Entenda o sistema nervoso DO ZERO: Aula 2 - Organização do Sistema Nervoso
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the instructor explains the organization of the nervous system in a detailed yet accessible manner. The system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Key structures such as the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves are discussed, with a focus on how information is transmitted between sensory and motor neurons. The video also touches on the regenerative abilities of the PNS and the protective role of meninges and cerebrospinal fluid in the CNS. The session provides an essential foundation for understanding the intricate workings of the nervous system.
Takeaways
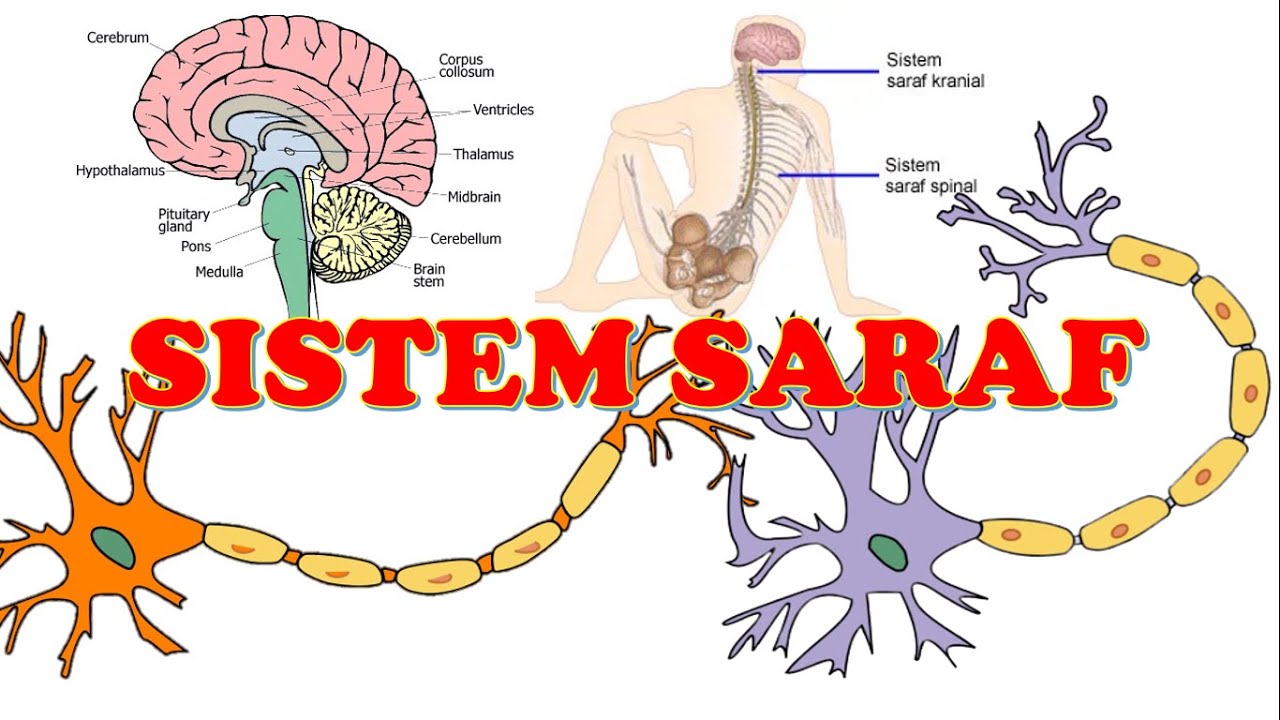
- 😀 The nervous system is divided into two main subsystems: the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
- 😀 The Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord, protected by three layers of meninges.
- 😀 The brain includes various structures like the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem (mesencephalon, pons, and medulla).
- 😀 The spinal cord is housed within the vertebral column and ends around the second lumbar vertebra (L2).
- 😀 Peripheral nerves include cranial and spinal nerves, with spinal nerves being mixed (both sensory and motor).
- 😀 Sensory neurons (afferent) bring information to the CNS, while motor neurons (efferent) send commands to muscles.
- 😀 The PNS has ganglia, which are clusters of neuron cell bodies, playing a key role in sensory and motor processing.
- 😀 The meninges (dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater) protect the CNS and are involved in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- 😀 CSF circulates between the layers of the meninges and helps protect the CNS by absorbing shocks and impacts.
- 😀 Injuries to the PNS can be reversible because of its regenerative capabilities, unlike the CNS, where damage is typically irreversible.
Q & A
What are the two main subsystems of the nervous system?
-The two main subsystems of the nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
What is the central nervous system composed of?
-The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord, which are housed within the skull and the vertebral column, respectively.
What is the difference between the brain and the encephalon?
-The brain is just one part of the encephalon. The encephalon includes all structures within the skull, such as the brain, cerebellum, and brainstem.
Where does the spinal cord (medulla spinalis) end?
-The spinal cord ends around the level of the second lumbar vertebra (L2), with its conical structure called the 'conus medullaris'.
What is the function of the peripheral nervous system?
-The peripheral nervous system connects the central nervous system to the rest of the body through nerves that transmit sensory and motor information.
What are the components of the peripheral nervous system?
-The peripheral nervous system consists of spinal nerves, cranial nerves, and ganglia, which are clusters of nerve cell bodies.
What is the role of the ganglion in the nervous system?
-A ganglion is a cluster of nerve cell bodies located outside the central nervous system, acting as a point of integration for sensory and motor information.
What is the difference between afferent and efferent neurons?
-Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) carry information from the body to the central nervous system, while efferent neurons (motor neurons) carry information from the central nervous system to muscles or glands.
What are meninges, and what is their role in the nervous system?
-Meninges are three layers of connective tissue membranes that protect the central nervous system. The three layers are the dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater.
How does cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) contribute to brain protection?
-Cerebrospinal fluid circulates around the brain and spinal cord, cushioning and absorbing impacts, while also helping to maintain a stable chemical environment for the central nervous system.
What happens if there is an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricles?
-If cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the ventricles and is not properly reabsorbed, it can lead to a condition called hydrocephalus, which results in increased intracranial pressure.
What are the primary functions of the brainstem (mesencephalon, pons, and medulla oblongata)?
-The brainstem regulates essential functions such as heart rate, respiratory rate, and vomiting reflex. It also plays a role in the control of eye movements and basic motor coordination.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)