavelengths.
- 💧 Thin film interference occurs when light reflects off layers of material, such as soap bubbles or oil on water, creating colorful patterns.
- 🔄 Newton's Rings are circular patterns formed by the interference of light reflecting off a lens and a glass plate, demonstrating constructive and destructive interference.
- 🎨 Light can be polarized, meaning that its electric field oscillates in a specific direction, allowing for the filtering of light through polarizing filters.
- 🕶️ Polarized sunglasses work by blocking horizontally polarized light, which helps reduce glare from surfaces like water.
- 🔬 Understanding the nature of light allows us to analyze the composition of light sources and utilize various optical phenomena in practical applications.
Q & A
What is the nature of light as described in the video?
-Light behaves both as a wave and a particle. It travels in straight lines, reflects off surfaces, refracts through materials, and changes direction.
How does diffraction occur and what does it demonstrate?
-Diffraction occurs when light passes through narrow slits, creating patterns due to constructive and destructive interference. It demonstrates how light waves interact with each other.
What is a diffraction grating and why is it useful?
-A diffraction grating consists of multiple equally spaced slits. It produces more intense diffraction patterns, making it easier to measure and analyze different wavelengths of light.
What information can be obtained from analyzing spectra?
-Analyzing spectra allows us to determine the elemental composition of a light source by identifying the distinct patterns of wavelengths emitted or absorbed by elements.
What is the difference between line spectra and continuous spectra?
-Line spectra are produced by heated gases under low pressure and show distinct lines at specific wavelengths. Continuous spectra come from solids or high-pressure gases and cover a wide range of wavelengths.
What causes the colorful patterns seen on soap bubbles?
-The colorful patterns on soap bubbles are a result of thin film interference, where varying thickness of the soap film causes different wavelengths of light to constructively or destructively interfere.
What are Newton's Rings and how are they formed?
-Newton's Rings are circular patterns formed by the interference of light between a lens and a glass plate. They arise from the phase shifts of light waves reflecting off the surfaces.
What is polarization in the context of light?
-Polarization is the filtering of light based on the direction of its electric field oscillation. It allows specific orientations of light waves to pass through while blocking others.
How do polarized sunglasses work?
-Polarized sunglasses use vertical filters that allow only vertically polarized light to pass through, blocking horizontally polarized light, which reduces glare from reflective surfaces like water.
What did the video conclude about the manipulation and analysis of light?
-The video concluded that understanding diffraction, interference, and polarization enables us to analyze light sources and manipulate their properties for various applications in science and technology.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Propagation of Light (Reflection and Refraction) as Explained by the Wave and Particle Models

Fisika Kelas 11 | Gelombang Cahaya

Cahaya IPA SMP Kelas 8 #Part1Cahaya

Introduction to light | Electronic structure of atoms | Chemistry | Khan Academy

FISIKA Kelas 11 - Gelombang Cahaya | GIA Academy
Electromagnetic Energy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)