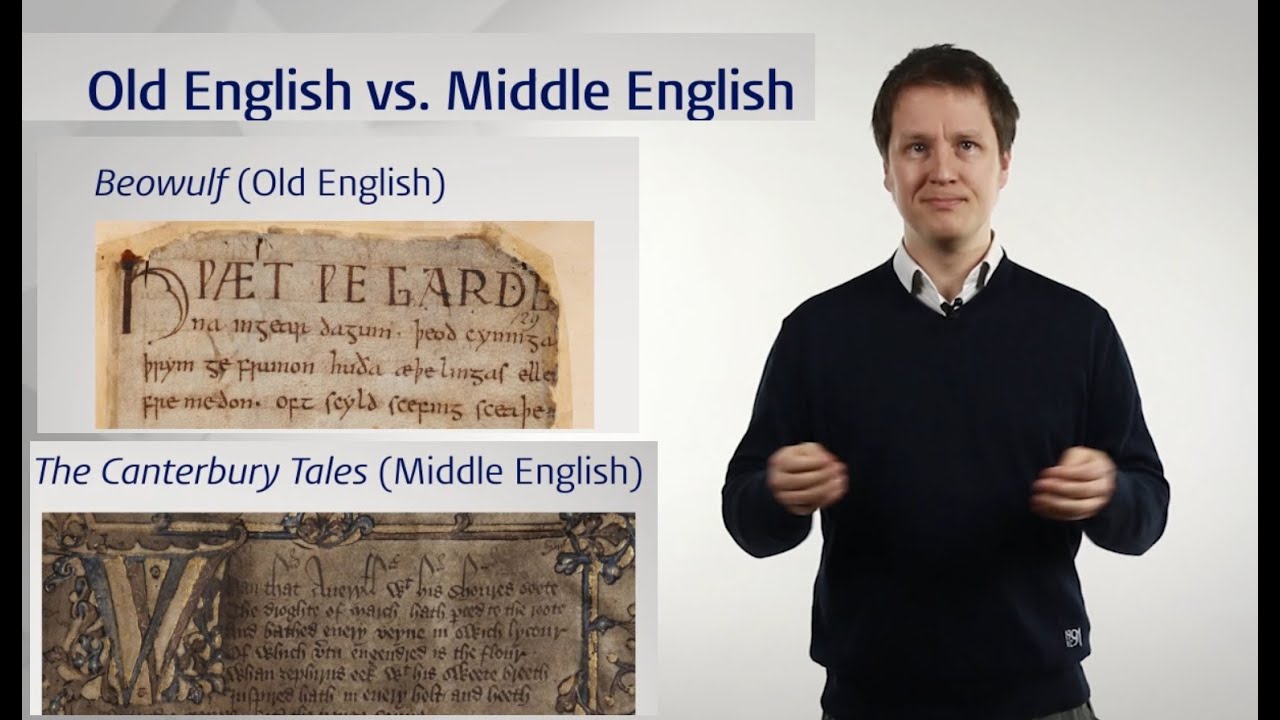
Middle English literature (1066–1500)
Summary
TLDRMiddle English literature, spanning from 1066 to 1500, saw a shift from Anglo-Saxon to French influence post-Norman conquest. It evolved into Middle English with regional dialects, gaining literary prominence through works like 'Piers Plowman' and 'Sir Gawain and the Green Knight.' Religious texts like Wyclif's Bible and 'Revelations of Divine Love' by Julian of Norwich contributed to its legitimacy, alongside secular works like Chaucer's 'Canterbury Tales.' The rise of the Chancery standard and the printing press eventually standardized the language.
Takeaways
- 🏰 The Norman Conquest in 1066 led to French becoming the dominant language in courts, parliament, and polite society.
- 📜 Anglo-Saxon language and literature diminished in prominence as Middle English evolved under the influence of Anglo-Norman.
- 🕊️ Religious literature remained popular, with works like 'The Life of Saint Audrey Edmonds' being adapted and translated.
- 🏰📚 Lawman's 'Brut' was a significant work that adapted Norman French to produce the first English-language historical narrative.
- 📖 Wyclif's Bible translations were instrumental in establishing English as a literary language and inspired a pre-Reformation movement.
- 🔱 The genre of romances, such as 'King Horn' and 'Havelock the Dane', appeared in English from the 13th century, based on Anglo-Norman originals.
- 🎭 Major English writers like William Langland, Geoffrey Chaucer, and the 'Pearl' poet emerged in the 14th century, contributing significantly to Middle English literature.
- 📝 'Piers Plowman' by Langland is an allegorical narrative poem notable for its unrhymed alliterative verse.
- 🏵️ 'Sir Gawain and the Green Knight' is a late 14th-century alliterative romance that explores themes of honor and chivalry.
- 🌐 Middle English literature was characterized by a diversity of dialects, reflecting the regional, historical, and cultural backgrounds of writers.
- 📚🖨️ Middle English lasted until the 1470s when the Chancery Standard and the printing press helped standardize the English language.
Q & A
What was the impact of the Norman Conquest on the English language and literature?
-The Norman Conquest of England in 1066 led to the decline of the Anglo-Saxon language in written form. French became the standard language of courts, parliament, and polite society, while the Norman dialects mingled with the native language, leading to the development of Anglo-Norman and Middle English.
How did Middle English literature evolve from Anglo-Saxon literature?
-Middle English evolved from Anglo-Saxon as the political power shifted, and West Saxon literary language lost its dominance. The literature of this period was written in various dialects corresponding to the regions, history, culture, and background of individual writers.
What was the role of religious literature in Middle English literature?
-Religious literature continued to be popular during the Middle English period. Works like the life of Saint Audrey and Bible translations, including Wyclif's Bible, helped to establish English as a literary language.
Who was Lawman, and what is his significance in Middle English literature?
-Lawman was a poet who adapted Norman French to produce the first English-language work presenting the legends of King Arthur and the Knights of the Round Table. His work marked a significant step in the development of English historiography since the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle.
What is Wyclif's Bible, and why is it important?
-Wyclif's Bible refers to a group of Bible translations into Middle English made under the direction of John Wycliffe between 1382 and 1395. These translations were instrumental in the pre-Reformation movement that questioned the teachings of the Roman Catholic Church and helped to establish English as a literary language.
What are some examples of Middle English romances?
-Middle English romances include works like 'King Horn' and 'Havelock the Dane,' which were based on Anglo-Norman originals. These romances began appearing in English from the 13th century.
Who were the major writers of Middle English literature in the 14th century?
-Major writers of Middle English literature in the 14th century included William Langland, Geoffrey Chaucer, and the Pearl Poet, known for works such as 'Piers Plowman' and 'Sir Gawain and the Green Knight.'
What is 'Piers Plowman' and why is it significant?
-'Piers Plowman' is a Middle English allegorical narrative poem written by William Langland, significant for its use of unrhymed alliterative verse and its exploration of social, moral, and religious themes.
How does the language of 'Sir Gawain and the Green Knight' differ from that of Geoffrey Chaucer's works?
-The language of 'Sir Gawain and the Green Knight' is from the Midlands and contains many dialect words, often of Scandinavian origin, which is markedly different from the London-based English dialect used by Chaucer.
What led to the decline of Middle English and the rise of Modern English?
-Middle English declined with the widespread adoption of the Chancery Standard, a London-based form of English, and the standardization of the language through the printing press in the late 15th century.
Who was John Gower, and how does his work illustrate the multilingual nature of 14th-century English literature?
-John Gower was a contemporary of William Langland and a personal friend of Chaucer. His major works, 'Vox Clamantis,' 'Speculum Meditantis,' and 'Confessio Amantis,' were written in Anglo-Norman, Latin, and Middle English respectively, showcasing the multilingual literary landscape of the time.
What is the significance of 'The Book of Margery Kempe' in the context of English literature?
-Julian of Norwich's 'Revelations of Divine Love' is believed to be the first published book written by a woman in the English language, marking a significant milestone for women's voices in English literature.
Why is 'Le Morte d'Arthur' by Sir Thomas Malory important?
-'Le Morte d'Arthur' is a compilation of Arthurian romances and was one of the earliest books printed in England. It was influential in reviving interest in the Arthurian legends and is considered a major work of the 15th century.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)