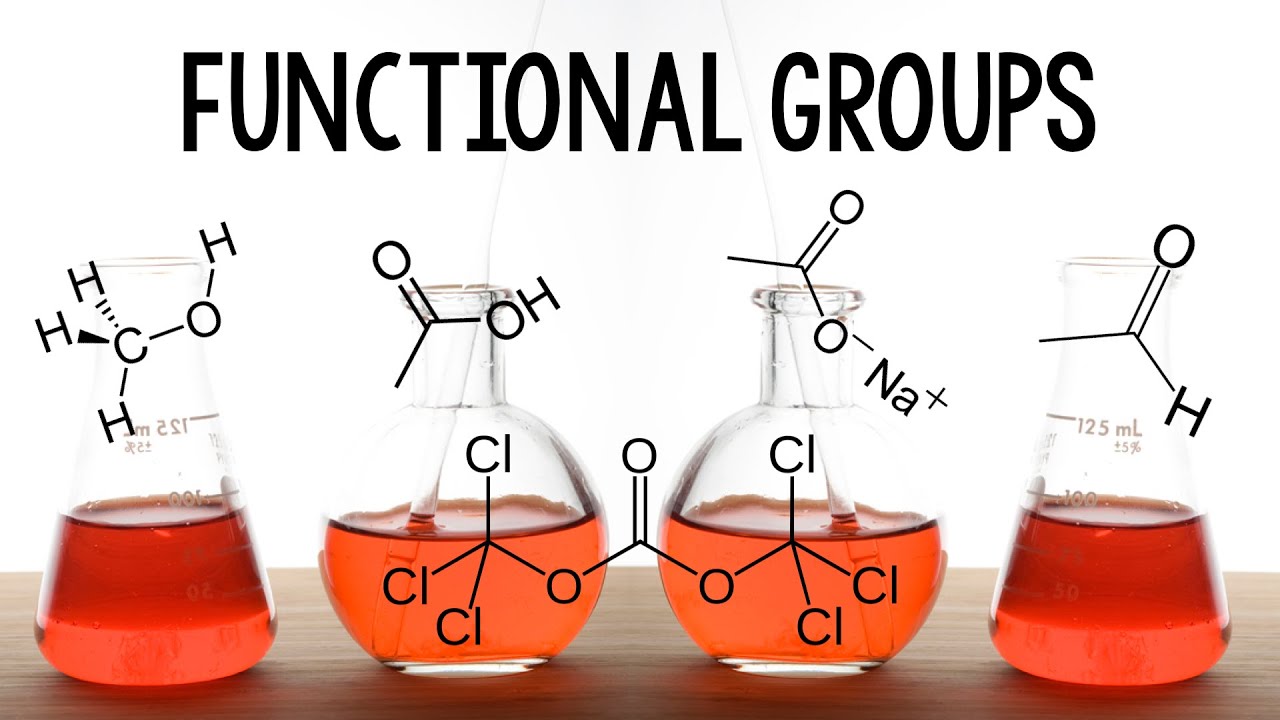
The Functional Group Concept Explained | Organic Chemistry | FuseSchool
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the basics of organic chemistry, focusing on hydrocarbons and functional groups. It explains that hydrocarbons are compounds made only of hydrogen and carbon, with examples like methane, ethane, propane, and butane from the alkane series, and alkenes containing double bonds. The concept of functional groups is discussed, showing how they give molecules similar properties, such as alcohols (-ol) and carboxylic acids (-oic acid). The video emphasizes how organic chemistry is the study of carbon-based molecules and how functional groups impact the behavior and characteristics of these molecules.
Takeaways
- 🧪 Organic chemistry is the study of carbon-based molecules, known as organic compounds.
- 🧬 Hydrocarbons are compounds made of only hydrogen and carbon atoms.
- 🔗 Methane, the simplest hydrocarbon, has one carbon atom with four covalent bonds to hydrogen atoms.
- 🧱 Alkanes are hydrocarbons that consist of single bonds between carbon atoms, like methane, ethane, propane, and butane.
- ✏️ Alkenes are hydrocarbons with at least one double bond between two carbon atoms, such as ethene, propene, and butene.
- 🧑🔬 Functional groups are groups of atoms that give molecules similar properties and affect how they react.
- 🍷 Alcohols contain a hydroxyl group (-OH), which can be attached to alkanes, and their names end in '-ol', such as methanol and ethanol.
- 🧪 Carboxylic acids have a carboxyl group (-COOH) and their names end in '-oic acid', like methanoic and ethanoic acid.
- 🌸 Esters give molecules sweet smells, making them useful in perfumes and flavorings.
- 💊 Amines and ketones are examples of functional groups with specialized uses, such as in dyes, solvents, and medicines.
Q & A
What is organic chemistry?
-Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds, including a vast array of molecules made from carbon and other elements such as hydrogen.
What are hydrocarbons?
-Hydrocarbons are compounds made only of hydrogen and carbon atoms.
What is the simplest hydrocarbon, and what is its structure?
-The simplest hydrocarbon is methane, which consists of one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms via covalent bonds.
What is the difference between alkanes and alkenes?
-Alkanes are hydrocarbons with single covalent bonds between carbon atoms, while alkenes contain at least one double covalent bond between two carbon atoms.
What is the structure of hexane, and how is it classified?
-Hexane consists of six carbon atoms connected by single covalent bonds and is classified as an alkane.
What are functional groups in organic chemistry?
-Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that give the molecules similar properties and characteristic reactions.
What is an alcohol functional group, and how does it modify alkanes?
-An alcohol functional group consists of a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom. When added to alkanes, the molecule becomes an alcohol and is named with the suffix '-ol,' such as methanol or ethanol.
What is a carboxylic acid, and what is the functional group responsible for it?
-A carboxylic acid contains a carboxyl group (-COOH) that gives the molecule acidic properties. Examples include methanoic acid and ethanoic acid.
How do functional groups affect the properties of organic molecules?
-Functional groups determine the chemical properties and reactivity of organic molecules, causing molecules with similar groups to behave in similar ways. For instance, alcohols can form hydrogen bonds and dissolve in water.
Can molecules have more than one functional group? Provide an example.
-Yes, molecules can have more than one functional group, which can result in a combination of different properties. For example, esters, which contain both an alcohol and a carboxyl group, are known for their pleasant fragrances.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)