🔴 Hati - hati‼️Jamur Mikoriza Bisa Bersifat Parasit dan Membahayakan Tanaman Pertanian Anda👹#tanaman
Summary
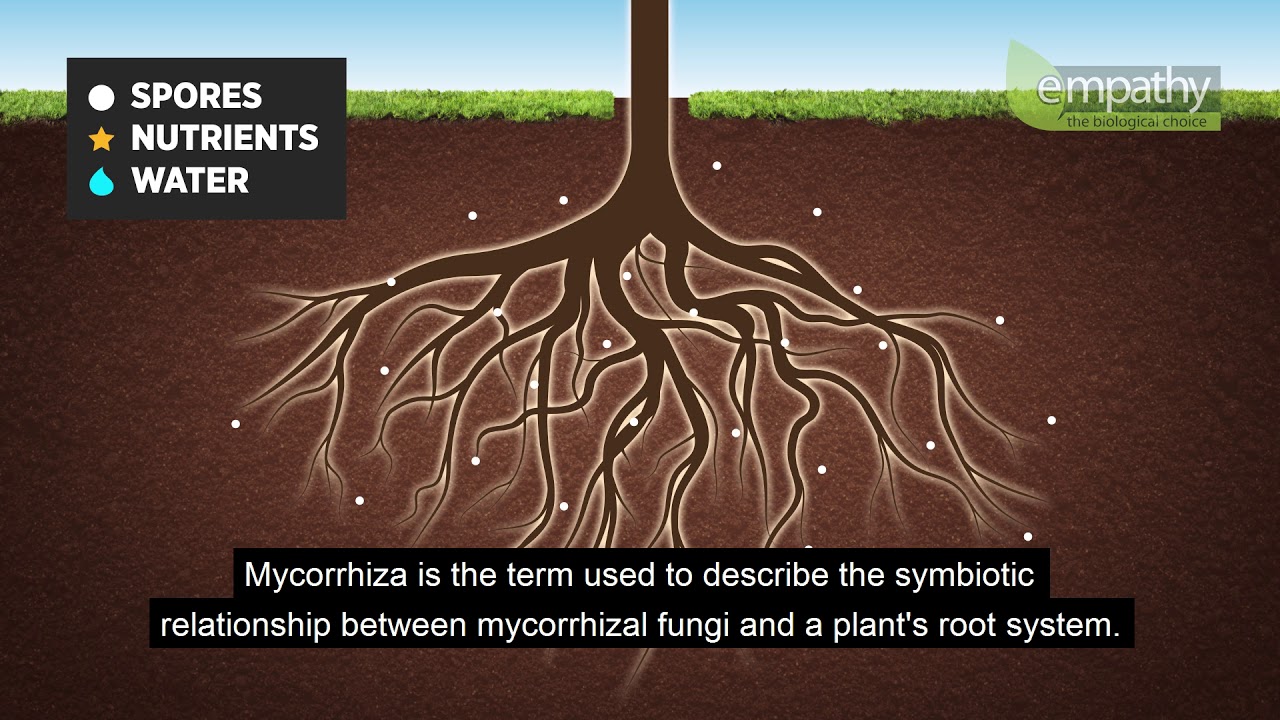
TLDRThis video discusses the dual nature of mycorrhiza, a type of fungus that can form a symbiotic relationship with plant roots. The speaker emphasizes the importance of understanding both the positive and negative aspects of mycorrhiza. On the positive side, it helps plants absorb nutrients and water, improving growth. However, under certain extreme environmental conditions, it can act parasitically, harming the plants. The video explores different types of mycorrhiza—ectomycorrhiza and endomycorrhiza—and provides guidance on when and how to use them, stressing the importance of ensuring compatibility with the plants and considering environmental factors.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mikoriza is a type of fungus that can form a symbiotic relationship with plant roots, benefiting both the fungus and the plant.
- 😀 Mikoriza can have both positive and negative effects, depending on the environmental conditions. It can be beneficial in some cases and parasitic in others.
- 😀 The term 'mikoriza' refers to fungi that collaborate with plant roots, not a specific fungus species. It is derived from the Greek words 'Miko' (fungus) and 'Riza' (root).
- 😀 Mikoriza needs roots to survive and cannot live independently. Without the root connection, it dies.
- 😀 Not all plants can form symbiotic relationships with mikoriza; only certain plants are compatible with this fungus.
- 😀 The symbiotic relationship between mikoriza and plant roots is not automatic and requires mutual agreement between both parties.
- 😀 Two main types of mikoriza are ektomikoriza (affecting trees and perennial plants) and endomikoriza (affecting annual plants like vegetables).
- 😀 Ektomikoriza fungi infect the outer root surface, commonly found in trees and long-lived plants like avocado, durian, and palm oil.
- 😀 Endomikoriza fungi infect inside the plant’s root cells and are suitable for short-lived plants like vegetables, including cabbages and peppers.
- 😀 Mikoriza cannot thrive in environments that have been contaminated with synthetic fertilizers or pesticides, as these chemicals disrupt its growth and function.
- 😀 The relationship with mikoriza is permanent, meaning it remains with the plant until the plant dies or is harvested, at which point the mikoriza also dies.
Q & A
What is mikoriza and how is it categorized?
-Mikoriza is a type of fungus that can form a symbiotic relationship with the roots of plants. It is categorized as a 'macroorganism' because its structure, which includes hyphae, is visible to the naked eye. Mikoriza is not a specific species of fungi but rather a term for fungi that can cooperate with plant roots.
Why is it important to differentiate between the two types of mikoriza?
-There are two main types of mikoriza: ectomikoriza and endomikoriza. Ectomikoriza affects trees and perennial plants by forming a symbiotic relationship with the outside of the plant roots, whereas endomikoriza affects short-term crops like vegetables by infiltrating the plant root cells. Using the wrong type for a particular plant can be ineffective or even harmful.
Can mikoriza be beneficial for all types of plants?
-No, not all plants can form a symbiotic relationship with mikoriza. Only specific plants, particularly those that can engage in mutualistic relationships with fungi, will benefit from mikoriza. The compatibility depends on the plant type and its ability to communicate and agree to cooperate with the mikoriza.
What is the primary function of mikoriza in its relationship with plants?
-Mikoriza helps plants by enhancing their ability to absorb nutrients, especially phosphorus and water, from the soil. In return, the plant provides the mikoriza with carbohydrates, which the fungi need for growth and survival.
How does mikoriza form a symbiotic relationship with plant roots?
-Mikoriza and plant roots form a relationship through mutual signaling. When mikoriza detects a suitable plant, it sends signals to the plant. If the plant agrees, it reciprocates with signals of its own, which initiates the collaboration. The relationship can then evolve into a symbiotic partnership where both parties benefit.
Can mikoriza be harmful to plants in certain conditions?
-Yes, mikoriza can become parasitic under certain conditions, such as extreme environmental stresses like drought. When plants are unable to provide mikoriza with sufficient resources, mikoriza may continue to extract nutrients from the plant, leading to dehydration and eventual plant death.
What are the different environmental factors that influence mikoriza's behavior?
-Mikoriza's behavior can be influenced by soil conditions, such as the presence of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which can make the environment inhospitable. Additionally, extreme weather conditions, like drought or heat, can cause mikoriza to act parasitically rather than beneficially.
How does mikoriza affect plants during extreme weather conditions?
-During extreme conditions like drought, mikoriza may fail to supply the plant with enough water or nutrients, which leads to a breakdown in the symbiotic relationship. In these cases, mikoriza can become parasitic by continuing to extract carbohydrates from the plant, while the plant suffers from dehydration and nutrient loss.
What are the practical applications of mikoriza in farming?
-Mikoriza can be used in organic farming as a natural solution for enhancing soil fertility and plant growth. However, it is crucial to use it in areas free from synthetic chemicals, as these can interfere with mikoriza’s ability to thrive. It is most effective for long-term crops like trees or specific vegetable crops, depending on the type of mikoriza.
How should farmers decide whether to use mikoriza on their land?
-Farmers should assess whether their land is suitable for mikoriza, which includes ensuring it is free from synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Additionally, they should consider whether their crops are compatible with the type of mikoriza available, as some mikoriza strains are better suited for trees and long-term crops, while others are better for short-term vegetable crops.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)