Sistema Nervoso 6/6: Sinapses Químicas e Elétricas | Anatomia e etc
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, the concept of synapses is explored, focusing on the transmission of nerve impulses between neurons. The video explains the two types of synapses: chemical and electrical. Chemical synapses involve neurotransmitters that transmit signals across a synaptic cleft, with excitatory or inhibitory effects on the postsynaptic neuron. Electrical synapses, in contrast, allow direct ion flow between neurons through connexin protein channels, enabling bidirectional communication. The lesson highlights the differences in speed, directionality, and function of these synaptic processes, providing a comprehensive understanding of neural communication.
Takeaways
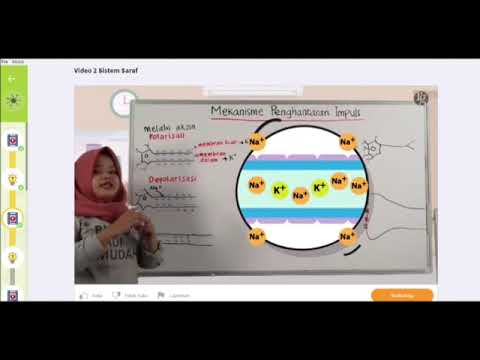
- 😀 A synapse is the communication region between neurons, or between a neuron and an organ like a muscle or gland.
- 😀 There are two types of synapses: chemical and electrical.
- 😀 Chemical synapses are the most common and involve neurotransmitters to transmit signals between neurons.
- 😀 In chemical synapses, the information flows in one direction from the presynaptic neuron to the postsynaptic neuron.
- 😀 The space between neurons in a chemical synapse is called the synaptic cleft.
- 😀 Neurotransmitters are stored in vesicles in the presynaptic neuron and released into the synaptic cleft upon stimulation.
- 😀 The release of neurotransmitters is triggered by the influx of calcium ions into the presynaptic neuron.
- 😀 Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, either stimulating or inhibiting its activity.
- 😀 Excitatory neurotransmitters like serotonin, glutamate, and acetylcholine promote the generation of an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron.
- 😀 Inhibitory neurotransmitters like GABA and glycine prevent the generation of an action potential by hyperpolarizing the postsynaptic neuron.
- 😀 Electrical synapses are less common and involve gap junctions that allow ions to pass directly between neurons, facilitating rapid, bidirectional communication.
Q & A
What is the role of a synapse in the nervous system?
-A synapse is the communication region between neurons or between a neuron and an effector organ (such as a muscle or gland), allowing the transfer of electrical signals from one cell to another.
What are the two main types of synapses discussed in the video?
-The two main types of synapses discussed are chemical synapses and electrical synapses.
How does a chemical synapse differ from an electrical synapse in terms of directionality?
-Chemical synapses are unidirectional, meaning the signal flows from the pre-synaptic neuron to the post-synaptic neuron, whereas electrical synapses are bidirectional, allowing signals to flow in both directions.
What is the function of neurotransmitters in chemical synapses?
-Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals from the pre-synaptic neuron to the post-synaptic neuron by crossing the synaptic cleft and binding to receptors on the post-synaptic neuron.
What triggers the release of neurotransmitters from the pre-synaptic neuron?
-The arrival of an action potential at the pre-synaptic terminal triggers the opening of calcium ion channels. The influx of calcium ions causes synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters to fuse with the membrane and release their contents into the synaptic cleft.
What are the roles of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters in the post-synaptic neuron?
-Excitatory neurotransmitters, like serotonin and glutamate, stimulate the post-synaptic neuron, potentially leading to a new action potential. Inhibitory neurotransmitters, such as GABA and glycine, make the post-synaptic neuron less likely to fire an action potential by hyperpolarizing it.
What is the synaptic cleft, and why is it important?
-The synaptic cleft is the small gap between the pre-synaptic and post-synaptic neurons. It is crucial because it is where neurotransmitters are released from the pre-synaptic neuron and bind to receptors on the post-synaptic neuron, allowing signal transmission.
What is the function of connexins in electrical synapses?
-Connexins are proteins that form gap junctions between neurons in electrical synapses, allowing ions to pass directly from one neuron to another, enabling faster communication between cells.
Why are electrical synapses faster than chemical synapses?
-Electrical synapses are faster because they allow direct ion flow between neurons through gap junctions, bypassing the need for neurotransmitter release and receptor binding, making signal transmission almost instantaneous.
Where in the body are electrical synapses typically found?
-Electrical synapses are found in specific parts of the brain, where they facilitate rapid and coordinated communication between neurons.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)