How does a Thermal power plant work?
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the inner workings of a coal-based thermal power plant, detailing how it generates electricity using the Rankine cycle. It covers the process of turning high-pressure steam into mechanical energy via a steam turbine, and the techniques used to enhance efficiency, such as superheating, reheating, and feedwater heating. The script also discusses the environmental controls in place, including the use of electrostatic precipitators to reduce pollutant emissions. With modern advancements, these plants operate at an efficiency of 40-45%, providing a sustainable and efficient solution for meeting global energy demands.
Takeaways
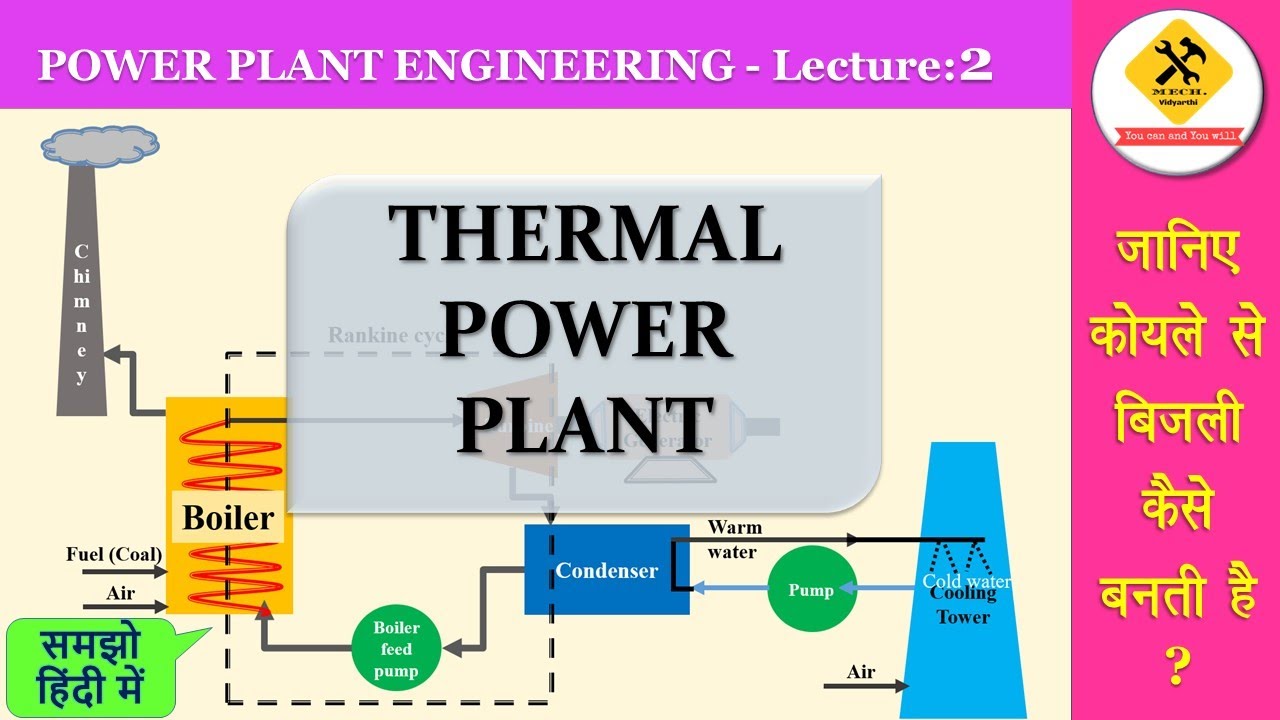
- 😀 Thermal power plants generate nearly half of the world's electricity, using water as the working fluid.
- 😀 The steam turbine is the heart of the power plant, where high-pressure steam is converted into mechanical energy to generate electricity.
- 😀 The Rankine cycle is the basic process in thermal power plants, where steam is condensed, pressurized, heated, and expanded to produce power.
- 😀 To achieve high efficiency, a low-pressure steam is condensed and turned back into liquid before being pressurized and reheated.
- 😀 A compressor is not used for steam, as compressing steam requires too much energy; instead, steam is condensed into liquid and pressurized.
- 😀 Boilers in thermal plants, especially water-tube boilers, burn pulverized coal to heat water and convert it into steam.
- 😀 Superheating steam after it is produced increases efficiency by raising its temperature beyond its boiling point.
- 😀 Reheating steam after the first turbine stage increases steam temperature, improving power output and overall efficiency.
- 😀 Feedwater heaters are used to remove dissolved gases from the feedwater and preheat it, improving plant efficiency.
- 😀 Modern thermal power plants operate with an efficiency range of 40-45% due to techniques like superheating, reheating, and feedwater heating.
- 😀 Cooling towers are used to cool the water after it absorbs heat in the condenser, ensuring a continuous supply of cold water.
- 😀 Electrostatic Precipitators (ESP) clean exhaust gases from burning coal by trapping pollutants using high-voltage static electricity.
Q & A
What role do thermal power plants play in the global energy supply?
-Thermal power plants provide nearly half of the world's power demand by converting heat energy into electricity.
How do thermal power plants achieve green efficiency?
-Modern thermal power plants meet stringent environmental standards, ensuring that they operate efficiently while minimizing their environmental impact.
What is the main function of the steam turbine in a thermal power plant?
-The steam turbine is the heart of the power plant, converting high-energy steam into mechanical energy that drives the generator to produce electricity.
How does steam lose energy in the turbine?
-As the steam passes through the turbine, it loses energy in the form of pressure and temperature, which decreases toward the turbine's outlet.
Why are multiple stages of steam turbines used in high-capacity power plants?
-High-capacity plants use multiple stages of steam turbines (high pressure, intermediate pressure, and low pressure) to efficiently extract energy from the steam at different pressure levels.
How is the low-pressure steam recycled back into the system?
-The low-pressure steam is condensed into water in the condenser, and then the water is pumped back into the system to increase its pressure and temperature for reuse.
What is the purpose of the condenser in the thermal power plant?
-The condenser cools the steam by transferring heat to a cold water stream, causing the steam to condense back into liquid water, which is then pumped to increase its pressure.
How is the temperature of the steam raised again after condensation?
-After condensation, the temperature of the water is raised by adding heat in a boiler, which uses the burning of pulverized coal to turn water into high-pressure, high-temperature steam.
What is the significance of superheating in thermal power plants?
-Superheating involves adding extra heat to the steam, increasing its temperature, which improves the efficiency of the Rankine cycle and thus the overall power plant performance.
How does reheating contribute to the efficiency of a thermal power plant?
-Reheating adds heat to the steam after the first turbine stage, restoring its temperature and improving the power output and efficiency of the cycle.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)