Medical Terminology | 1 | Medical term parts
Summary
TLDRThis lesson delves into the origins and structure of medical terminology, highlighting its roots in Greek and Latin languages. It explains the three main components of medical terms: prefixes, roots, and suffixes, which together convey the meaning of medical words. The lesson clarifies that not all terms contain all three elements and introduces combining vowels that link roots and suffixes. Examples are provided to illustrate how these components work together, such as 'Gastroduodenostomy' for a connection between the stomach and small intestine. The lesson also touches on unique terms like 'Virus' and eponyms like 'Alzheimer's disease,' setting the stage for further exploration of medical language.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Medical terms originate from early Greek and Latin languages, reflecting the ancient civilizations' contributions to the field of medicine.
- 🔤 Medical terms are constructed using three main word elements: prefixes, roots, and suffixes, although not all terms contain all three.
- 🌱 Roots provide the core meaning of a medical term, often identifying a body part or action, and can be modified by adding prefixes or suffixes.
- 🔗 Combining vowels like 'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', or 'u' are used to join roots or combining forms to other elements in a medical term.
- 🔎 Multiple roots can share the same meaning, such as 'Pneumon' and 'Pulmon', both relating to the lung or air.
- 📚 Examples like 'Hemopneumothorax' illustrate how multiple roots and a suffix combine to describe a medical condition involving blood and air in the pleural cavity.
- 🔖 Suffixes modify the meaning of a root or combining form and can be categorized by their purpose, such as diagnostic, surgical, pathologic, or adjectival.
- 🏷️ Adjectival suffixes, of which there are 28, are used to describe a root and include examples like '-ac' in 'Cardiac', meaning 'pertaining to the heart'.
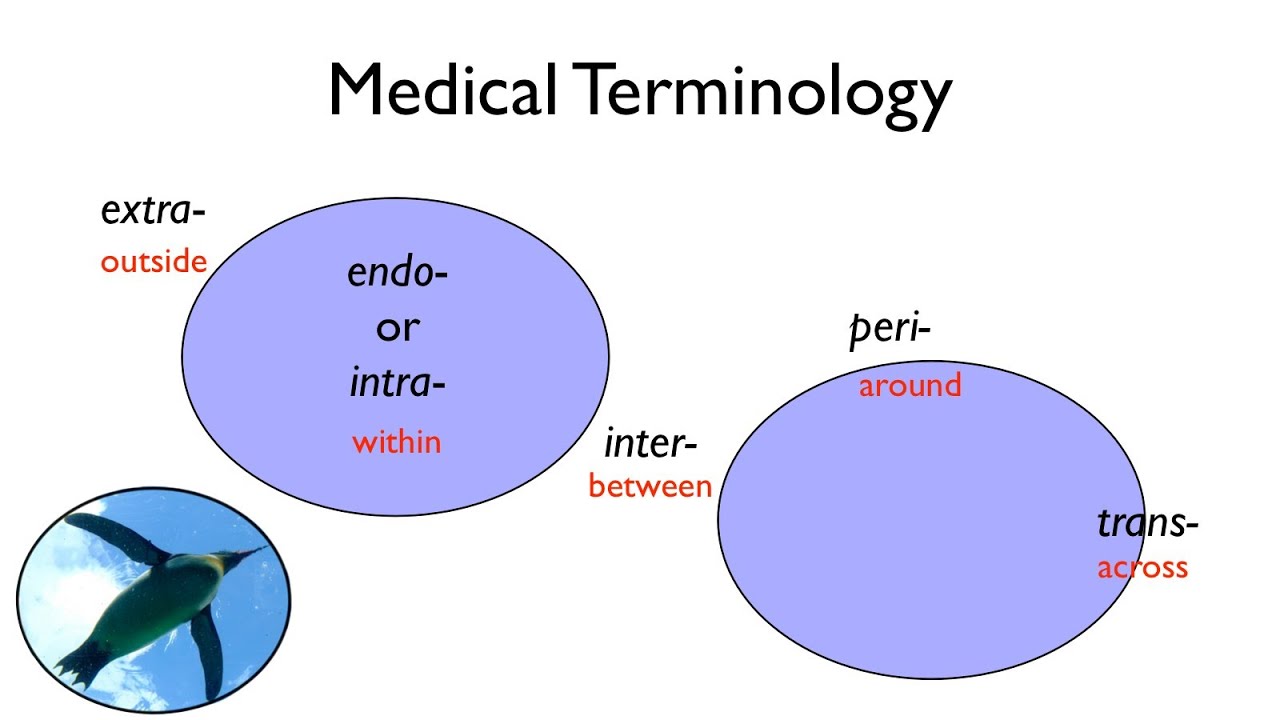
- 📌 Prefixes, such as 'epi-' for 'above' or 'bi-' for 'two', are added to the beginning of a root to indicate number, time, position, direction, or negation.
- 📝 Some medical terms, like 'Virus' and 'toxin', are 'solid' and cannot be broken down into elements; they must be memorized for their specific meanings.
- 👤 Eponyms in medical terminology are terms derived from a person's name, often to honor the discoverer or someone associated with a disease or medical concept, like 'Alzheimer's disease'.
Q & A
What are the origins of medical terms?
-Medical terms generally derive from early Greek and Latin languages, as both the Romans and Greeks advanced the study and practice of medicine in ancient times.
Why are medical terms considered efficient?
-Medical terms are efficient because they can reduce an entire phrase to a single word, such as 'Gastroduodenostomy' which represents a communication between the stomach and the first part of the small intestine.
What are the three word elements that make up medical terms?
-Medical terms are made up of prefixes, roots, and suffixes. However, not all terms have all three parts.
What is the function of a root in medical terms?
-The root provides the core meaning of the word and usually identifies a body part or an action.
Can you provide an example of a term with more than one root?
-Yes, the term 'Hemopneumothorax' has the roots 'Hem' meaning blood and 'Pneum' meaning air or lung, along with the suffix '-thorax' meaning chest.
What is a combining vowel and why is it used?
-A combining vowel is a vowel (a, e, i, o, or u) used to join a root or a combining form to another root or to a suffix, facilitating the formation of complex medical terms.
How do suffixes modify medical terms?
-Suffixes are added to the end of a medical root or a combining form to modify its meaning and to change its part of speech.
Give an example of a diagnostic suffix.
-The combining form 'Cardio' with the suffix '-graph' produces a medical term that is a diagnosis or a procedure to identify the nature of an illness, meaning an instrument used to record heart activity.
What is the purpose of prefixes in medical terms?
-Prefixes are attached to the beginning of a root and indicate a number, time, position, direction, or negation, changing the meaning of the word.
What is an eponym in medical terminology?
-An eponym is a word created from the name of a person, often used to name a disease, a test, or another facet of medicine after the person who discovered it, suffered from it, or contributed to it in some way.
Are there medical terms that cannot be broken down into elements?
-Yes, some medical terms like 'Virus' and 'toxin' are solid and cannot be broken down into elements. They must be recognized and their meanings memorized.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)