¿Qué son las razones trigonométricas? @MatematicasprofeAlex
Summary
TLDRThis video serves as an introduction to trigonometric ratios, specifically in right-angled triangles. It explains the basic concepts, such as the names of the sides (hypotenuse, opposite, and adjacent), and introduces the six trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant. The focus is on understanding the relationships between the sides of the triangle in relation to the angles, particularly acute angles. Through examples and exercises, the video demonstrates how these ratios depend on the angle and how they can be used to solve for unknown sides or angles in right-angled triangles.
Takeaways
- 😀 Trigonometric ratios are key for solving right triangle problems, defining the relationships between the sides and angles.
- 😀 A right triangle has three sides: the hypotenuse (longest side), opposite (side opposite the angle), and adjacent (side next to the angle).
- 😀 There are six key trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant.
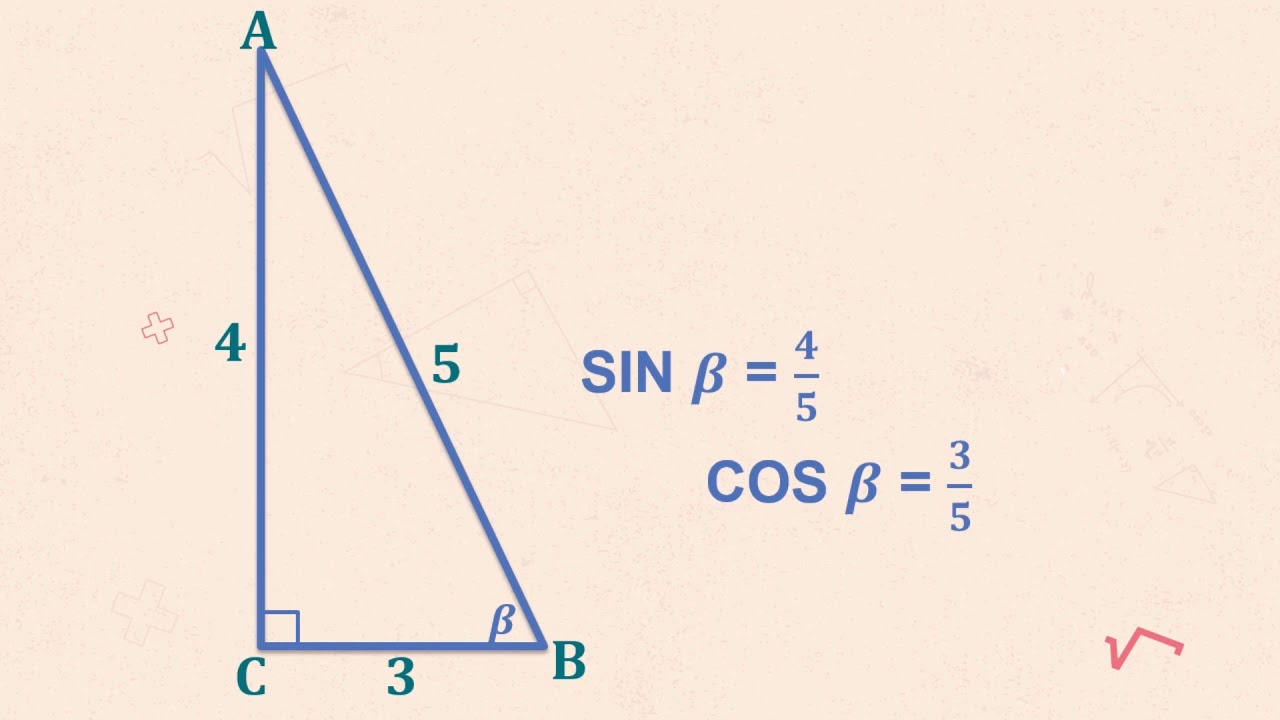
- 😀 Sine (sin) is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse (sin = opposite/hypotenuse).
- 😀 Cosine (cos) is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse (cos = adjacent/hypotenuse).
- 😀 Tangent (tan) is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side (tan = opposite/adjacent).
- 😀 Cotangent (cot) is the inverse of tangent, the ratio of the adjacent side to the opposite side (cot = adjacent/opposite).
- 😀 Secant (sec) is the inverse of cosine, the ratio of the hypotenuse to the adjacent side (sec = hypotenuse/adjacent).
- 😀 Cosecant (csc) is the inverse of sine, the ratio of the hypotenuse to the opposite side (csc = hypotenuse/opposite).
- 😀 Trigonometric ratios depend on the angle, not on the size of the triangle, allowing them to be applied universally across different-sized triangles.
Q & A
What are trigonometric ratios used for in right-angled triangles?
-Trigonometric ratios are used to relate the sides of a right-angled triangle to the angles, excluding the right angle. These ratios help in calculating unknown sides or angles in the triangle.
What defines a right-angled triangle?
-A right-angled triangle is a triangle that has one angle measuring exactly 90 degrees, marked by a small square in the corner of the triangle.
What are the names of the sides in a right-angled triangle?
-In a right-angled triangle, the longest side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse, while the other two sides are called the adjacent and opposite sides, depending on the angle being considered.
What is the difference between the opposite and adjacent sides in a right-angled triangle?
-The opposite side is the side directly across from the angle being considered, while the adjacent side is the side next to the angle, excluding the hypotenuse.
How many trigonometric ratios exist, and what are they?
-There are six main trigonometric ratios: sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan), cosecant (csc), secant (sec), and cotangent (cot). These ratios are based on the relationships between the sides of the triangle.
What does the sine of an angle represent in a right-angled triangle?
-The sine of an angle is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle.
What is the cosine ratio in trigonometry?
-The cosine of an angle is the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle.
What is the significance of the tangent ratio?
-The tangent of an angle is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side in a right-angled triangle.
How does the cotangent ratio relate to the tangent ratio?
-The cotangent is the reciprocal of the tangent ratio, meaning it is the ratio of the adjacent side to the opposite side in a right-angled triangle.
Why do trigonometric ratios depend on the angle rather than the size of the triangle?
-Trigonometric ratios are based on the relationships between the sides of the triangle relative to a specific angle. The ratios remain consistent for the same angle, regardless of the size of the triangle.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
Video Pembelajaran Perbandingan Trigonometri Kelas X SMK

Video Pembelajaran Matematika Materi Trigonometri Kelas 10 - Nilai Trigonometri pada Sudut Istimewa
Matematika SMA - Trigonometri (1) - Pengenalan Trigonometri, Perbandingan Trigonometri (A)

Trigonometric Ratios (Tagalog Math)

Trigonometri Matematika Kelas 10 • Part 4: Perbandingan Trigonometri Sudut Istimewa

Manipulating the Trig Ratios in Geometry (example question)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
