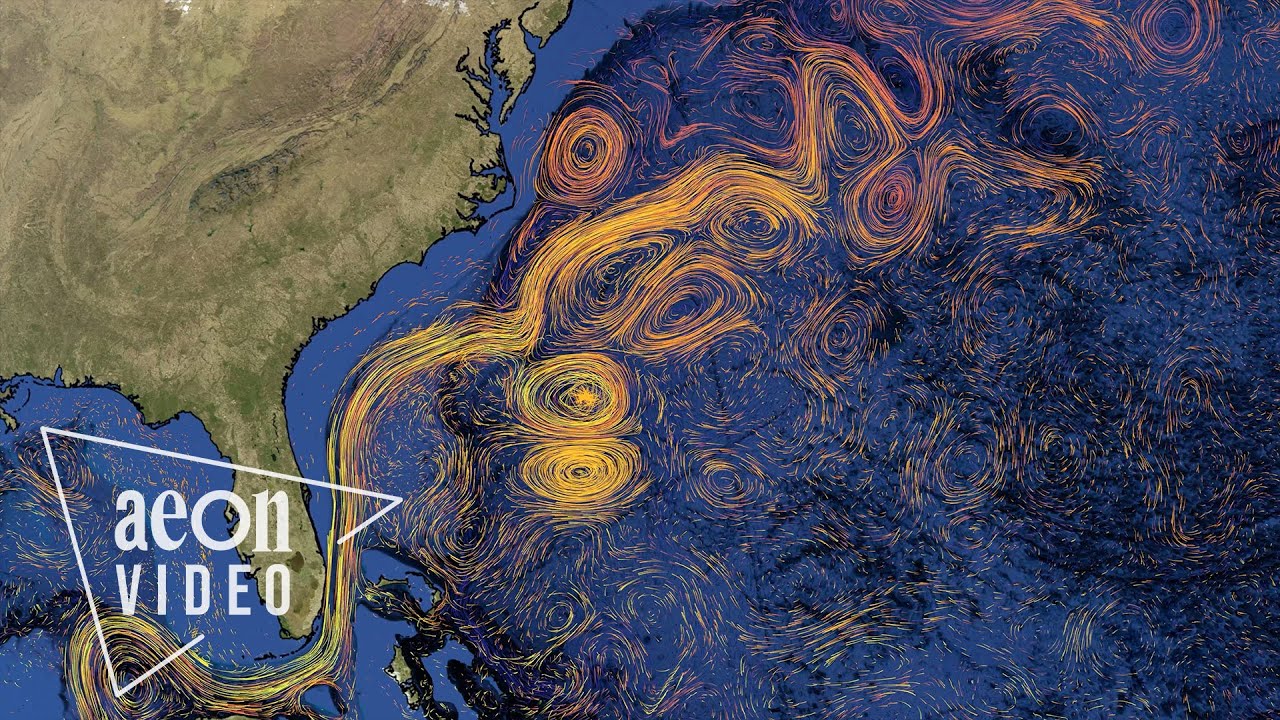
Aus für den Golfstrom? Droht Europa die nächste Eiszeit? | Terra X plus
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses the Atlantic Ocean's Gulf Stream System, which transports warmth from the south to Europe. It explains the system's role in Europe's mild climate and the potential consequences of its weakening due to climate change. The script debunks the likelihood of an immediate ice age but highlights increased risks of extreme weather events like storms and heatwaves. It emphasizes the importance of climate protection to stabilize the Gulf Stream and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Takeaways
- 🌊 The Gulf Stream System is a massive water current in the Atlantic, responsible for bringing heat from the south to Europe.
- 🔥 Despite its importance, the Gulf Stream is weakening, raising concerns about potential climatic changes.
- 🌍 The system is part of a global network of interconnected ocean currents, crucial for climate regulation.
- 🌡️ The Gulf Stream's warm surface water, up to 30 degrees Celsius, plays a significant role in Europe's mild climate.
- 🌀 The 'Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation' (AMOC), which includes the Gulf Stream, involves the overturning of massive water masses, with cold water sinking and warm water taking its place.
- 🌾 Europe's agriculture and climate are heavily dependent on the warmth provided by the Gulf Stream.
- ❄️ A collapse of the Gulf Stream System, as depicted in 'The Day after Tomorrow', could lead to a significant drop in temperature, though such a scenario is considered unlikely.
- 🌐 The melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet due to global warming is a serious threat to the Gulf Stream, as fresh water from melting ice is less dense and disrupts the circulation.
- 📉 Since 1950, the Gulf Stream has already lost 15% of its strength, and if climate change continues unchecked, it could become half as strong by the end of the century.
- 🌡️ While a weaker Gulf Stream could lead to cooler temperatures, the overall effect of climate change is likely to make Europe warmer, not colder.
- 🌪️ Changes in the Gulf Stream could also affect weather patterns, potentially leading to more frequent and severe storms and heatwaves.
Q & A
What is the Gulf Stream System and how does it affect Europe's climate?
-The Gulf Stream System is a massive water current in the Atlantic Ocean that brings heat from the south to Europe. It is part of a larger circulation system known as the 'Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation' (AMOC). The Gulf Stream's warm surface water, up to 30 degrees Celsius, is transported northward where it transitions into the North Atlantic Current, which carries warmth to Europe, resulting in a mild climate.
Why is the Gulf Stream System weakening?
-The Gulf Stream System is weakening due to global warming, which causes the melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet. The influx of large amounts of fresh water from the melting ice makes the surface water less dense, preventing it from sinking as effectively, which slows down the overall circulation and reduces the amount of heat transported to Europe.
What is the potential impact of a complete shutdown of the Gulf Stream System?
-While a complete shutdown of the Gulf Stream System is not considered realistic in the near future, it could lead to a significant cooling of Europe by 5 to 10 degrees Celsius, similar to the conditions during the peak of the last ice age. However, climate protection measures could prevent such a drastic weakening of the Gulf Stream.
How does the melting of the polar ice caps in Antarctica relate to the Gulf Stream System?
-The script does not directly link the melting of the Antarctic ice caps to the Gulf Stream System. Instead, it focuses on the impact of Greenland's melting ice sheet, which is closer and more directly influences the North Atlantic Current and the Gulf Stream System due to its proximity and the freshwater input into the North Atlantic.
What role does the freshwater from the melting ice sheets play in the Gulf Stream System?
-Freshwater from melting ice sheets, particularly Greenland's, is a significant problem for the Gulf Stream System because it is lighter than saltwater. When the Gulf Stream incorporates this freshwater, it becomes less dense and cannot sink as effectively, which slows down the deep-water return flow and, consequently, the heat transport from the Gulf Stream.
What has been the observed decline in the strength of the Gulf Stream since 1950?
-According to the script, the Gulf Stream has already lost 15 percent of its strength since 1950. If no action is taken against climate change, it could become even weaker and potentially unstable by the end of the century.
What are the current observable effects of the weakening Gulf Stream System?
-The weakening of the Gulf Stream System is already observable in the form of warmer waters along the U.S. coast, leading to rising sea levels, and potentially more severe hurricanes and flooding. In Europe, it could lead to more frequent cold winter storms and heatwaves, as well as a potential decrease in summer rainfall.
How does the weakening of the Gulf Stream System affect the Jetstream?
-The weakening of the Gulf Stream System could affect the Jetstream, a strong wind current high in the atmosphere, by causing it to waver. This could lead to the formation of a 'cold dome' in the North Atlantic, which might cause the Jetstream to meander, allowing hot air from the Sahara to reach Europe and contributing to heatwaves.
What are the potential agricultural impacts of the Gulf Stream System's weakening?
-The weakening of the Gulf Stream System could lead to a combination of drier summers and hotter temperatures, which might harm agriculture by reducing rainfall and increasing the risk of wildfires, if no countermeasures are taken.
How does the script suggest we should prepare for the future in relation to the Gulf Stream System?
-Instead of fearing an ice age, the script suggests that we should prepare for more frequent heatwaves and winter storms. It emphasizes the importance of climate protection to stabilize the Gulf Stream System and the Jetstream, mitigating the impacts of a weaker Gulf Stream on weather patterns and agriculture.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)