BIO 1 4 : Tipe Ekosistem
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script introduces various types of ecosystems, both terrestrial and aquatic. It explains the concept of ecosystems developed by Roy in 1930, highlighting the interaction between living organisms and their physical environment. The script covers different biomes like tropical rainforests, temperate forests, tundra, and deserts, describing their unique abiotic and biotic characteristics. It also delves into aquatic ecosystems, discussing the distinctions between freshwater and saltwater habitats, and the diverse life forms within them, such as plankton, nekton, benthos, and periphyton.
Takeaways
- 🌿 The term 'ecosystem' was developed by Roy H. Whittaker in 1930 to classify the relationships between living communities and their physical environment.
- 🌳 Ecosystems consist of two components: biotic (living organisms like plants, animals, and fungi) and abiotic (non-living elements such as temperature, water, and sunlight).
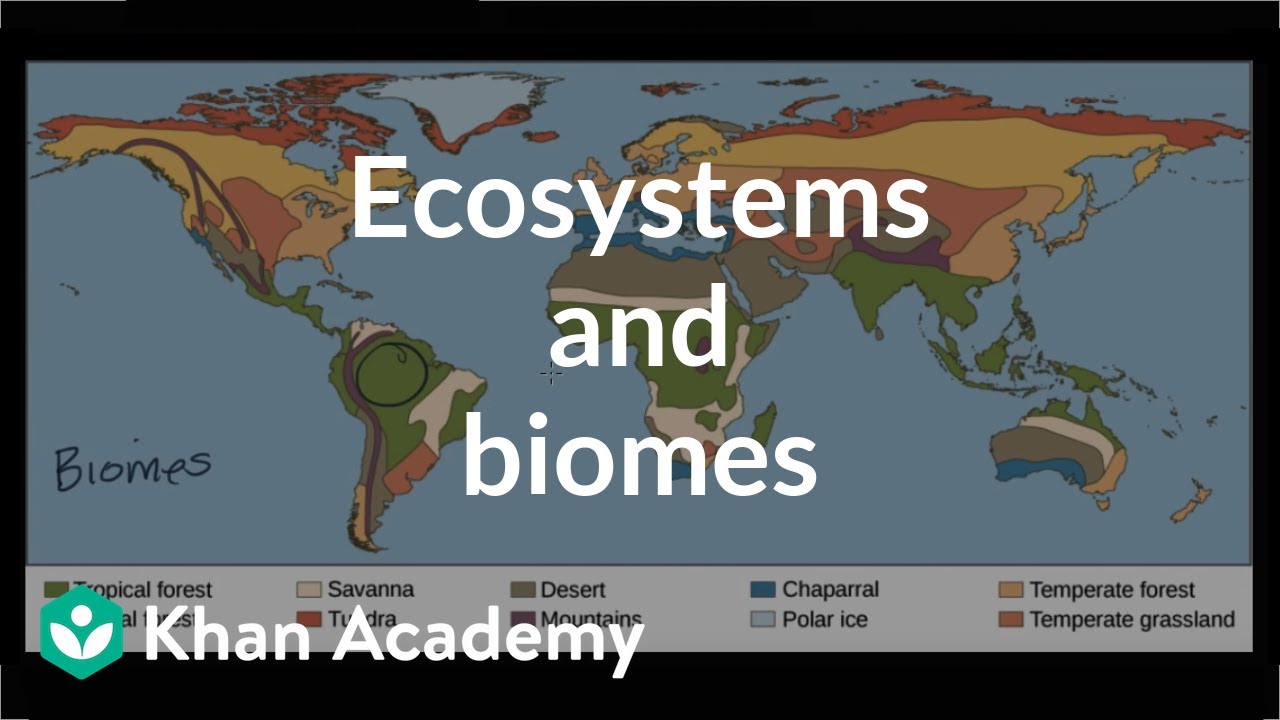
- 🌍 Ecosystems are categorized into terrestrial (land-based) and aquatic (water-based) ecosystems.
- 🏞️ Terrestrial ecosystems cover about 30% of Earth's surface and include biomes like tropical rainforests, boreal forests, grasslands, deserts, and tundra.
- 🌦️ Tropical rainforests are characterized by high rainfall (200-400 cm annually), year-round sunlight, and temperatures between 20-31°C.
- 🍂 Temperate deciduous forests experience four seasons with moderate rainfall (75-100 cm annually) and can have very cold winters and hot summers.
- 🌲 Boreal forests, also known as taiga, have low rainfall (35-40 cm annually) and a large temperature difference between winter and summer.
- 🌾 Grasslands, or savannas, have hot temperatures year-round with seasonal rainfall (90-150 cm annually) and long periods of drought.
- 🏜️ Deserts have very low rainfall (less than 25 cm annually), extreme temperature fluctuations, and sandy, dry soil.
- 🌊 Aquatic ecosystems are divided into freshwater and saltwater ecosystems based on salinity levels.
- 🐠 Aquatic ecosystems also include different groups of organisms: plankton, nekton, newuston, benthos, and periphyton, each with distinct characteristics and roles.
Q & A
What is the term 'ecosystem' developed by Roy to classify?
-The term 'ecosystem' was developed by Roy to classify the relationship between living communities and the physical environment around them.
What are the two main components of an ecosystem?
-An ecosystem consists of two main components: biotic components, which include living organisms such as plants, animals, and fungi, and abiotic components, which include non-living elements like temperature, water, and sunlight.
What are the two types of ecosystems mentioned in the script?
-The two types of ecosystems mentioned are terrestrial ecosystems, which are land-based, and aquatic ecosystems, which are water-based.
What is the difference between a tropical rainforest and a deciduous forest in terms of climate?
-Tropical rainforests have high rainfall (200-400 cm per year), constant sunlight, and temperatures between 20-31 degrees Celsius. Deciduous forests experience four seasons with rainfall of 75-100 cm per year and temperatures that can be very cold in winter and hot in summer, reaching up to 30 degrees Celsius.
What are the characteristics of a boreal forest or taiga?
-Boreal forests or taiga are found in subarctic regions with low rainfall (35-40 cm per year) and a large difference between winter and summer temperatures. They are characterized by homogenous vegetation, primarily consisting of a single species of tree like pine, spruce, or fir.
What are the abiotic characteristics of a savanna?
-Savannas have hot temperatures year-round, seasonal rainfall between 90-150 cm per year, and a very long dry season. They are characterized by grasslands with scattered trees.
What are the main types of plants and animals found in a tundra ecosystem?
-Tundra ecosystems have low precipitation (25-50 cm per year, sometimes up to 100 cm), irregular rainfall, and a variety of plant life including dwarf shrubs and grasses. Animal communities include bison, birds, snakes, and large herbivores.
What are the distinguishing features of a desert ecosystem?
-Desert ecosystems have very low rainfall (below 25 cm per year), high evaporation rates, extreme temperature changes, and sandy, dry soil. They include plants like cacti and succulents and animals such as mice, snakes, and camels.
How are aquatic ecosystems categorized based on salinity?
-Aquatic ecosystems are categorized into freshwater ecosystems, which have low salinity, and marine ecosystems, which have high salinity.
What are the different groups of organisms found in aquatic ecosystems based on their mobility and habitat?
-Aquatic ecosystems include plankton (which are further divided into phytoplankton and zooplankton), nekton (mobile organisms like fish and shrimp), neustons (organisms that float on the water surface), benthos (organisms living on the bottom), and periphyton (organisms that attach to other organisms).
What is the significance of learning about different types of ecosystems?
-Learning about different types of ecosystems helps us to better understand the variety of environments on our planet and the interactions between living organisms and their physical surroundings.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Animasi Ekosistem - Video Dokumenter

Makhluk Hidup dan Lingkungannya_Mapel IPAS Kelas 10 SMK
Ecosystems and biomes | Ecology and natural systems | High school biology | Khan Academy

EKOSISTEM (KOMPONEN DAN INTERAKSINYA) KELAS X SMA

ENVI 01999213-64 Ep.02

What is an ecosystem | Ecosystem video for kids | Ecosystem Types |
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)