Motherboard Default settings could be COOKING your CPU!
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host addresses a persistent issue with motherboards and CPUs, particularly Intel processors, where default settings can lead to excessive temperatures and potential damage. The discussion focuses on 'optimized defaults' that often result in higher voltage and power limits, causing CPUs to run hotter than necessary. The host demonstrates how these settings can be adjusted to adhere to Intel's recommended limits, thereby reducing temperatures and maintaining performance. The video serves as a guide for users experiencing high CPU temperatures and aims to educate on the importance of checking BIOS settings to ensure optimal and safe operation of computer hardware.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses an ongoing issue with CPU and motherboard combinations that can lead to high temperatures and potential damage.
- 🛠️ NZXT's BL is promoted as a solution for building a gaming PC on a budget, offering pre-configured systems with Intel's 14th gen CPUs for improved gaming performance.
- ⚙️ The video highlights a problem with 'optimized defaults' on motherboards, which can lead to increased voltage and temperature limits, causing CPUs to run hotter than necessary.
- 📈 The issue is not exclusive to Intel CPUs but is more prevalent due to the widespread availability of unlocked and overclockable Intel processors.
- 🔧 The video emphasizes that ASUS is a significant offender, but other motherboard manufacturers also implement similar optimized defaults.
- 📊 The 'let BIOS optimize' feature often overrides Intel's default settings, leading to higher power limits and voltages that can cause excessive heat.
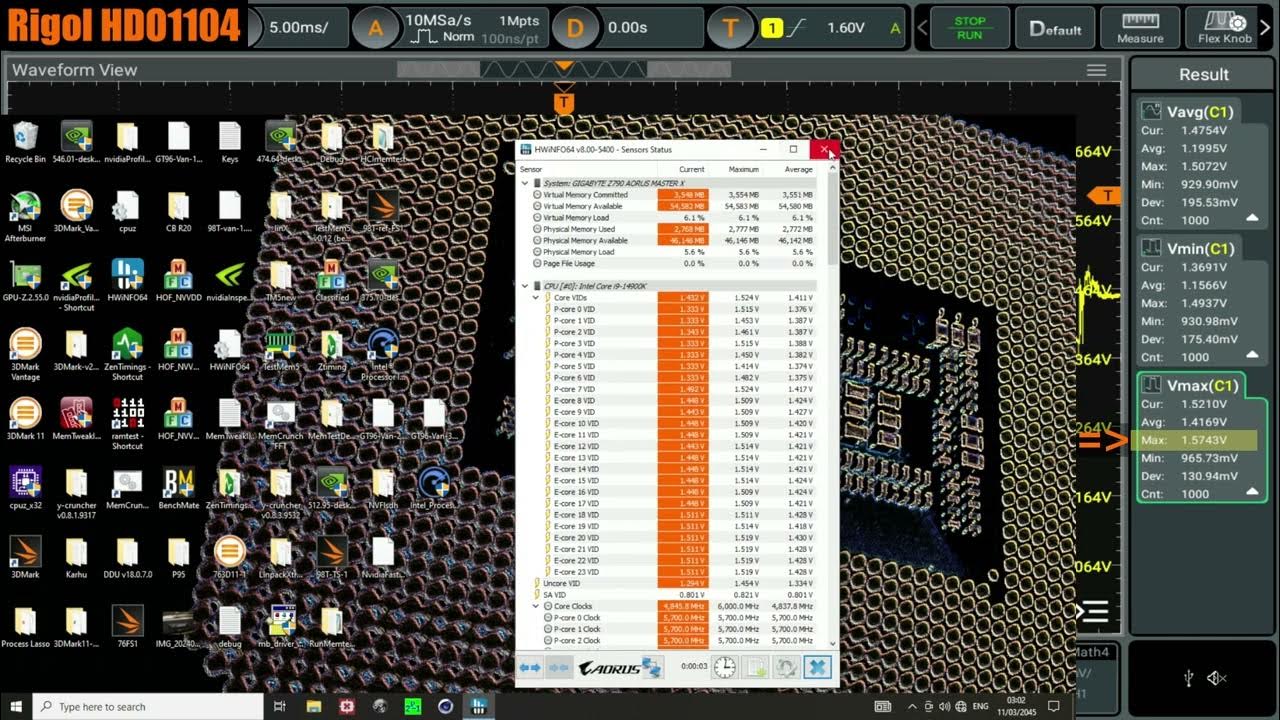
- 💻 The video provides a practical demonstration of how these settings can affect CPU performance and temperature, using Cinebench R23 and hardware monitor tools.
- ⚠️ The video urges viewers to check their motherboard settings, especially the Intel limits, to prevent unnecessary overheating and ensure they are getting the full performance of their CPU.
- 🔩 The script suggests that motherboard manufacturers should load Intel's limits by default to avoid misleading users about their CPU's performance and thermal capabilities.
- 📝 The video concludes with a call to action for viewers to share the information and educate others about the importance of checking motherboard settings to avoid thermal issues.
Q & A
What is the main issue discussed in the video script?
-The main issue discussed is the problem of motherboards applying optimized defaults that can lead to excessive CPU temperatures and power consumption, potentially causing damage or reducing the lifespan of the CPU.
Why does the script mention NZXT's BL and its configurator?
-The script mentions NZXT's BL and its configurator as an example of a tool that allows users to build a gaming PC on a budget, including the option to use Intel's 14th gen CPUs, which is relevant to the discussion of CPU performance and settings.
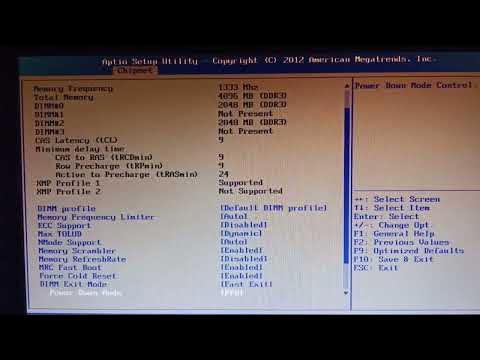
What is the significance of 'optimized defaults' in motherboards as discussed in the script?
-The 'optimized defaults' in motherboards refer to settings that automatically apply potential overclocks and changes to voltage and power limits based on the manufacturer's testing. This can lead to higher temperatures and power consumption, which is a concern raised in the script.
Why does the script focus on Intel CPUs for this issue?
-The script focuses on Intel CPUs because they are commonly overclocked and have unlocked multipliers, making them more susceptible to the effects of the 'optimized defaults' that can lead to higher temperatures and power usage.
What is the role of XMP in the context of the script?
-XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) is mentioned as a feature that some users might enable, but the script emphasizes that the issue of high temperatures and power consumption is often due to the motherboard's default settings, not necessarily because of XMP.
What does the script suggest users do if they experience high CPU temperatures?
-The script suggests that users experiencing high CPU temperatures should check their motherboard settings, specifically looking for and enabling 'Intel limits' to ensure the CPU operates within safe parameters.
Why does the script criticize motherboard manufacturers for their default settings?
-The script criticizes motherboard manufacturers for their default settings because they often enable higher power and voltage limits than necessary, which can lead to higher temperatures and potentially reduce the lifespan of the CPU.
What is the significance of the 'let BIOS optimize' setting as discussed in the script?
-The 'let BIOS optimize' setting is significant because it allows the motherboard to automatically adjust settings, often leading to higher power consumption and temperatures. The script argues that this should not be the default setting.
What is the role of Cinebench R23 in the script?
-Cinebench R23 is used in the script as a benchmarking tool to test the CPU's performance and temperature under different settings, helping to illustrate the impact of the motherboard's optimized defaults.
Why does the script mention the importance of ambient temperature in relation to CPU temperatures?
-The script mentions the importance of ambient temperature because it can affect the cooling efficiency of the system. A cooler room can help keep CPU temperatures lower, but the script emphasizes that high temperatures due to motherboard settings are a concern regardless of the room temperature.
What is the script's stance on the relationship between CPU manufacturers, motherboard manufacturers, and reviewers?
-The script suggests there is a point of contention between CPU manufacturers, motherboard manufacturers, and reviewers regarding the appropriate voltage and power limits for CPUs. It argues that motherboard manufacturers often provide more voltage than necessary, which can lead to stability issues and reduced performance.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Turning off "Intel Default Settings" with Microcode 0x129 DISABLES THE VID/VCORE LIMIT

Why We Can't Recommend Intel CPUs - Stability Story So Far

How to reduce temperatures in 12th gen processors!!??

Intel 13900K & 13600K Temperature Myths BUSTED
REVIEW MOBO VARRO PART 1 - BIOS

Das große CPU-Sterben - Was ist los bei Intel?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)