KALKULUS | INTEGRAL | INTEGRAL TENTU
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of definite integrals is explored, building upon the previously discussed indefinite integrals. The video illustrates how to compute the area under a curve, using the example of the function y = x² + 1. By partitioning the area into smaller regions and applying both lower and upper polygonal approximations, the video demonstrates how the integral approach refines the estimation. The video covers integral properties, such as the effect of changing bounds and constants, and provides several example problems to showcase these properties in practice. It concludes with a clear understanding of the integral's role in finding exact areas under curves.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video introduces the concept of definite integrals, explaining the difference between definite and indefinite integrals.
- 😀 The focus is on calculating the area under a curve, particularly the curve y = x^2 + 1, between x = 0 and x = 2.
- 😀 The method of approximating areas under the curve involves partitioning the area into rectangles, which are used to estimate the total area.
- 😀 Two types of approximations are made: lower polygon approximation (under the curve) and upper polygon approximation (over the curve).
- 😀 The actual area under the curve is determined by taking the limit of the approximations as the number of partitions approaches infinity.
- 😀 The video presents the integral formula for calculating the exact area: ∫_0^2 (x^2 + 1) dx.
- 😀 Properties of definite integrals are discussed, such as reversing limits, which involves multiplying the result by -1 when the limits are swapped.
- 😀 The property of zero intervals is explained: if the upper and lower limits of the integral are the same, the result is zero.
- 😀 Constants can be factored out of the integral, and the linearity of integrals allows the splitting of sums and differences into separate integrals.
- 😀 The video includes example problems to demonstrate how to apply the properties of definite integrals and compute results efficiently.
Q & A
What is the concept of definite integrals discussed in the video?
-The concept of definite integrals is introduced as a method to calculate the area under a curve, particularly when the curve is irregular and cannot be measured with basic geometric formulas.
What is the function used to demonstrate the concept of definite integrals?
-The function used in the video to demonstrate the concept is y = x² + 1, which represents a parabola.
What are the limits of integration in the given example?
-In the example, the limits of integration are x = 0 for the left boundary and x = 2 for the right boundary.
How is the area under the curve approximated in the video?
-The area under the curve is approximated by dividing the region into smaller parts, forming rectangles (polygons). These are calculated using two approaches: the 'lower polygon' and the 'upper polygon' method.
What is the formula used to calculate the area of the rectangles?
-The formula used for calculating the area of the rectangles is the area of a rectangle: Area = base * height, where the base is the width of the rectangle and the height is the function value at that point.
Why does the area approximation error occur when using the lower and upper polygons?
-The error occurs because the lower polygon underestimates the area (as it is below the curve), and the upper polygon overestimates it (as it extends above the curve).
What happens when the partition of the area is increased?
-As the partition (number of sections) increases, the error decreases, and the approximation becomes more accurate, approaching the actual area under the curve.
What is the general definition of a definite integral according to the video?
-The definite integral is defined as the area under a curve from a lower bound (x = a) to an upper bound (x = b), expressed as ∫ from a to b of f(x) dx.
What are some properties of definite integrals mentioned in the video?
-Some properties include: 1) Flipping the limits of integration changes the sign of the integral, 2) The integral of a constant function is zero when the limits are the same, 3) Constants can be factored out of an integral, 4) The integral of the sum or difference of functions is the sum or difference of their integrals.
How does the video explain the integral of a constant multiplied by a function?
-The video explains that the integral of a constant multiplied by a function can be simplified by factoring out the constant, making the integration process easier.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

MATEMATIKA Kelas 11 - Integral Tak Tentu | GIA Academy
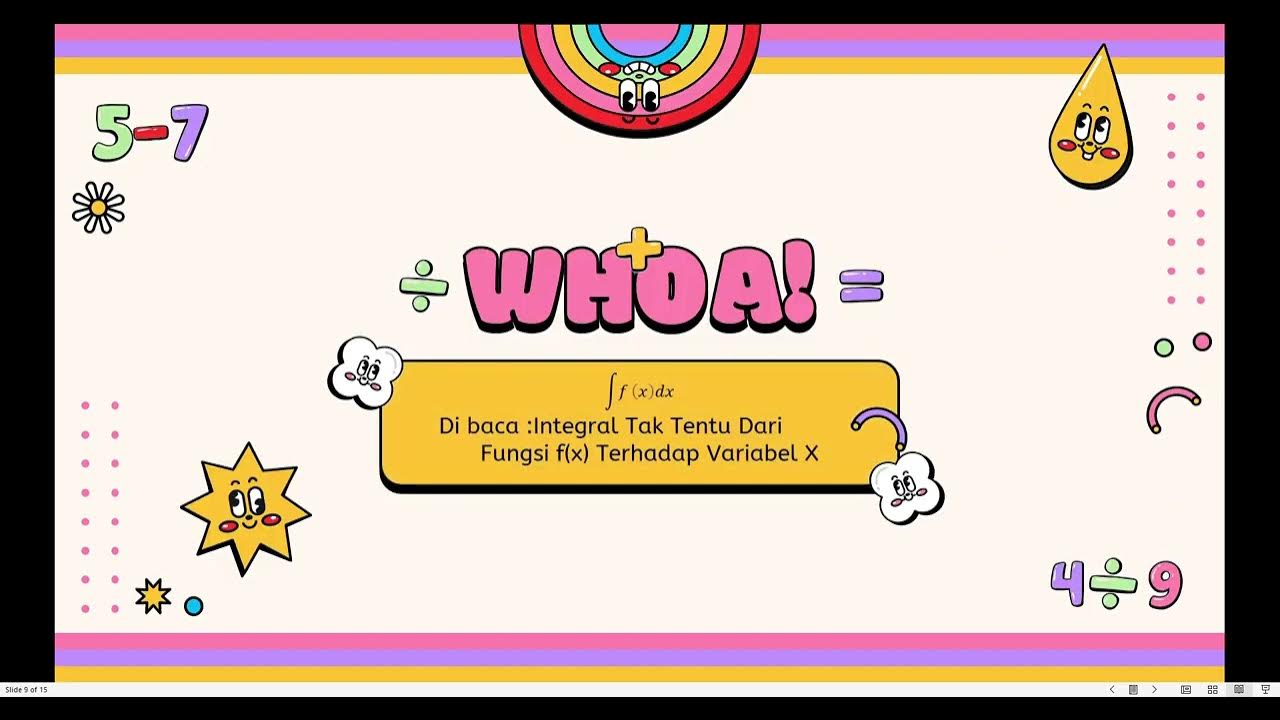
Menemukan Konsep Integral tak Tentu sebagai kebalikan dari Turunan

LENGKAP Integral tak tentu, integral tertentu, integral subtitusi dan integral parsial

INTEGRAL LIPAT 2 #KALKULUS 2

#06 Konsep Dasar Integral dalam Matematika untuk Fisika Bagian #1

Integral (Tak Tentu)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
