[DSS03B-ID] Entity Relationship Modeling Part 1
Summary
TLDRThis lecture introduces Module 8 on Entity Relationship Modeling in relational database systems. It explains the four components of an ER diagram: entities, relationships, attributes, and multiplicity. The example given involves two entities, 'customer' and 'order,' with a one-to-many relationship. The lecture also touches on the types of relationships (binary, ternary, and quaternary) and the concept of recursive relationships. It distinguishes between strong and weak entities, with the latter being dependent on a parent entity. Further details on attributes and multiplicity are promised in Module 9.
Takeaways
- 📚 The lecture is about Module 8 of the database system course.
- 🔍 It focuses on Entity Relationship Modeling (ERM) in relational modeling.
- 📈 ERM can be visualized using an Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD).
- 📝 ERD consists of four components: Entities, Relationships, Attributes, and Multiplicity.
- 👥 An example in the script shows two entities and one relationship between them.
- 🏢 The 'customer' entity has four attributes, and the 'order' entity has three attributes.
- 🔗 Multiplicity 'one to many' between 'customer' and 'order' means one customer can have multiple orders, but one order is made by one customer.
- 🔢 There are three types of relationships based on the degree: binary (degree 2), ternary (degree 3), and quaternary (degree 4).
- 🔄 Recursive relationships are those that connect the same entity with different roles, like supervisor and supervisee.
- 💪 Strong entities can exist independently, like 'customer', while weak entities depend on the existence of their parent entity, like 'reference'.
- 📅 More details about attributes and multiplicity will be explained in Module 9.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lecture?
-The main topic of the lecture is Module 8, which discusses Entity Relationship Modeling in relational database systems.
What are the four components of an Entity Relationship Diagram?
-The four components of an Entity Relationship Diagram are entities, relationships, attributes, and multiplicity.
What is an example of an entity mentioned in the script?
-An example of an entity mentioned in the script is 'customer', which has four attributes.
What is an example of a relationship mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions a relationship between 'customer' and 'order' entities.
What does the multiplicity 'one to many' represent?
-The multiplicity 'one to many' represents that one customer can make many orders, and one order is made by one customer.
What are the three types of relationships based on degree?
-The three types of relationships based on degree are binary (degree 2), ternary (degree 3), and quaternary (degree 4).
What is a recursive relationship?
-A recursive relationship is a relationship that connects the same entity type but with different roles, such as supervisor and supervisee.
What is the difference between strong and weak entities?
-A strong entity can exist independently, while a weak entity cannot exist without its parent entity.
Can you provide an example of a strong entity from the script?
-An example of a strong entity from the script is 'customer'.
What is the role of a weak entity?
-A weak entity depends on a strong entity and must be owned by it, such as 'referensis' which must be owned by 'customer'.
What will be discussed in the next module?
-The next module will discuss attributes and multiplicity in more detail.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Banco de Dados - Aula 13

[DSS03C-ID] Entity Relationship Modeling Part 2

Database Design One to Many Relationships: 7 Steps to Create Them (With Examples)

Aula 01 de Modelagem Relacional (Banco de Dados)
Relational Database Design: Data Modeling for Beginners Part 1 of 2
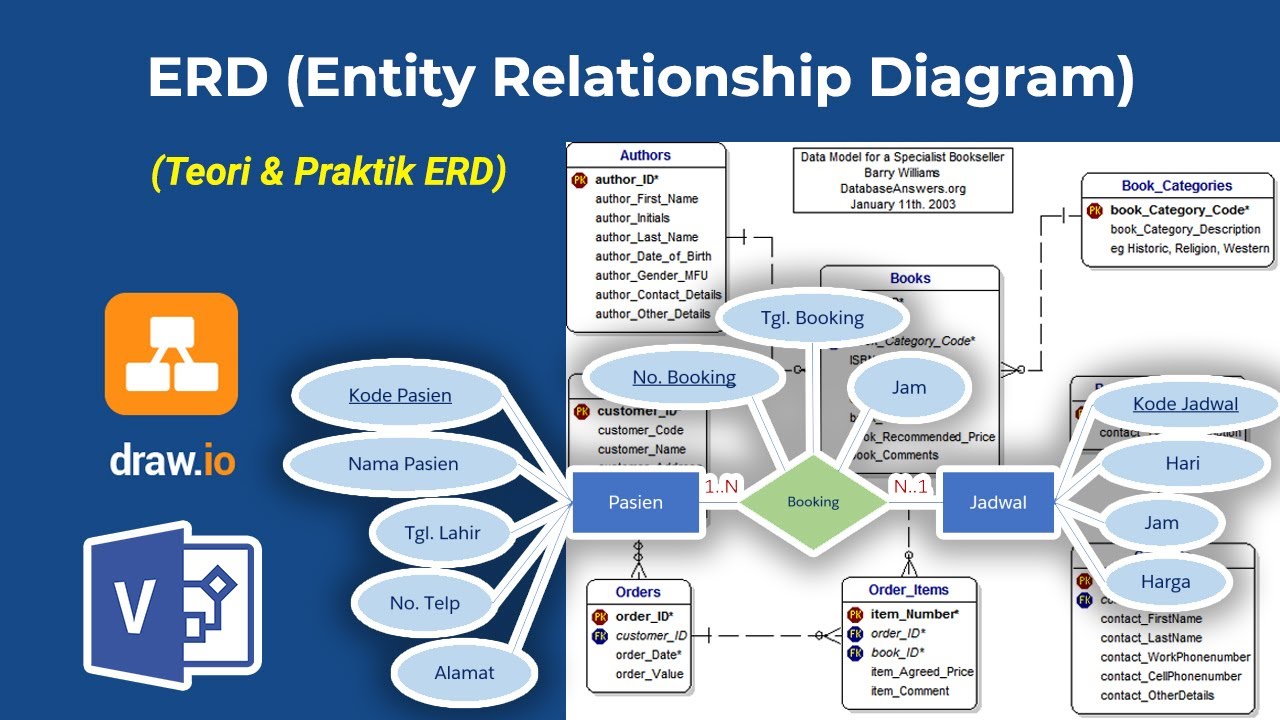
Belajar Membuat ERD (Entity Relationship Diagram) | Belajar UML & Perancangan Sistem
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)