HISTOLOGÍA DEL SISTEMA ENDOCRINO - Eje Hipotálamo Hipofisario
Summary
Please replace the link and try again.
Takeaways
- 😀 The endocrine system operates through negative feedback: when the body reaches its hormonal target, production stops until it's needed again.
- 😀 Hormones like T3 and T4 play a crucial role in regulating body temperature, and their levels directly influence the activity of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
- 😀 If there’s a deficiency in thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), the hypothalamus signals the pituitary to produce TSH, which then stimulates the thyroid to produce these hormones.
- 😀 Once T3 and T4 levels are adequate, negative feedback signals the hypothalamus and pituitary to stop stimulating the thyroid, preventing excess hormone production.
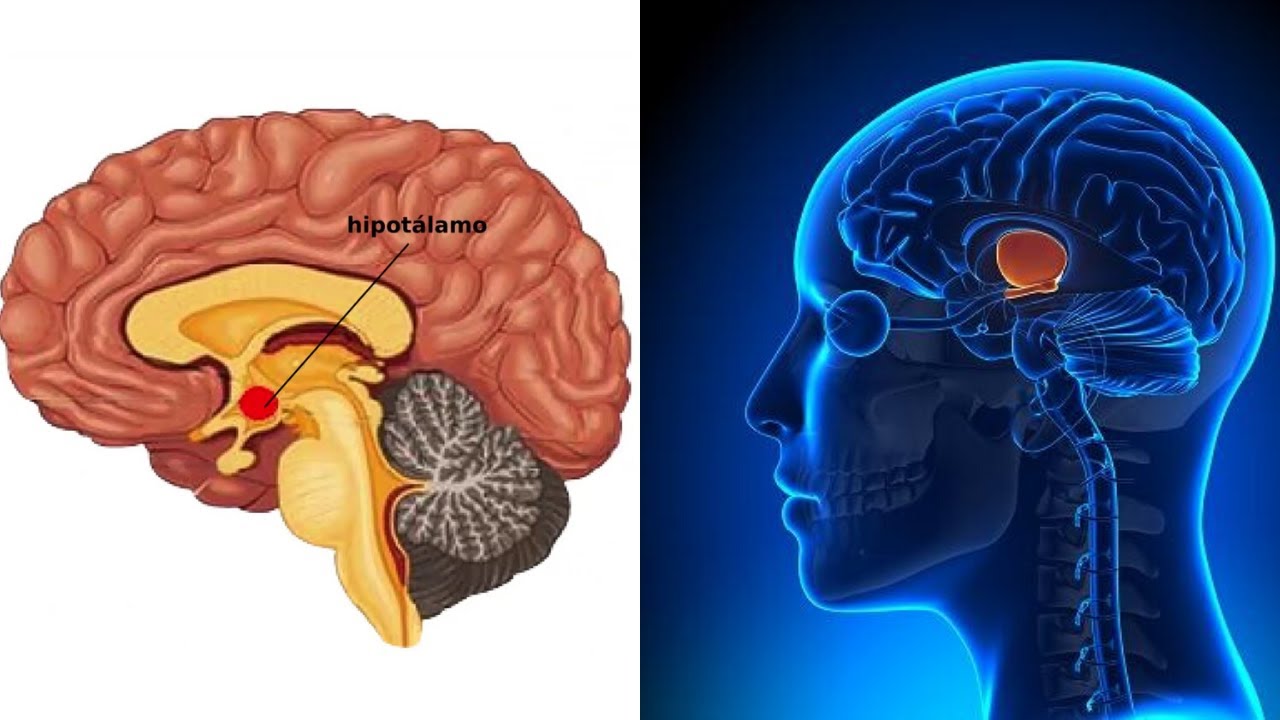
- 😀 The hypothalamus is the 'boss' of the system, while the pituitary gland acts as the 'manager,' and the thyroid is the 'worker' that produces the necessary hormones.
- 😀 The neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary) stores and releases hormones (oxytocin and vasopressin) but does not produce them.
- 😀 Oxytocin, produced in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, plays a key role in childbirth and lactation.
- 😀 Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), produced in the supraoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus, helps regulate water retention by the kidneys.
- 😀 The hypothalamus sends axons to the neurohypophysis to store and release the hormones it produces, like oxytocin and vasopressin.
- 😀 The system operates in a feedback loop: hormone production is stimulated when there's a deficiency and halted when there's an excess, ensuring balance and proper functioning.
Q & A
What is the concept of negative feedback in hormone regulation?
-Negative feedback is a mechanism where the body adjusts the production of hormones based on their levels. When hormone levels reach a certain point, the body stops producing them. If hormone levels fall, production is stimulated again, maintaining balance.
How does the hypothalamus contribute to hormone regulation?
-The hypothalamus acts as the 'boss' of the system. It produces releasing hormones that stimulate the pituitary gland to release other hormones. These, in turn, stimulate target organs like the thyroid to produce necessary hormones.
What happens when there is an excess of T3 and T4 in the body?
-When there is an excess of T3 and T4 hormones, the hypothalamus stops signaling the pituitary gland to produce more hormones, thus preventing further production and maintaining balance.
What is the role of TSH in the thyroid hormone production process?
-TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) is released by the pituitary gland in response to signals from the hypothalamus. It stimulates the thyroid to produce T3 and T4 hormones, which are crucial for various metabolic processes.
How does the body stop hormone production once it reaches the desired level?
-Once the desired hormone levels are achieved, the hypothalamus reduces its signaling to the pituitary gland, halting the production of the stimulating hormones. This feedback loop prevents overproduction of hormones.
What does the term 'retroalimentación negativa' mean in this context?
-'Retroalimentación negativa' refers to the negative feedback mechanism, where an excess of hormones inhibits further production by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland to prevent imbalance.
What is the difference between the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis and the neurohypophysis?
-The hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis involves the production of hormones like T3 and T4, with a feedback loop regulating their levels. The neurohypophysis, however, does not produce hormones but stores and releases hormones like oxytocin and vasopressin that are synthesized in the hypothalamus.
What hormones are produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the neurohypophysis?
-The hypothalamus produces oxytocin and vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), which are then stored in the neurohypophysis for later release into the bloodstream.
What is the function of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone)?
-Vasopressin helps the body retain water by promoting the reabsorption of water in the kidneys, thus regulating fluid balance.
What is the function of oxytocin during childbirth and lactation?
-During childbirth, oxytocin causes the uterus to contract, facilitating the delivery of the baby. It also plays a role in milk ejection during lactation by stimulating the epithelial cells of the mammary glands.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Fisiología endocrina I: Eje Hipotálamo-Hipófisis

Qué es el Eje hipotalámico-hipofisario-adrenal

El sistema endócrino fisiología de glándulas y hormonas

EMBRIOLOGÍA: EJE HIPOTALÁMICO-HIPOFISIARIO-GONADAL | Leo de medicina

CORTICOESTEROIDES
The HYPOTHALAMUS explained: its parts, hormones, functions, diseases🧠
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)