ESTERILIZACIÓN Y DESINFECCIÓN- MICROBIOLOGIA
Summary
TLDRThe transcript covers various methods of sterilization, including both physical and chemical techniques. It explains how sterilization aims to eliminate all microorganisms, using methods such as heat (both direct and indirect), autoclaving, and filtration. The transcript also discusses the use of radiations and chemical sterilization methods like disinfectants and antiseptics. Special emphasis is placed on the efficiency of autoclaves and heat sterilization for specific materials, as well as the limitations of certain methods in eliminating bacterial spores. It concludes with a focus on the diverse applications of these methods, particularly in medical and laboratory settings.
Takeaways
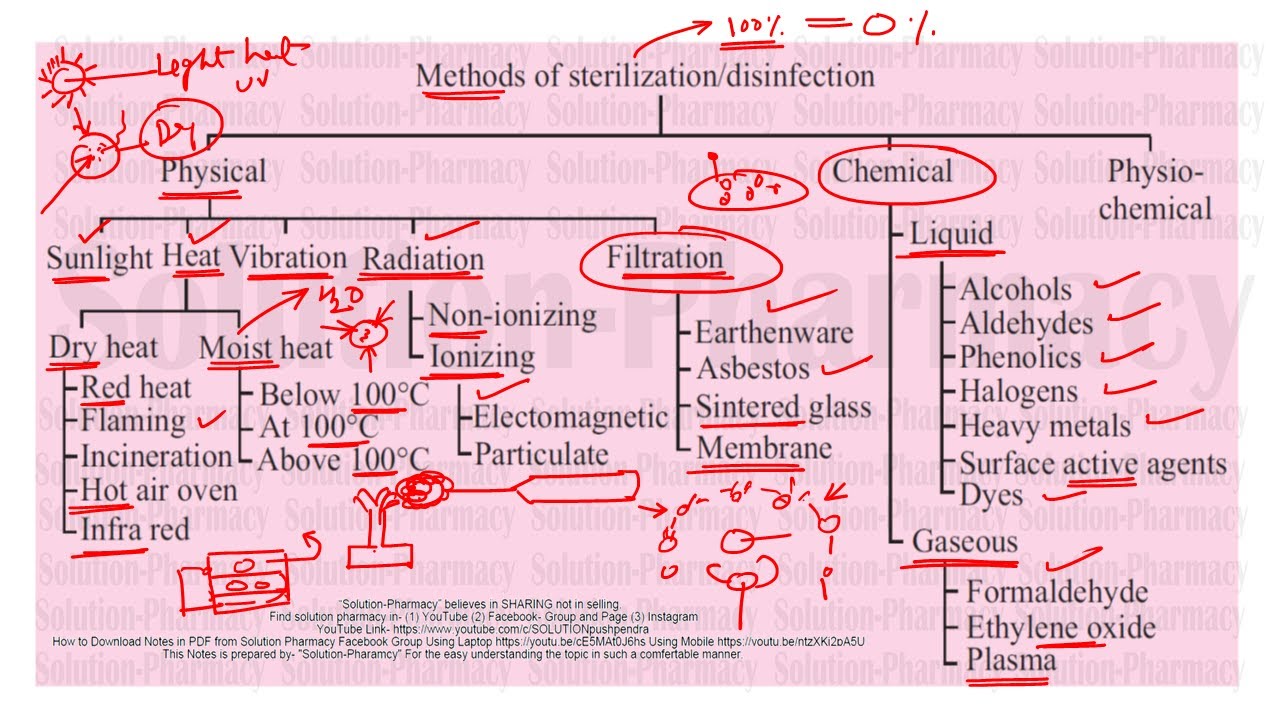
- 😀 Sterility refers to the total absence of microorganisms, and sterilization aims to completely destroy them.
- 😀 Physical sterilization methods include heat, which can be applied directly or indirectly to materials.
- 😀 Direct heat sterilization involves flaming with a bronze burner, often used on the mouth of tubes.
- 😀 Indirect heat sterilization uses dry heat, and moist heat sterilization combines temperature with high humidity to effectively destroy microorganisms.
- 😀 Autoclaving is one of the most effective methods of sterilization, utilizing steam and pressure.
- 😀 Some materials, such as those used in cell cultures, cannot withstand high temperatures during sterilization.
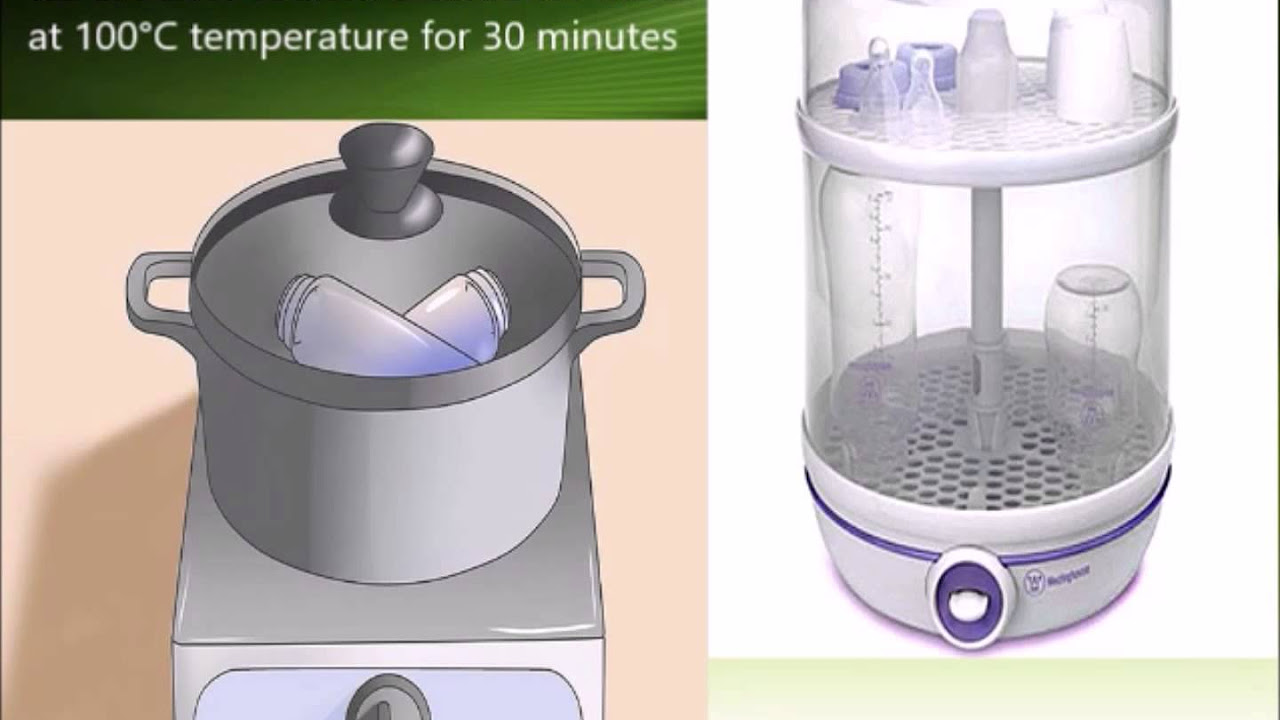
- 😀 Boiling water at 100°C can destroy vegetative forms of bacteria and viruses, used for sterilizing items like jars and syringes.
- 😀 Pasteurization, invented by Louis Pasteur, is a technique to eliminate pathogens in food without significantly altering its organoleptic properties.
- 😀 Filtration sterilization passes liquids through porous substances to trap particles, but it is not effective for sterilizing viruses.
- 😀 Ionizing radiation is used for sterilization by rearranging molecules and damaging cells, while non-ionizing radiation acts on DNA to prevent replication.
- 😀 Chemical sterilization methods include disinfectants, which destroy microorganisms on surfaces but do not eliminate spores, and antiseptics, which prevent microorganism growth on living tissues.
Q & A
What is sterility, and how does it relate to sterilization?
-Sterility refers to the complete absence of microorganisms, and sterilization is the process designed to destroy all microorganisms present on the surface or inside a material.
What are the two main categories of sterilization methods?
-Sterilization methods can be categorized into physical and chemical methods. Physical methods include heat, filtration, and radiation, while chemical methods involve the use of disinfectants, antiseptics, and sterilizing gases.
How does direct heat sterilization work, and where is it applied?
-Direct heat sterilization involves using an open flame, like a Bunsen burner, to sterilize materials, such as the opening of test tubes. This method applies intense heat to destroy microorganisms.
What is the difference between dry heat and moist heat sterilization?
-Dry heat sterilization uses high temperatures without moisture, while moist heat sterilization involves high temperature combined with moisture, which is more effective at killing microorganisms by coagulating their proteins.
Why is autoclaving considered one of the most effective sterilization methods?
-Autoclaving uses steam under high pressure to sterilize materials, making it one of the most effective methods due to its ability to destroy microorganisms quickly and thoroughly.
What is the limitation of boiling water in sterilization?
-Boiling water only reaches 100°C, which is effective for killing vegetative forms of bacteria and viruses but does not eliminate spores, making it less effective than other methods like autoclaving.
How does pasteurization work, and what is its primary purpose?
-Pasteurization is a process that heats liquids, like milk, to a specific temperature to kill harmful microorganisms without significantly altering the taste or nutritional value of the product.
What role does filtration play in sterilization, and what is its limitation?
-Filtration involves passing a liquid through a porous material to trap microorganisms. While effective for larger particles, it cannot filter out viruses or the smallest microorganisms, limiting its effectiveness.
How does ionizing radiation contribute to sterilization?
-Ionizing radiation uses high-energy particles to ionize water molecules inside cells, creating compounds that damage the cells and kill microorganisms. This method is effective but costly.
What is the difference between disinfectants and antiseptics?
-Disinfectants are chemicals that destroy microorganisms on non-living surfaces, while antiseptics are used to prevent the growth of microorganisms on living tissues, such as skin.
What is a sterilizing gas, and how is it used?
-A sterilizing gas, like ethylene oxide, is used in a special chamber to sterilize sensitive equipment, such as electronic devices or medical instruments, without damaging them.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)