The Colors Of Skin - What Is Skin Color Determined By - Ways The Skin Changes Colors
Summary
TLDRSkin color diversity stems from melanin, a pigment produced by melanocytes in the epidermis. Two types, eumelanin and pheomelanin, determine shades, with darker skin having more eumelanin. Factors like heredity, UV exposure leading to tanning, and conditions like albinism affect melanin production. Other influences include blood flow, freckles, dietary beta-carotene, and bruises, which can alter skin's appearance. Tattoos, made by injecting ink into the dermis, also change skin color, illustrating the complex interplay of biology and environment in skin coloration.
Takeaways
- 🌈 Skin color varies widely among individuals due to differences in melanin production.
- 🎨 Melanin, produced by melanocytes in the epidermis, determines skin color and protects DNA from UV damage.
- 🔍 There are two types of melanin: eumelanin, which leads to darker skin, and pheomelanin, which leads to lighter skin.
- 👶 The number of melanocytes is consistent across all humans, but genetic factors determine the type and amount of melanin they produce.
- 🦄 Albinism is a condition where melanocytes do not produce melanin, resulting in a lack of pigmentation in skin, hair, and eyes.
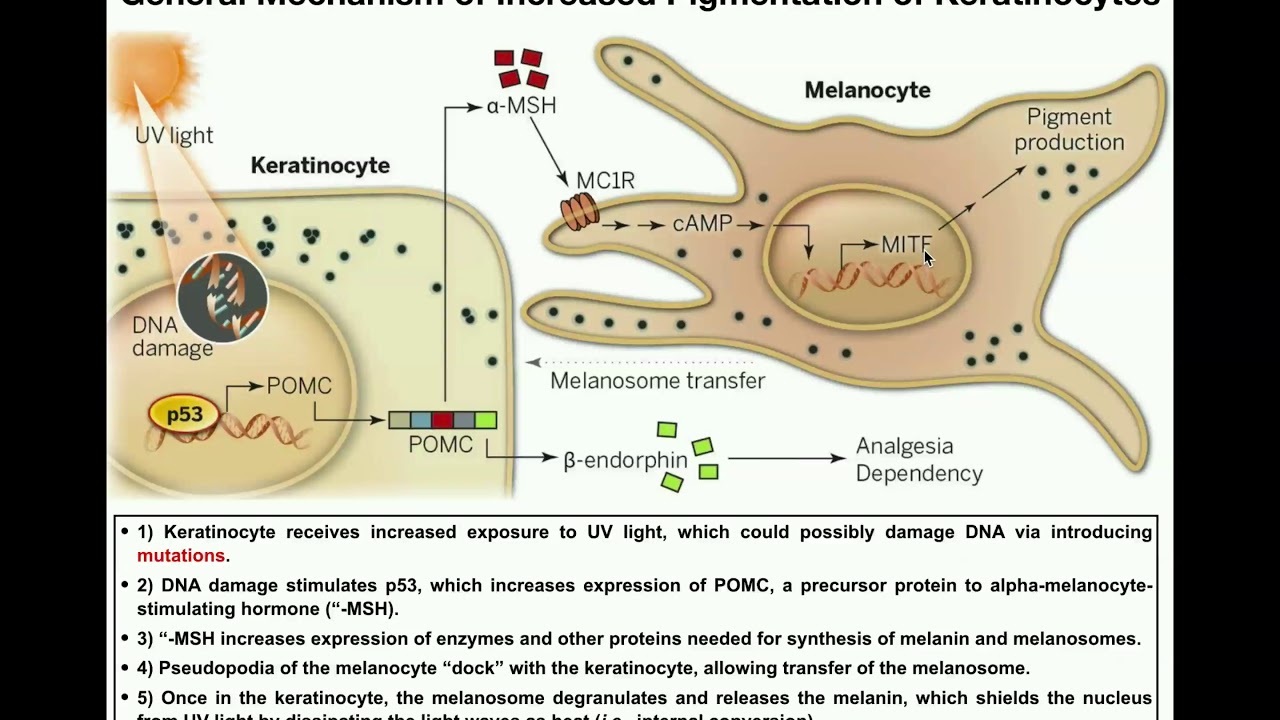
- 🌞 Sun exposure stimulates melanocytes to produce more melanin, causing the skin to tan as a protective response.
- 🍠 Beta-carotene, found in foods like carrots and sweet potatoes, can influence skin color when consumed in high amounts, causing a yellow-orange hue.
- 🏼 Freckles are areas of increased melanocyte activity and their appearance is influenced by genetics and sun exposure.
- 💧 Bruises change skin color due to blood leakage into the skin tissues, with the color evolving as the body heals.
- 🖊️ Tattoos alter skin color by depositing ink into the dermis layer, which remains stable over time with minimal fading.
Q & A
What determines the color of a person's skin?
-The color of a person's skin is determined by the amount and type of melanin released by melanocytes cells in the epidermis of the skin.
What is melanin and what is its role in skin coloration?
-Melanin is a pigment produced by melanocytes cells that gets transferred to keratinocyte cells to protect DNA from mutating due to ultraviolet radiation. It plays a crucial role in skin coloration.
How does the number of melanocytes cells vary among humans?
-The number of melanocytes cells is about the same in all humans, but the amount and type of melanin they produce vary, leading to different skin colors.
What are the two main types of melanin, and how do they affect skin color?
-The two main types of melanin are eumelanin and pheomelanin. Darker-skinned individuals produce more eumelanin, while lighter-skinned individuals produce more pheomelanin.
What is the role of heredity in the production of melanin?
-Heredity is the key factor in determining the type of melanin produced by melanocytes cells.
What is albinism and how does it affect skin color?
-Albinism is a condition where melanocytes cells cannot produce melanin, resulting in the absence of pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes.
How does exposure to sunlight affect skin color?
-Sunlight triggers melanocytes to produce more melanin, leading to a darkening of the skin or tanning as a method to protect DNA in the nucleus of cells.
What causes dark age spots on the skin and how are they related to UV radiation?
-Consistent overexposure to UV radiation can influence the overproduction of melanin, causing dark age spots on the skin.
Why does the skin sometimes appear reddish or pinkish, and what causes this?
-The skin can appear reddish or pinkish due to vasodilation of blood vessels in the dermis, allowing more blood to flow through them and making the red tones of hemoglobin and red blood cells more visible.
What are freckles and how do they form?
-Freckles are yellowish-brown spots that occur on certain areas of the body as a result of increased melanocyte cell activity. Their pigmentation depends on heredity and exposure to the sun.
How can the consumption of certain foods affect skin color?
-High consumption of beta-carotene foods, such as carrots, corn, and sweet potatoes, can cause a yellow-orange coloration of the skin as the body converts beta-carotene to vitamin A.
How do bruises alter skin color and what is the healing process like?
-Bruises alter skin color by causing blood to leak into tissues beneath the skin, initially appearing reddish due to hemoglobin. As the body heals, the bruise may change to bluish-purple and then yellowish before returning to normal skin color.
How do tattoos change the color of the skin and what happens to the ink?
-Tattoos change the color of the skin by depositing ink into the dermis layer. The ink stays in place with slight fading or spreading over time, but the body's immune response can also remove some of the ink and transport it to lymph nodes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

The science of skin color - Angela Koine Flynn

The Integumentary System, Part 1 - Skin Deep: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #6
How do Melanocytes Make Melanin?: Melanogenesis Mechanism

How Your Skin Works

Pewarisan Sifat pada Makhluk Hidup dan Kelainan Sifat yang Diturunkan | IPA Kelas 9 | Materi BAB 3

Melasma - चेहरे पर काले धब्बे | Medicine | Treatment | Doctor | Pharmacy | Nursing | MBBS | BHMS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)