Lecture 16: Induced Voltage in a Coil in a Rotating Machine
Summary
TLDRThe script discusses the generation of EMF in an electrical machine, specifically focusing on the Electromechanical II's 16th unit. It explores the concept through examples and diagrams, explaining how the direction of the magnetic field and the movement of conductors within contribute to the production of EMF. The lecture also delves into the impact of varying the number of turns and the speed of rotation on the generated EMF, using the right-hand rule to demonstrate the relationship between magnetic field orientation and induced current. The summary also touches on the practical aspects of using multiple coils to increase the efficiency of EMF generation and the importance of understanding the principles behind AC and DC electrical systems.
Takeaways
- 🔧 The lecture discusses the generation of EMF in a DC machine, specifically the 16th unit of 'Electrical Machines II'.
- 📚 The instructor uses diagrams to explain the concepts, starting with the direction of the magnetic field and how it affects the machine.
- 🧲 The magnetic field is depicted as pointing upwards, and a conductor is shown moving through it, illustrating the principles of electromagnetic induction.
- 🏗️ The concept of flux linkage is introduced, explaining how it is provided when the machine starts and how it relates to the induced electromotive force (EMF).
- 🔋 The absence of voltage results in a back EMF of 0, which is a critical point in understanding the machine's operation.
- 📉 The instructor demonstrates the relationship between the movement of the conductor and the induced EMF, using mathematical representations.
- 🔌 The lecture introduces the idea of a transformer and how it can be used to step up or step down voltage, explaining the principle of mutual induction.
- 🔄 The concept of rotating machines is touched upon, where the machine's operation is likened to a rotating mechanical system.
- ⚙️ The lecture explains the importance of understanding the number of conductors and how they are arranged, which affects the distribution of the magnetic field (B).
- 🌀 The instructor discusses the concept of alternating current (AC) machines, emphasizing that they are never designed with a single conductor due to the sinusoidal distribution of the magnetic field.
Q & A
What is the primary topic discussed in the script?
-The primary topic discussed in the script is the generation of EMF (Electromotive Force) in electrical machines, specifically focusing on the principles and calculations related to it.
What is the significance of the direction of the magnetic field as mentioned in the script?
-The direction of the magnetic field is significant because it determines the direction of the induced EMF and the resulting current in the electrical machine.
How does the script describe the movement of the conductor in relation to EMF generation?
-The script describes that when a conductor moves through a magnetic field, it cuts through the magnetic flux lines, which induces an EMF according to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
What is the role of the number of turns (n) in the EMF generation process as discussed in the script?
-The number of turns (n) in the coil is crucial as it affects the total EMF generated. The script explains that the total EMF is proportional to the number of turns, with the formula EMF = n * (change in magnetic flux)/(time).
What is the concept of 'flux linkage' mentioned in the script, and how is it related to EMF?
-Flux linkage refers to the product of the number of turns in a coil and the magnetic flux through the coil. It is directly related to EMF as the change in flux linkage over time determines the induced EMF in the coil.
How does the script explain the effect of the number of conductors on the EMF?
-The script explains that increasing the number of conductors in a given space can increase the total EMF generated, which is beneficial for ensuring a smoother distribution of magnetic flux and reducing the chances of magnetic saturation.
What is the significance of the term 'synchronous speed' mentioned in the script?
-The term 'synchronous speed' refers to the rotational speed at which the rotor of an electrical machine must rotate to maintain synchrony with the rotating magnetic field. It is crucial for the proper operation of the machine and is calculated based on the number of poles and the frequency of the supply.
How does the script describe the concept of 'back EMF' in electrical machines?
-Back EMF, or counter EMF, is described as the voltage generated in the opposite direction to the applied voltage in an electrical machine. It is a result of the machine's inherent inductance and is an important factor in determining the machine's performance and efficiency.
What is the purpose of having multiple coils in an electrical machine as discussed in the script?
-The purpose of having multiple coils in an electrical machine is to distribute the magnetic flux more evenly and to increase the total EMF generated. This also helps in reducing the complexity of the machine's design and improving its overall efficiency.
How does the script differentiate between DC and AC machines in terms of EMF generation?
-The script differentiates between DC and AC machines by explaining that in DC machines, the EMF generated is unidirectional, while in AC machines, the EMF varies sinusoidally with time. The script also mentions that the principles of electromagnetic induction apply to both types of machines.
What is the role of the mechanical rotation in the context of EMF generation as explained in the script?
-The mechanical rotation of the rotor within the stator's magnetic field is essential for generating EMF in an electrical machine. The rotation ensures that the magnetic flux through the coils changes, which in turn induces an alternating EMF in the case of AC machines.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

ഇലക്ട്രിക് സ്കൂട്ടർ മോട്ടോറിന്റെ വർക്കിംഗ് | EV | Electric Scooter Motor Explained | Ajith Buddy
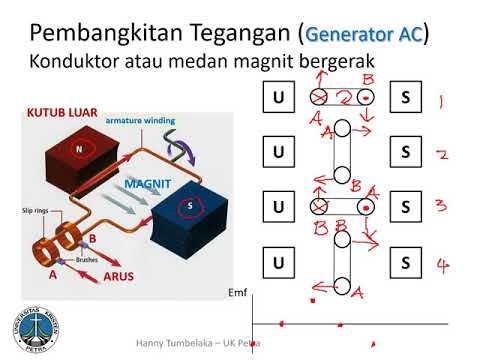
Prinsip Kerja Generator AC

OS COMPUTADORES HERÓIS da Segunda Guerra Mundial #SagaDosComputadores Ep. 3

How Relays Work - Basic working principle electronics engineering electrician amp

GGL INDUKSI PADA SUATU KUMPARAN

Electromotive Force
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)