WHAT IS SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT ? 5 MINUTES EXPLANATION !!
Summary
TLDRThis video offers a concise introduction to supply chain management, explaining its key components and flows. It uses the example of a milk supply chain to illustrate the journey from raw materials to end customers. The video identifies five main participants: suppliers, producers, distributors, retailers, and customers. It outlines three major flows: product, information, and financial. Lastly, it defines supply chain management as overseeing the entire manufacturing and delivery process, touching on processes like manufacturing, warehousing, strategic planning, demand forecasting, and transportation.
Takeaways
- 🌐 A supply chain is a global network that coordinates the production and distribution of goods and services from raw materials to end customers.
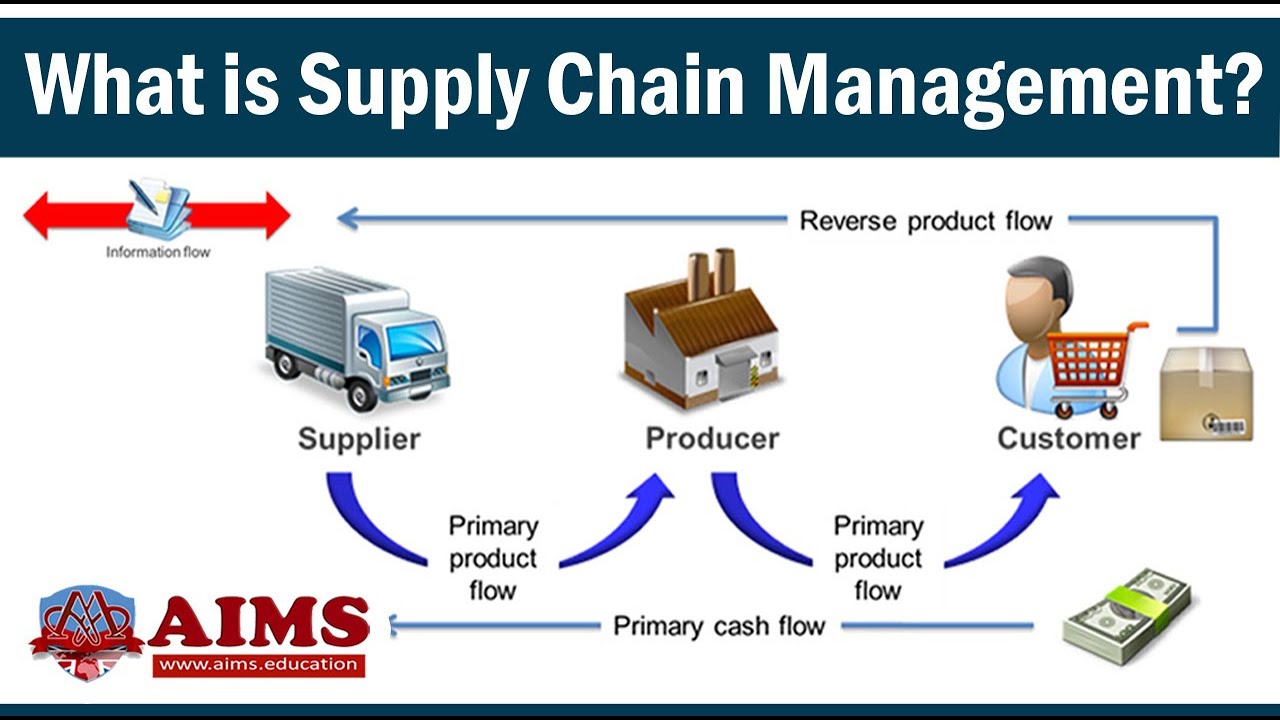
- 🚚 The supply chain involves three key flows: product flow, information flow, and financial flow, which are essential for its operation.
- 🛒 Key participants in a supply chain include suppliers, producers, distributors, retailers, and customers, each playing a specific role in the process.
- 🏭 Producers, also known as manufacturers or service providers, transform raw materials into finished goods or services.
- 📦 Distributors purchase products in bulk from producers and sell them to customers in larger quantities than individual consumers would buy.
- 🏬 Retailers sell products in smaller quantities directly to end customers, fulfilling their immediate needs.
- 💼 Supply chain management encompasses the entire process of manufacturing a product or service, from raw materials to delivery to the customer.
- 🔍 Strategic planning, demand forecasting, and supply planning are crucial processes within supply chain management for efficient operations.
- 📈 Information flow is bi-directional and includes data such as product specifications, inventory levels, and order details, acting as the 'fuel' for the supply chain.
- 💵 Financial flow involves the movement of funds from the end customer back through the supply chain, with the final consumer being the primary source of revenue.
- 📝 Supply chain management also involves processes like order fulfillment, procurement, and transportation planning to ensure product distribution and delivery.
Q & A
What is the definition of a supply chain?
-A supply chain is a global network that produces and distributes goods and services from raw materials to end customers via information flows, product flows, and financial flows. It is a multi-level system that generally crosses the boundaries of several companies to coordinate the related flows.
Can you provide a simple example of a supply chain?
-A simple example of a supply chain is the milk supply chain, where milk goes from dairy farms to storage in a warehouse, then to processing in a manufacturing facility, followed by storage in distribution centers, and finally transported to retailers like supermarkets for customers to purchase.
What are the five key participants in every supply chain?
-The five key participants in every supply chain are suppliers, producers, distributors, retailers, and customers. Suppliers provide raw materials or services, producers manufacture goods or services, distributors deliver products in bulk to customers, retailers sell products in smaller quantities to individual customers, and customers are the end-users of the products or services.
What is the role of a supplier in the supply chain?
-A supplier is a person or a company that sells a product or service to another entity, providing raw materials, components for assembly, energy, and so on. They are the starting point in the supply chain, ensuring that the necessary materials are available for production.
What does the term 'producer' refer to in the context of supply chains?
-In the context of supply chains, a producer, also known as a manufacturer or service provider, is a business that manufactures goods or services. They process raw materials and produce finished goods, which may also include assembling products using components called sub-assemblies provided by suppliers.
What is the function of distributors in the supply chain?
-Distributors, also known as wholesalers, buy inventory in bulk from producers and deliver it to customers in a bundle of related product lines. They typically sell to other businesses and in larger quantities than individual consumers would purchase.
How do retailers contribute to the supply chain?
-Retailers keep goods on hand and sell in smaller quantities to customers. They offer products and services to fulfill the needs of individual customers who purchase in small quantities, acting as the final point of sale before the product reaches the end consumer.
What are the three major supply chain flows?
-The three major supply chain flows are product flow, information flow, and financial flow. Product flow is the movement of goods from the supplier to the customer. Information flow involves data such as bills of materials, product data, inventory data, and order details. Financial flow refers to the movement of funds from the end customer back through the supply chain.
What is supply chain management and what processes does it involve?
-Supply chain management refers to the management of a product or service's entire manufacturing flow from raw materials to the delivery of the finished product to the customer. It involves processes such as manufacturing, warehousing, strategic planning, demand planning, supply planning, order fulfillment, procurement, and transportation planning.
Why is information flow considered crucial in supply chain management?
-Information flow is considered crucial in supply chain management because it involves data such as product specifications, inventory data, and order details, which are essential for coordinating the supply chain activities. It is bi-directional and acts as the 'fuel' that drives the supply chain, ensuring that all participants have the necessary information to make informed decisions.
How does financial flow work within the supply chain?
-Financial flow in the supply chain involves the movement of funds from the end customer, who is usually the only source of real money in the network, back down the chain. This flow of funds or revenues passes through the supply chain's various links, from the final consumer to the suppliers, ensuring that all parties are compensated for their contributions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

#1.1 Konsep Dasar Manjemen Rantai Pasok (Pengantar SCM)

SCM - Process & Process Flow (New Version)
What is Supply Chain Management? Definition, Introduction, Process & Examples - AIMS UK

(PART 1) : Aktifitas Manajemen Logistik

Microprocessors|General architecture of a Computer|Bca/Bsc.cs ,electronics,instrumentation, printing

Supply Chain Management (SCM) Explained in 18 min
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)