Sejarah Bangkit Dan Jatuhnya Kekaisaran Islam TERLUAS Di DUNIA | Kekhalifahan Umayyah | Historia #5
Summary
TLDRThe Umayyad Caliphate was the first Islamic empire to expand Islam's influence across vast territories, including the Middle East, North Africa, parts of India, and Europe. It marked a golden age for cultural, scientific, and architectural development, with significant advancements in maritime trade and the establishment of organized administrative systems. Despite initial success, internal conflicts and the eventual rise of the Abbasid dynasty led to its decline. The Umayyad legacy, however, continues to influence Islamic culture and architecture, leaving an indelible mark on history.
Takeaways
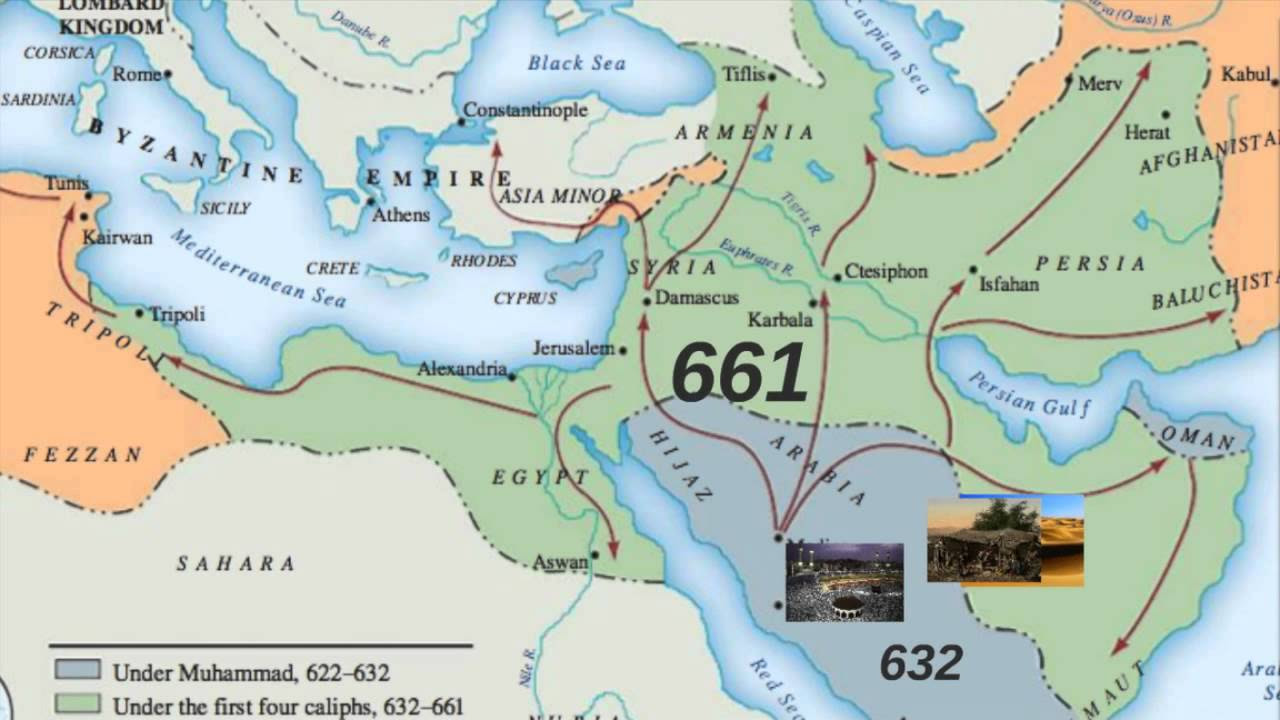
- 🌍 The Umayyad Caliphate was the first Islamic state to expand the Islamic dominion to various corners of the world, including significant parts of the Middle East, North Africa, Transoxiana, parts of the Indian subcontinent, islands around the Mediterranean, and even Spain (Al-Andalus).
- 🏛️ The Umayyad period was a golden age for cultural, artistic, architectural, and scientific development, with the establishment of new cities and grand mosques such as the Umayyad Mosque in Damascus.
- 🔄 The Umayyads promoted the translation of Greek works into Arabic, which laid the foundation for the great translations by the later Abbasid Caliphate and continued the chain of knowledge.
- 🛃 They introduced well-organized administrative systems, including tax and postal systems, which strengthened their rule and facilitated trade and communication.
- 🚢 The Umayyads were also known for their advancements in maritime affairs, strengthening their navy and expanding trade routes, which bolstered their position in international trade.
- ⚖️ The Umayyads effectively built a strong and assertive caliphal authority, adopting a strict approach to rebellion and often using force as a primary tool to suppress any form of opposition.
- 🏗️ The architectural style of the Umayyads influenced building designs worldwide, particularly in the Islamic world, with their style leaving a lasting legacy.
- 🕊️ Despite being centered on Islam, the Umayyad Dynasty was known for its relative tolerance towards other religions, allowing non-Muslims like Jews and Christians to practice their faith and contribute to society.
- 📚 The Umayyad Caliphate's rise, expansion, and eventual decline and replacement are marked by significant historical events, including the assassination of key figures and internal conflicts that led to its downfall.
- 📜 The Umayyads' legacy is still visible today, especially in architecture and art, and their contributions to the development of the Arabic language and monumental architecture have left an indelible mark on Islamic civilization.
Q & A
What was the extent of the Umayyad Caliphate's territory at its peak?
-At its peak, the Umayyad Caliphate's territory included most of the Middle East, North Africa, Transoxiana, parts of the Indian subcontinent, some islands around the Mediterranean, and even Spain (Al-Andalus).
How did the Umayyad Caliphate contribute to cultural and scientific development?
-The Umayyad Caliphate was a golden age for cultural development, art, architecture, and scientific knowledge. They established new cities, built grand mosques like the Umayyad Mosque in Damascus, and promoted the translation of Greek works into Arabic, which laid the foundation for the great translations by the Abbasids and continued the chain of knowledge.
What administrative systems did the Umayyads introduce?
-The Umayyads introduced well-organized administrative systems, including tax and postal systems, which helped maintain the stability and security of the Caliphate.
How did the Umayyad Caliphate advance in maritime affairs?
-The Umayyads strengthened their naval forces and expanded trade routes across the seas, which reinforced their position in international trade.
What was the Umayyad's approach to dealing with rebellions and maintaining authority?
-The Umayyads were known for their firm approach to rebellions, often using force as a primary instrument to suppress any form of opposition and showing no tolerance towards rebels.
How did the Umayyad Caliphate's influence persist in architecture and art?
-The Umayyad architectural style influenced building designs worldwide, especially in the Islamic world. Their cultural influence can still be seen today, particularly in architecture and art.
What was the significance of the transition from the Rashidun Caliphs to the Umayyad Caliphate?
-The transition from the Rashidun Caliphs to the Umayyad Caliphate marked the end of a period of leadership that was seen as just and righteous, and the beginning of a new era with the rise of the Umayyad dynasty, which effectively spread Islam across the world.
How did the Umayyad Caliphate expand its territories during the rule of Muawiyah?
-Muawiyah, during his rule, initiated expansion by conquering Tunisia and continued to expand eastward, controlling areas up to the Oxus River, including what is now Afghanistan and Kabul. His naval forces also actively attacked the Byzantine capital, Constantinople.
What was the significance of Muawiyah's decision to appoint his son Yazid as his successor?
-Muawiyah's appointment of his son Yazid as his successor marked a significant change in leadership succession from an elected caliphate by a council or shura to a hereditary monarchy, which caused controversy and dissatisfaction among some Muslim groups.
What were the consequences of the Battle of Karbala for the Umayyad Caliphate?
-The Battle of Karbala, where Husain bin Ali and his followers were tragically defeated, led to the second fitna or civil war in Islamic history and further deepened the divisions and conflicts within the Muslim community, contributing to the eventual downfall of the Umayyad Caliphate.
How did the Umayyad Caliphate's policies towards non-Muslims affect its legitimacy?
-The Umayyad Caliphate's policies, particularly the discriminatory tax system that favored Muslims over non-Muslims, contradicted the Islamic principles of equality among all Muslims regardless of ethnicity or nationality, which damaged their legitimacy and contributed to rebellions and internal conflicts.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)