Stratified Sampling
Summary
TLDRThis script explains the concept of stratified sampling, a technique that involves dividing a population into distinct groups, or strata, based on shared characteristics. The video demonstrates how to apply simple random sampling (SRS) within each stratum to select a sample size of 12 individuals, ensuring equal representation from different groups. The process emphasizes the importance of avoiding repetition and maintaining randomness to achieve a balanced and representative sample.
Takeaways
- 📚 The script discusses stratified sampling, a technique that builds upon simple random sampling (SRS).
- 🔄 Stratified sampling is not abbreviated as SS, but simply referred to by its name.
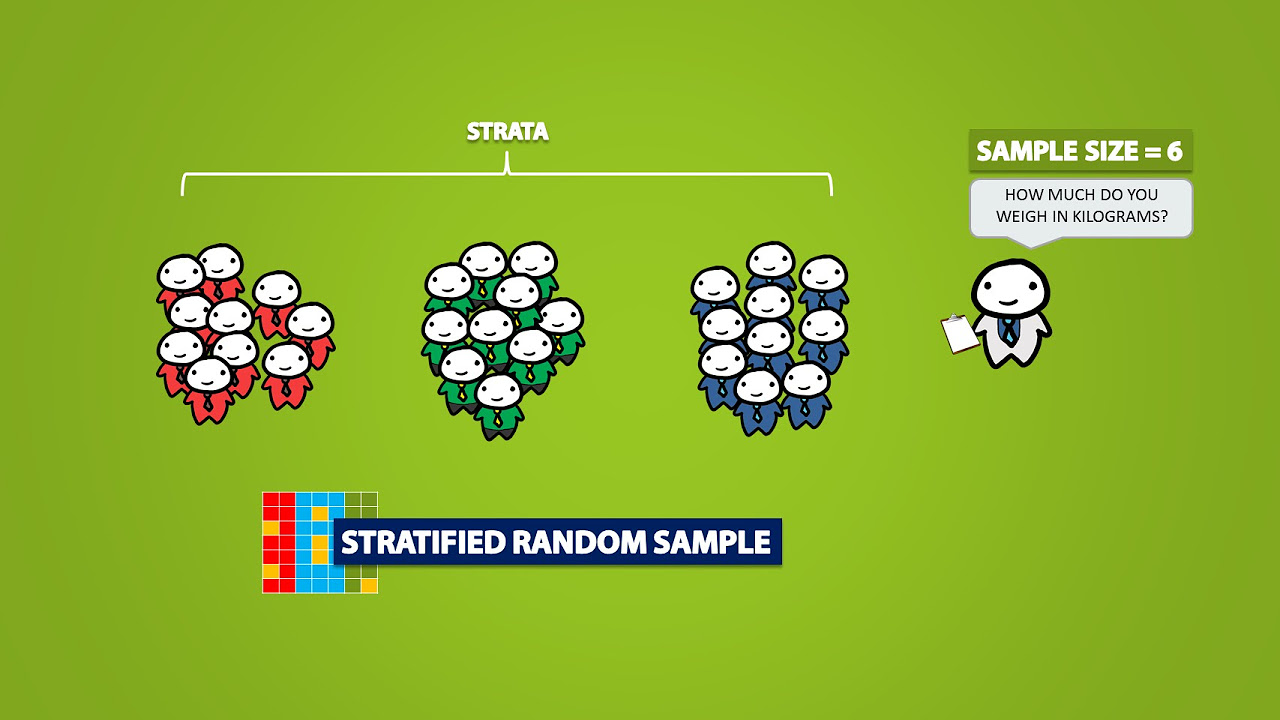
- 👥 The population is divided into groups based on a specific characteristic, creating strata.
- 🎨 The example given uses color to group individuals, emphasizing it's a characteristic for grouping, not a discriminatory act.
- 🔢 The goal is to have an equal or nearly equal number of individuals from each group in the sample.
- 🔄 After stratifying the population, SRS is used within each stratum to select individuals for the sample.
- 📝 The script illustrates the process of numbering individuals within each stratum to facilitate SRS.
- 🚫 It's important to avoid selecting the same individual more than once within a stratum.
- 🔢 The script provides a step-by-step example of selecting four individuals from each of three strata to achieve a sample size of twelve.
- 📉 The process involves random selection within each stratum, ensuring that the sample is representative of the entire population.
- 📈 Stratified sampling helps to ensure that the sample is more representative of the population's diversity compared to simple random sampling.
Q & A
What is stratified sampling?
-Stratified sampling is a technique where the population is divided into subgroups, or strata, based on a specific characteristic, and then simple random sampling (SRS) is applied to each stratum to obtain a representative sample from each group.
Why is stratified sampling used instead of simple random sampling alone?
-Stratified sampling is used to ensure that all subgroups within a population are represented in the sample, which can lead to a more accurate and representative sample, especially when there are distinct and important differences between the subgroups.
How does the script define a 'stratum'?
-In the script, a 'stratum' is defined as a subgroup of the population that has been grouped together based on a specific characteristic, such as color or appearance in the example provided.
What is the purpose of grouping individuals by a characteristic in stratified sampling?
-Grouping individuals by a characteristic in stratified sampling ensures that the sample obtained from each group is representative of that specific characteristic, which helps in getting a more accurate overall sample.
How does the script ensure that no individual is sampled more than once?
-The script ensures that no individual is sampled more than once by skipping over numbers that have already been selected during the simple random sampling process for each stratum.
What is the sample size the script aims to achieve using stratified sampling?
-The script aims to achieve a sample size of 12 using stratified sampling, with an equal number of individuals (four) being sampled from each of the three strata.
Why does the script use a different set of numbers for SRS in each stratum?
-The script uses a different set of numbers for SRS in each stratum to ensure that the random selection process is independent for each group, which helps in maintaining the randomness and representativeness of the sample.
What happens if the same number comes up more than once during the SRS process in a stratum?
-If the same number comes up more than once during the SRS process in a stratum, that number is skipped to avoid sampling the same individual twice.
How does the script ensure equal representation from each stratum in the sample?
-The script ensures equal representation from each stratum by sampling an equal number of individuals from each stratum using SRS, thus maintaining the proportionate representation in the sample.
What is the advantage of stratified sampling over simple random sampling?
-The advantage of stratified sampling over simple random sampling is that it can reduce sampling error by ensuring that all subgroups are represented in the sample, which can lead to more accurate estimates and a better understanding of the population.
Can stratified sampling be used when the population characteristics are unknown?
-Stratified sampling requires knowledge of the population characteristics to group individuals into strata. If the characteristics are unknown, it would not be possible to use stratified sampling effectively.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)