TLE COOKERY 10 Lesson 1 LO1 PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF THE EGGS
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the physical structure and composition of eggs, detailing the shell, air cell, albumen, chalaza, germinal disc, and yolk. It emphasizes the egg's nutritional value, high-quality protein, and vitamin content, except for vitamin C. The script also touches on egg quality, grading, and size, influenced by breed, age, feed, and environment, concluding with the Philippine standard for egg quality and the importance of eggshell appearance for consumer appeal.
Takeaways
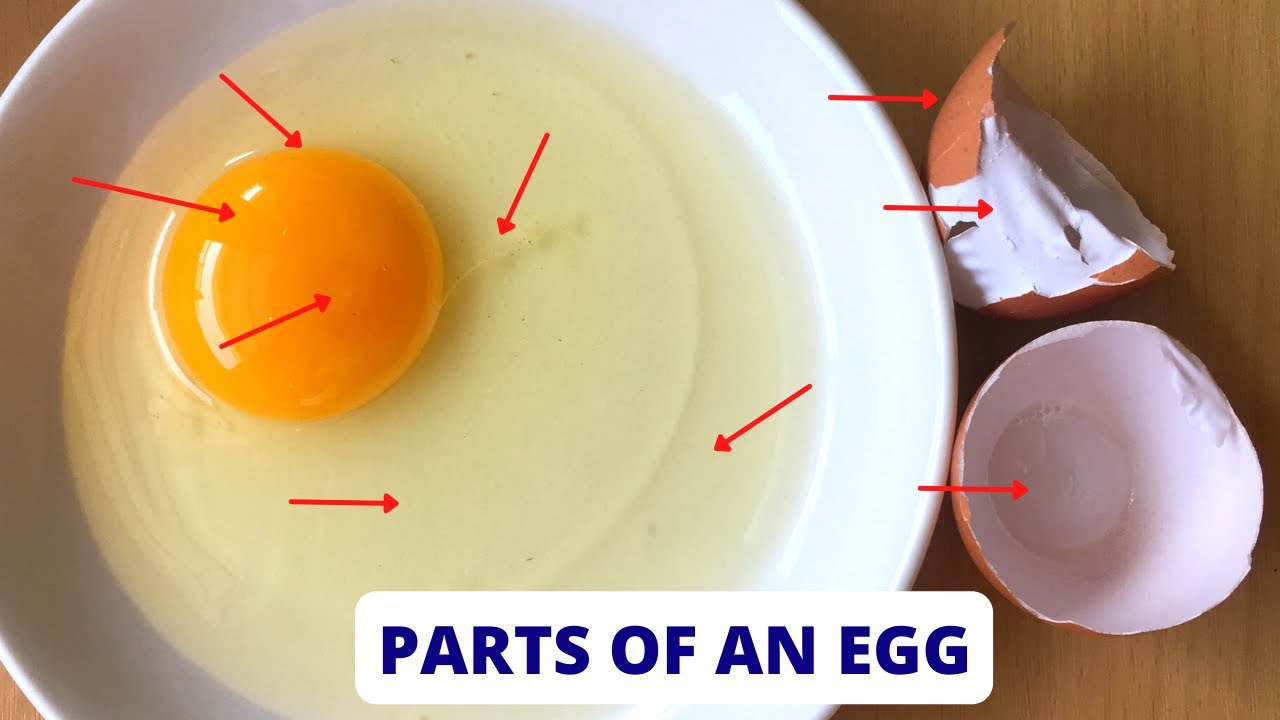
- 🥚 The physical structure of an egg consists of the shell, egg white (albumen), and egg yolk, with additional components including the air cell, chalaza, and germinal disc.
- 🔍 The shell is the egg's outer covering, accounting for 9-12% of the egg's weight and serves as the first line of defense against bacterial contamination.
- 💨 The air cell is the empty space between the egg white and shell, which forms as the egg cools after being laid.
- 🥚 The albumen or egg white makes up about 67% of the egg's liquid weight and has four alternating layers of thick and thin consistencies.
- 🌱 The chalaza are the strands of egg white that anchor the yolk and indicate the freshness of the egg.
- 🌀 The germinal disc is the site of potential embryonic development and is more noticeable in fertilized eggs.
- 🥚 The yolk, making up about 33% of the egg's liquid weight, is rich in nutrients and serves as a food source for embryonic development.
- 🥚 The egg's composition includes water, protein, fat, and ash, with the yolk containing most of the fat and nearly half of the protein.
- 🥚 Eggs are a complete food, containing high-quality protein with all essential amino acids, and are rich in vitamins and minerals except for vitamin C.
- 🏅 Egg quality is determined by shell quality (exterior) and interior quality, which affects the egg's functional properties.
- 📊 Egg grading is a quality control process that classifies eggs based on exterior and interior quality, with designations such as A, B, C, and D in the Philippines.
- 🥚 Factors influencing egg size include breed, age, weight, feed, and environmental conditions like heat stress and overcrowding.
Q & A
What are the three main parts of an egg?
-The three main parts of an egg are the shell, the egg white (albumen), and the egg yolk.
What is the function of the eggshell's outer coating, the bloom or cuticle?
-The bloom or cuticle on the eggshell somewhat seals the pores and helps in reducing moisture loss, acting as the egg's first line of defense against bacterial contamination.
What is the air cell in an egg and how does it form?
-The air cell is the empty space between the egg white and the shell at the large end of the egg. It is barely existent in newly laid eggs but forms as the egg cools and the contents contract, causing the inner and outer shell membranes to separate.
What is the albumen and what percentage of an egg's liquid weight does it account for?
-The albumen, also known as egg white, accounts for about 67 percent of an egg's liquid weight and is produced by the oviduct.
What is the chalaza and what is its purpose?
-The chalaza is the rooty strands of egg white on both sides of the egg that anchor the yolk in place. Its twist keeps the germinal disc always on top, regardless of the egg's position.
What is the germinal disc and its significance in fertilized eggs?
-The germinal disc is the entrance of the latibulum, the channel leading to the center of the yolk. In fertilized eggs, sperm enter through the germinal disc, travel to the center, and an embryo starts to form.
What are the two kinds of membranes found in an egg and their functions?
-The two kinds of membranes are the shell membrane and the vitelline membrane. The shell membrane is just under the shell and helps form the air cell, while the vitelline membrane protects the yolk from breaking.
What does the yolk represent in terms of the liquid weight of an egg and what is its role?
-The yolk makes up about 33 percent of the liquid weight of an egg and serves as a food source for embryonic development, containing all the fat and nearly half of the protein in the egg.
What are the main components of an egg's composition?
-An egg's composition mainly includes water (65.5%), protein (11.8%), fat (11%), and ash (11.7%). The albumen specifically contains 88% water, 11% protein, 0.2% fat, and 0.8% ash.
Why are eggs considered one of nature's complete foods?
-Eggs are considered complete foods because they contain high-quality protein with all essential amino acids, all vitamins except vitamin C, and many minerals, making them a highly nutritious food source.
What factors influence the size of an egg and what are the common egg sizes available?
-Factors influencing egg size include the breed of the chicken, the age and weight of the hen, feed, and environmental factors like heat stress and overcrowding. Common egg sizes available are jumbo, extra large, large, medium, small, and peewee.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

FOLIKULOGENESIS DAN OVUM TERNAK
PARTS OF AN EGG | Parts of an Egg and their Functions | Science Lesson

Virtual+Chicken SD

What If You Ate 4 EGGS A Day With The YOLKS For 30 Days?

4H Poultry Judging:Class I - Interior Egg Quality

Prenatal Development - From Conception to Birth - Germinal Stage, Embryonic Stage, Fetal Stage
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)