What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Gary Sims from Android Authority explores the Internet of Things (IoT), a global network that extends beyond human communication to interconnected devices, or 'things,' equipped with sensors. These devices collect and transmit data, leading to smarter homes and cities. Gary discusses the challenges of IoT, including technological hurdles, big data processing, and security concerns. He highlights Samsung's ambitious plan for IoT-enabled products and ARM's mbed OS, designed for low-power IoT devices. The video also touches on M2M communication and the potential of IoT in large-scale projects, emphasizing the transformative yet complex nature of this technology.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The Internet of Things (IoT) is a global network that extends the internet's reach beyond people and computers to everyday objects equipped with sensors.
- 📱 IoT devices, like smart thermostats and traffic monitors, collect data and transmit it to the cloud for analysis and decision-making.
- 🚀 IoT is poised to transform personal and professional lives, with more 'things' potentially outnumbering people on the internet.
- 🛠️ Technological challenges in IoT include hardware and software issues such as battery life, maintenance, interoperability, and compatibility.
- 🔒 Security and privacy are significant concerns as IoT devices can be vulnerable to hacking, as demonstrated by incidents involving webcams and baby monitors.
- 💡 Samsung has ambitious plans for IoT, aiming for all its products to be IoT-enabled within five years, with 90% connectivity by 2017.
- 📊 Big data is a critical component of IoT, requiring robust systems to process vast amounts of data for meaningful insights and actions.
- 🏗️ Smart cities and large-scale IoT projects hold significant potential for efficiency and cost savings but also present complex implementation challenges.
- 🛠️ ARM's mbed OS is a free operating system designed to facilitate the development of IoT devices, supporting various communication protocols and low power operations.
- 🔄 IoT's structure typically involves sensors transmitting data to a gateway device, which then sends it to the cloud for further processing and control.
- 🌟 The future of IoT is expected to bring seamless experiences and significant innovation, with potential for both consumer and large-scale industrial applications.
Q & A
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
-The Internet of Things refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity that enables these objects to collect and exchange data.
What are the three major actors that make up the internet as traditionally understood?
-The three major actors traditionally making up the internet are people, client devices they use, and servers.
What is a 'thing' in the context of the Internet of Things?
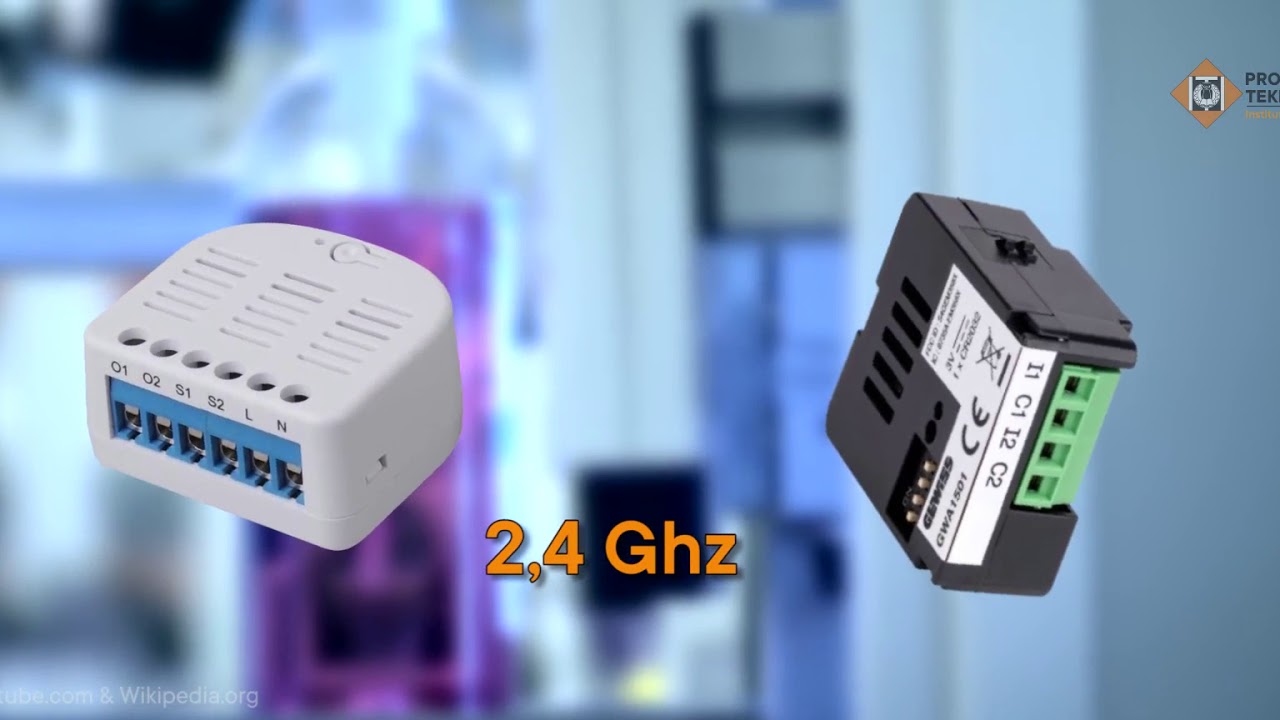
-In the context of IoT, a 'thing' is any object that has a sensor attached to it, capable of transmitting data from that sensor into the internet or the cloud for analysis and decision-making.
What are some examples of sensors used in IoT devices?
-Examples of sensors in IoT devices include temperature sensors, traffic sensors, flow rate sensors, and energy usage monitors.
How does the data from IoT devices typically flow?
-Data from IoT devices typically flows from the sensors to more complex devices or IoT gateways, then to the cloud, where it can be analyzed and used for decision-making.
What are the challenges faced by the IoT ecosystem?
-Challenges faced by IoT include technological issues like hardware and software limitations, big data concerns, security and privacy issues, and the need for seamless consumer experiences.
What did Samsung's co-CEO announce regarding IoT at CES 2015?
-Samsung's co-CEO announced that all Samsung products would be Internet of Things enabled within 5 years, with 90% of their products expected to connect to the web by 2017.
What is mbed OS and why is it significant for IoT devices?
-mbed OS is a free operating system designed for ARM's Cortex M range of microcontrollers, supporting various IoT protocols. It's significant for IoT devices because it's designed to be low power, event-driven, and suitable for devices with limited resources.
What is an IoT Gateway and why is it important?
-An IoT Gateway is a dedicated device that acts as a bridge between IoT devices and the internet, often handling data transmission and processing before sending it to the cloud. It's important because many sensors do not have direct internet connections and rely on the gateway for connectivity.
What are the security concerns associated with the growth of IoT devices?
-Security concerns with IoT devices include the potential for hacking and unauthorized access, as demonstrated by incidents involving webcams and baby monitors being compromised.
What is M2M communication in the context of IoT?
-M2M communication in IoT refers to the interaction between connected devices and the cloud, including how these devices are managed and the protocols used for data transmission and device management.
How does IoT potentially impact larger scale projects like smart cities?
-IoT can transform larger scale projects by enabling smart buildings, smart cities, and IoT-enabled businesses, leading to improved efficiency, cost savings, and innovative solutions for various infrastructure and business processes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)