Amazing Science Behind Worlds Fastest Train || Magnetic Levitation train || 3D Animation
Summary
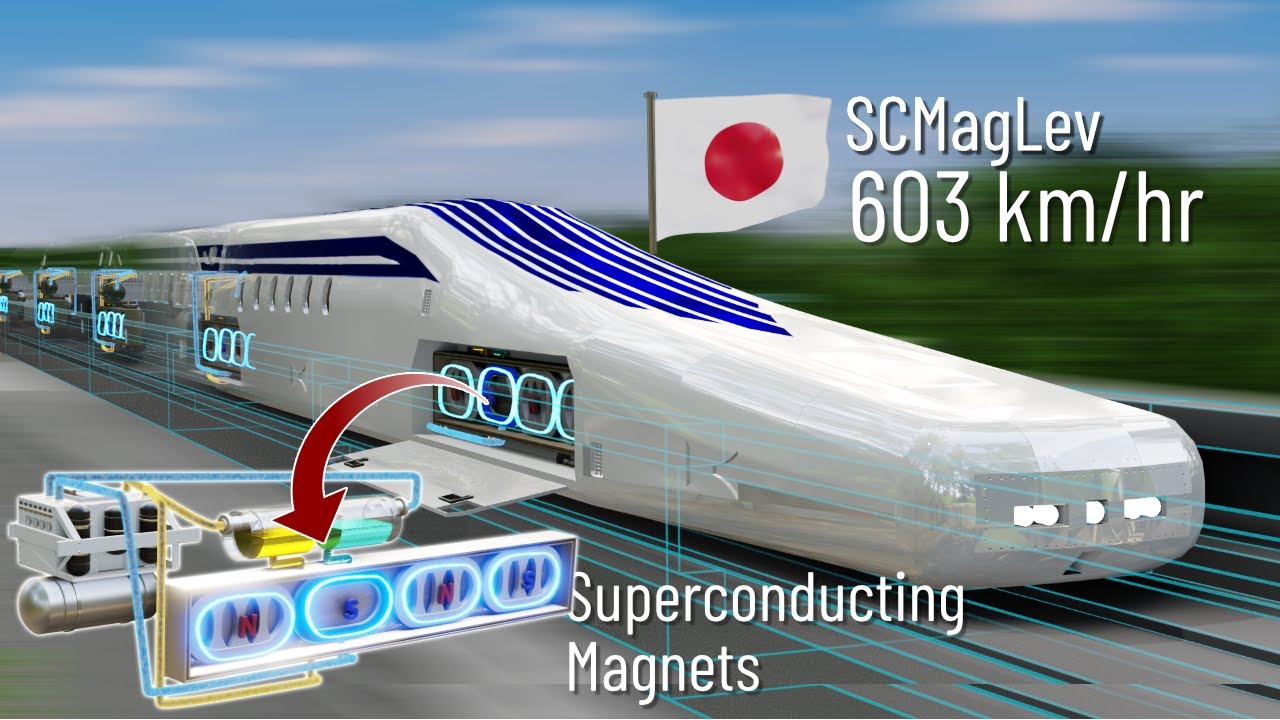
TLDRThe script delves into the technology behind maglev trains, highlighting their frictionless operation at speeds of 600 km/h using magnetic levitation. It explains the use of superconducting magnets for propulsion and levitation, detailing the challenges of maintaining a superconducting state with liquid helium cooling. The video also covers the guiding mechanism of maglev trains, the role of electromagnets in propulsion, and the innovative inductive power collection technology for a continuous electricity supply. The script concludes by emphasizing the safety measures like magnetic shields to protect passengers from powerful magnetic fields.
Takeaways
- 🚄 The Maglev train, which operates at speeds up to 600 km/h, uses magnetic levitation to reduce friction and eliminate the need for wheels like an airplane.
- 🧲 The Maglev train utilizes a combination of permanent magnets, electromagnets, and superconducting magnets for levitation, propulsion, and guidance.
- 🌀 Superconducting magnets are crucial for Maglev trains as they provide a strong, continuous magnetic field without energy loss due to their zero electrical resistance at low temperatures.
- ❄️ Liquid helium is used to cool the superconducting magnets, maintaining their superconducting state and preventing overheating from the high currents they carry.
- 🛡️ A radiation shield is employed to protect the superconducting magnets from external heat and to minimize eddy currents that could generate unwanted heat.
- 🔌 The Maglev train's propulsion system uses a series of electromagnets, known as propelling coils, which are powered alternately to create a magnetic field that pushes the train forward.
- 🔁 The polarity of the propelling coils is switched to control the speed and direction of the train, utilizing the principles of magnetic repulsion and attraction.
- ⚙️ Magnetic levitation is achieved through the use of '8' shaped coils that, when exposed to a moving magnetic field, induce an electromotive force (EMF) that creates lift.
- 🚦 Guidance of the Maglev train is maintained by interconnecting coils that detect and correct any deviation from the center of the track, ensuring stable travel.
- 🔋 Inductive power collection technology is used to supply electricity wirelessly to the train, avoiding the need for physical connections.
- 🛡️ Magnetic shields are installed on the sides of the Maglev train to protect passengers from the powerful magnetic fields generated by the superconducting magnets.
Q & A
What is the maximum speed of a maglev train mentioned in the script?
-The maximum speed of the maglev train mentioned in the script is 600 km/h.
How does a maglev train address the issue of friction compared to a normal train?
-A maglev train addresses the issue of friction by levitating above the track using magnetic fields, eliminating mechanical contact and thus reducing friction.
What are the three main requirements for operating a maglev train successfully?
-The three main requirements are: 1) Propulsion - to keep the train moving forward, 2) Levitation - to lift the train above the surface using magnets, and 3) Guidance - to keep the train on its path.
What type of magnet is used in a maglev train to achieve magnetic levitation?
-Superconducting magnets are used in maglev trains to achieve magnetic levitation due to their strong magnetic fields and zero electrical resistance.
Why are superconducting magnets more efficient than electromagnets for maglev trains?
-Superconducting magnets are more efficient because they have zero electrical resistance, allowing heavy currents to flow through them without generating heat, which is a limitation for electromagnets.
How is the superconducting magnet in a maglev train kept cool?
-The superconducting magnet is kept cool using liquid helium as a refrigerant, and helium compressors are used to maintain the liquid state of the helium.
What is the role of the 8-shaped coil in the magnetic levitation of a maglev train?
-The 8-shaped coil, when placed in a magnetic field, induces an electromotive force (EMF) as the magnetic field lines cut through it, creating a current that generates a magnetic field to lift the train.
How does a maglev train maintain guidance while in motion?
-The train maintains guidance through the use of interconnecting coils that adjust the current flow and magnetic field strength to keep the train centered on the track.
What technology is used to provide electricity to a maglev train?
-Inductive power collection technology, also known as wireless electricity, is used to provide electricity to a maglev train by inducing a magnetic field in coils installed on the ground and inside the train.
Why are magnetic shields used on the sides of a maglev train?
-Magnetic shields are used to protect passengers from the powerful magnetic fields generated by the superconducting magnets, ensuring their safety.
What is the historical significance of the maglev train mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions that Japanese engineers developed the maglev train in 1997, and it has since been adopted by a few other countries, showcasing its technological advancement and global impact.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)